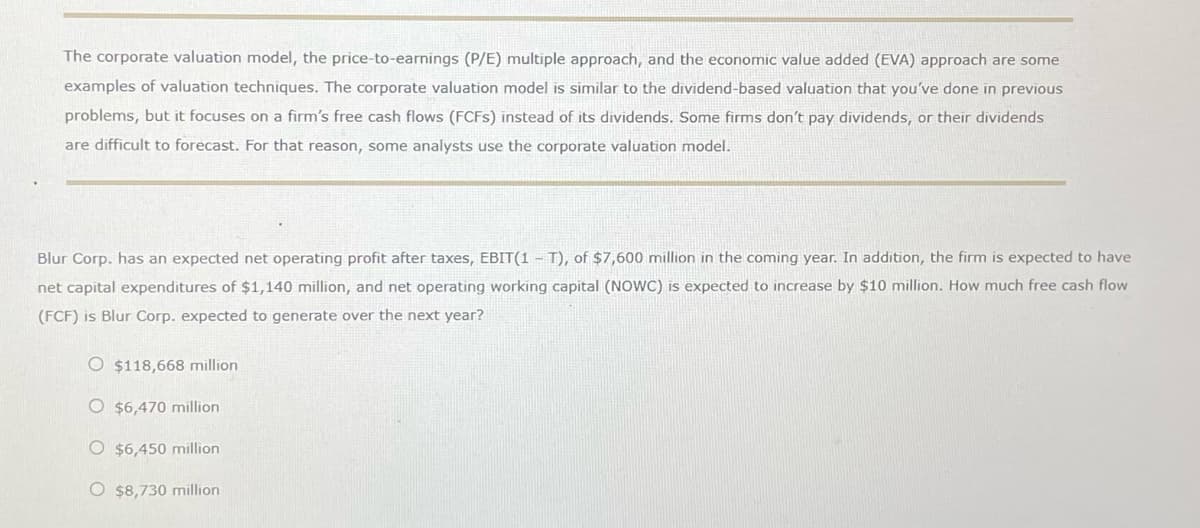
The corporate valuation model, the price-to-earnings (P/E) multiple approach, and the economic value added (EVA) approach are some examples of valuation techniques. The corporate valuation model is similar to the dividend-based valuation that you've done in previous problems, but it focuses on a firm's free cash flows (FCFS) instead of its dividends. Some firms don't pay dividends, or their dividends are difficult to forecast. For that reason, some analysts use the corporate valuation model. Blur Corp. has an expected net operating profit after taxes, EBIT(1-T), of $7,600 million in the coming year. In addition, the firm is expected to have net capital expenditures of $1,140 million, and net operating working capital (NOWC) is expected to increase by $10 million. How much free cash flow (FCF) is Blur Corp. expected to generate over the next year? O $118,668 million O $6,470 million O $6,450 million O $8,730 million
The corporate valuation model, the price-to-earnings (P/E) multiple approach, and the economic value added (EVA) approach are some examples of valuation techniques. The corporate valuation model is similar to the dividend-based valuation that you've done in previous problems, but it focuses on a firm's free cash flows (FCFS) instead of its dividends. Some firms don't pay dividends, or their dividends are difficult to forecast. For that reason, some analysts use the corporate valuation model. Blur Corp. has an expected net operating profit after taxes, EBIT(1-T), of $7,600 million in the coming year. In addition, the firm is expected to have net capital expenditures of $1,140 million, and net operating working capital (NOWC) is expected to increase by $10 million. How much free cash flow (FCF) is Blur Corp. expected to generate over the next year? O $118,668 million O $6,470 million O $6,450 million O $8,730 million
Financial Management: Theory & Practice
16th Edition
ISBN:9781337909730
Author:Brigham
Publisher:Brigham
Chapter21: Dynamic Capital Structures And Corporate Valuation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9P
Related questions
Question
4
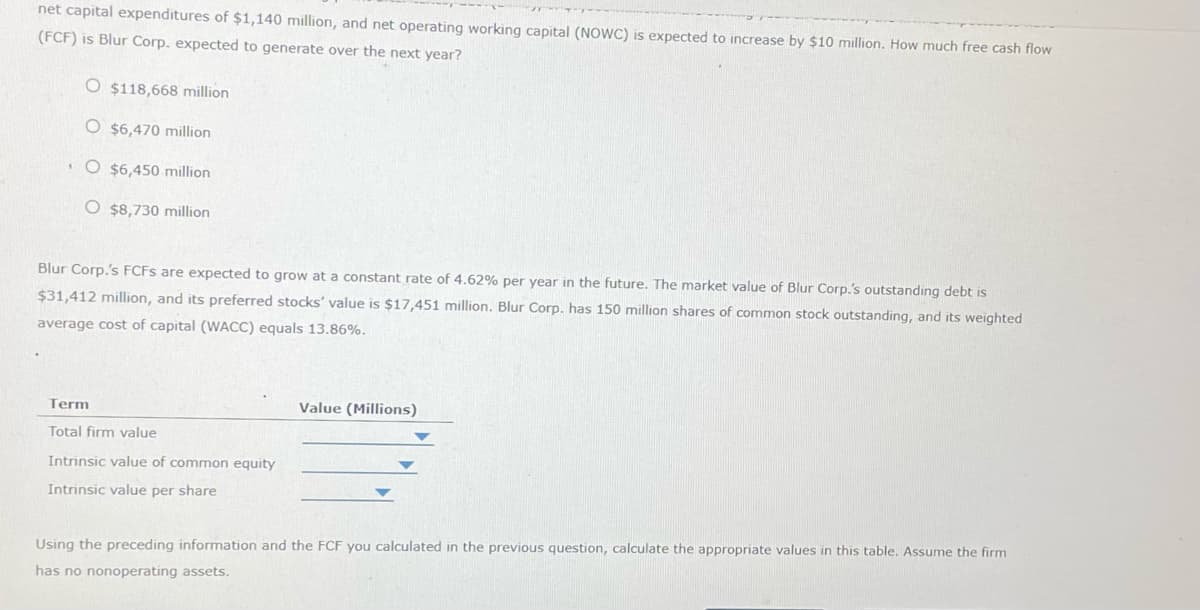
Transcribed Image Text:net capital expenditures of $1,140 million, and net operating working capital (NOWC) is expected to increase by $10 million. How much free cash flow
(FCF) is Blur Corp. expected to generate over the next year?
O $118,668 million
O $6,470 million
O $6,450 million
O $8,730 million
Blur Corp.'s FCFS are expected to grow at a constant rate of 4.62% per year in the future. The market value of Blur Corp.'s outstanding debt is
$31,412 million, and its preferred stocks' value is $17,451 million. Blur Corp. has 150 million shares of common stock outstanding, and its weighted
average cost of capital (WACC) equals 13.86%.
Term
Total firm value
Intrinsic value of common equity
Intrinsic value per share
Value (Millions)
Using the preceding information and the FCF you calculated in the previous question, calculate the appropriate values in this table. Assume the firm
has no nonoperating assets.
Transcribed Image Text:The corporate valuation model, the price-to-earnings (P/E) multiple approach, and the economic value added (EVA) approach are some
examples of valuation techniques. The corporate valuation model is similar to the dividend-based valuation that you've done in previous
problems, but it focuses on a firm's free cash flows (FCFS) instead of its dividends. Some firms don't pay dividends, or their dividends
are difficult to forecast. For that reason, some analysts use the corporate valuation model.
Blur Corp. has an expected net operating profit after taxes, EBIT(1-T), of $7,600 million in the coming year. In addition, the firm is expected to have
net capital expenditures of $1,140 million, and net operating working capital (NOWC) is expected to increase by $10 million. How much free cash flow
(FCF) is Blur Corp. expected to generate over the next year?
O $118,668 million
O $6,470 million
O $6,450 million
O $8,730 million
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub


EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub


Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning