The business problem facing the director of broadcasting operations for a television station was the issue of standby hours (io. hours in which unionized graphic artists at the station are paid but are not actually involved in any activity) and what factors were related to standby hours. A study of standby hours was conducted for 26 weeks. The variables in the study are described below and the data from the study are shown in the accompanying table. Complete parts a through e below. Standby hours (Y-Total number of standby hours in a week Total staff present (x,)-Weekly total of people-days Remote hours (X2)-Number of hours worked by employees off-site Click the icon to view the data table. PLEASE RUN SPSS TO OBTAIN THE REQUIRED DATA TO ANSWER THE QUESTIONS BELOW! a. State the multiple regression equation. Ý =D- (OX + OX2 (Round to one decimal place as needed.) b. Interpret the meaning of the slopes, b; and b2. in this problem. Choose the correct answer below. OA. For a given number of remote hours, each increase of one unit of total staff present and one unit increase in standby hours is estimated to result in a mean increase in remote hours of b; and bz units, respectively. OB. Each increase in standby hours is estimated to result in a mean increase in total staf present of b, units and a mean decrease in remote hours of the absolute value of bz units. OC. For a given number of remote hours, each increase of one unit of total staff present is estimated to result in a mean increase in standby hours of b, units. For a given number of total staff present, each increase of one unit in remote hours is estimated to result in a mean decrease in standby hours of the absolute value of b, units. OD. The slopes, b; and bz, cannot be interpreted individually. c. Explain why the regression coefficient, bg, has no practical meaning in the context of this problem. Choose the correct answer below. OA. The coefficient b, has no practical meaning in this context because Y depends on not only bn. but b, and b, as well, and their meaning cannot be separated. OB. The coefficient bo has no practical meaning in this context because it estimates the standby hours when there are no staff present and no remote hours. Oc. The coefficient bo has no practical meaning in this context because it corresponds to the number of staff present and the remote hours when there are no standby hours. OD. The coefficient bo has no practical meaning in this context because it is not close in value to any of the data values in the standby hours column. d. Predict the mean standby hours for a week in which the total staff present have 310 people-days and the remote hours are 400. There would be standby hours predicted for the week. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) e. What of the following is the best conclusion concening the standby hours model? OA. The model uses the number of remote hours to predict the number of standby hours. The number of staff present only affects the remote hours directly. OB. The model uses the number of staff present to predict the number of standby hours. The remote hours only affects the number of staff present directly. Oc. The model can use the number of staff present or the remote hours to predict the number standby hours, but not both. OD. The model uses both the number of staff present and the remote hours to predict the number of standby hours. This produces a better model than if only one variable were included.
The business problem facing the director of broadcasting operations for a television station was the issue of standby hours (io. hours in which unionized graphic artists at the station are paid but are not actually involved in any activity) and what factors were related to standby hours. A study of standby hours was conducted for 26 weeks. The variables in the study are described below and the data from the study are shown in the accompanying table. Complete parts a through e below. Standby hours (Y-Total number of standby hours in a week Total staff present (x,)-Weekly total of people-days Remote hours (X2)-Number of hours worked by employees off-site Click the icon to view the data table. PLEASE RUN SPSS TO OBTAIN THE REQUIRED DATA TO ANSWER THE QUESTIONS BELOW! a. State the multiple regression equation. Ý =D- (OX + OX2 (Round to one decimal place as needed.) b. Interpret the meaning of the slopes, b; and b2. in this problem. Choose the correct answer below. OA. For a given number of remote hours, each increase of one unit of total staff present and one unit increase in standby hours is estimated to result in a mean increase in remote hours of b; and bz units, respectively. OB. Each increase in standby hours is estimated to result in a mean increase in total staf present of b, units and a mean decrease in remote hours of the absolute value of bz units. OC. For a given number of remote hours, each increase of one unit of total staff present is estimated to result in a mean increase in standby hours of b, units. For a given number of total staff present, each increase of one unit in remote hours is estimated to result in a mean decrease in standby hours of the absolute value of b, units. OD. The slopes, b; and bz, cannot be interpreted individually. c. Explain why the regression coefficient, bg, has no practical meaning in the context of this problem. Choose the correct answer below. OA. The coefficient b, has no practical meaning in this context because Y depends on not only bn. but b, and b, as well, and their meaning cannot be separated. OB. The coefficient bo has no practical meaning in this context because it estimates the standby hours when there are no staff present and no remote hours. Oc. The coefficient bo has no practical meaning in this context because it corresponds to the number of staff present and the remote hours when there are no standby hours. OD. The coefficient bo has no practical meaning in this context because it is not close in value to any of the data values in the standby hours column. d. Predict the mean standby hours for a week in which the total staff present have 310 people-days and the remote hours are 400. There would be standby hours predicted for the week. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) e. What of the following is the best conclusion concening the standby hours model? OA. The model uses the number of remote hours to predict the number of standby hours. The number of staff present only affects the remote hours directly. OB. The model uses the number of staff present to predict the number of standby hours. The remote hours only affects the number of staff present directly. Oc. The model can use the number of staff present or the remote hours to predict the number standby hours, but not both. OD. The model uses both the number of staff present and the remote hours to predict the number of standby hours. This produces a better model than if only one variable were included.
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Chapter5: A Survey Of Other Common Functions
Section5.3: Modeling Data With Power Functions
Problem 6E: Urban Travel Times Population of cities and driving times are related, as shown in the accompanying...
Related questions
Question
Please fill in the blanks and select the correct answers over the image provided. Thank you
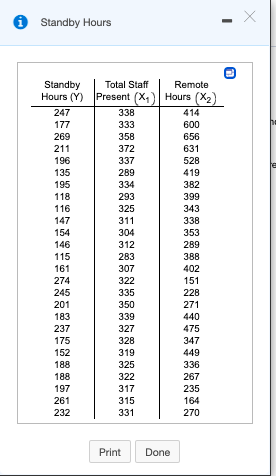
Transcribed Image Text:Standby Hours
Standby
Hours (Y) Present (X4) Hours (X2)
Total Staff
Remote
247
338
414
177
333
600
269
358
656
211
372
631
196
337
528
135
289
419
195
334
382
118
293
399
116
325
343
147
311
338
154
304
353
146
312
289
115
283
388
161
307
402
274
322
151
335
350
339
245
228
201
271
183
440
237
327
475
175
328
347
152
319
449
188
325
336
188
322
267
197
317
235
261
315
164
232
331
270
Print
Done
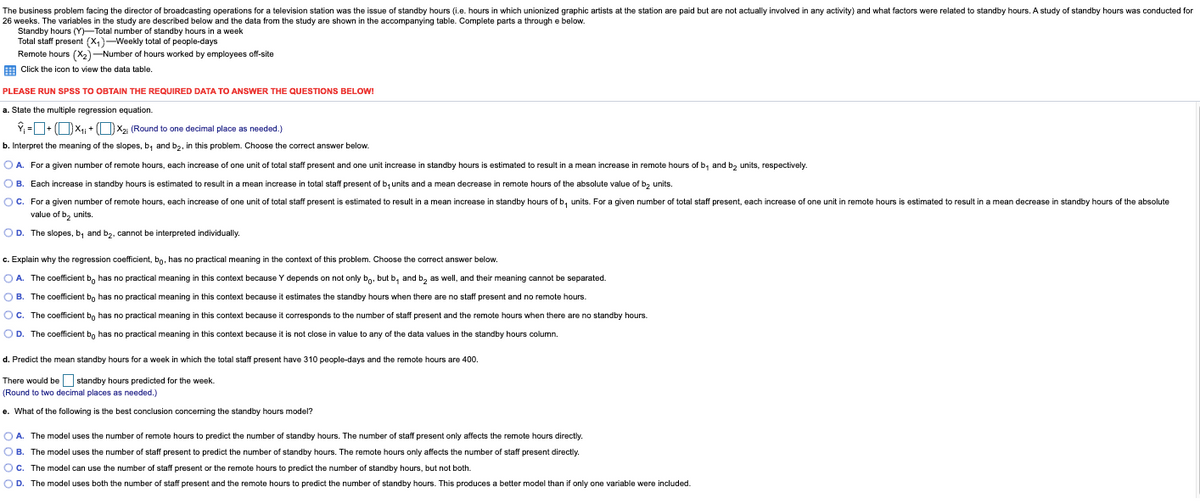
Transcribed Image Text:The business problem facing the director of broadcasting operations for a television station was the issue of standby hours (i.e. hours in which unionized graphic artists at the station are paid but are not actually involved in any activity) and what factors were related to standby hours. A study of standby hours was conducted for
26 weeks. The variables in the study are described below and the data from the study are shown in the accompanying table. Complete parts a through e below.
Standby hours (Y)-Total number of standby hours in a week
Total staff present (X,)-Weekly total of people-days
Remote hours (X2)-Number of hours worked by employees off-site
Click the icon to view the data table.
PLEASE RUN SPSS TO OBTAIN THE REQUIRED DATA TO ANSWER THE QUESTIONS BELOW!
a. State the multiple regression equation.
Y, =+ (OX1 + OX2 (Round to one decimal place as needed.)
b. Interpret the meaning of the slopes, b, and b2, in this problem. Choose the correct answer below.
O A. For a given number of remote hours, each increase of one unit of total staff present and one unit increase in standby hours is estimated to result in a mean increase in remote hours of b, and bz units, respectively
O B. Each increase
standby hours is estimated to result in a mean increase in total staff present of b, units and a mean decrease in remote hours of the absolute value of b, units.
OC. For a given number of remote hours, each increase of one unit of total staff present
estimated to result in a mean increase in standby hours of b, units. For a given number of total staff present, each increase of one unit in remote hours is estimated to result in a mean decrease in standby hours of the absolute
value of b, units.
O D. The slopes, b, and b2, cannot be interpreted individually.
c. Explain why the regression coefficient, bo, has no practical meaning in the context of this problem. Choose the correct answer below.
O A. The coefficient b, has no practical meaning in this context because Y depends on not only bo. but b, and b, as well, and their meaning cannot be separated.
O B. The coefficient bn has no practical meaning in this context because it estimates the standby hours when there are no staff present and no remote hours.
OC. The coefficient bn has no practical meaning in this context because it corresponds to the number of staff present and the remote hours when there are no standby hours.
O D. The coefficient bo has no practical meaning in this context because it is
t close in value to any of the data values in the standby hours column.
d. Predict the mean standby hours for a week in which the total staff present have 310 people-days and the remote hours are 400.
There would be standby hours predicted for the week.
(Rour
to two decimal places as needed.)
e. What of the following is the best conclusion concerning the standby hours model?
O A. The model uses the number of remote hours to predict the number of standby hours. The number of staff present only affects the remote hours directly.
O B. The model uses the number of staff present to predict the number of standby hours. The remote hours only affects the number of staff present directly.
OC. The model can use the number of staff present or the remote hours to predict the number of standby hours, but not both.
OD. The model uses both the number of staff present and the remote hours to predict the number of standby hours. This produces a better model than if only one variable were included.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill