The device is used to shine a beam on an object located nearby. The interference pattern is obsrved with a suitable infrared camera. After switching from a 1052 nm to a 1113 nm beam, the device must move 6.155 cm closer to the object in order to align the same order maxima and minima with their original locations on the object. How far Lo was the laser originally from the object? Assume the small-angle approximation applies, and enter the answer in units of meters. m
The device is used to shine a beam on an object located nearby. The interference pattern is obsrved with a suitable infrared camera. After switching from a 1052 nm to a 1113 nm beam, the device must move 6.155 cm closer to the object in order to align the same order maxima and minima with their original locations on the object. How far Lo was the laser originally from the object? Assume the small-angle approximation applies, and enter the answer in units of meters. m
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter27: Wave Optics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 32P
Related questions
Question
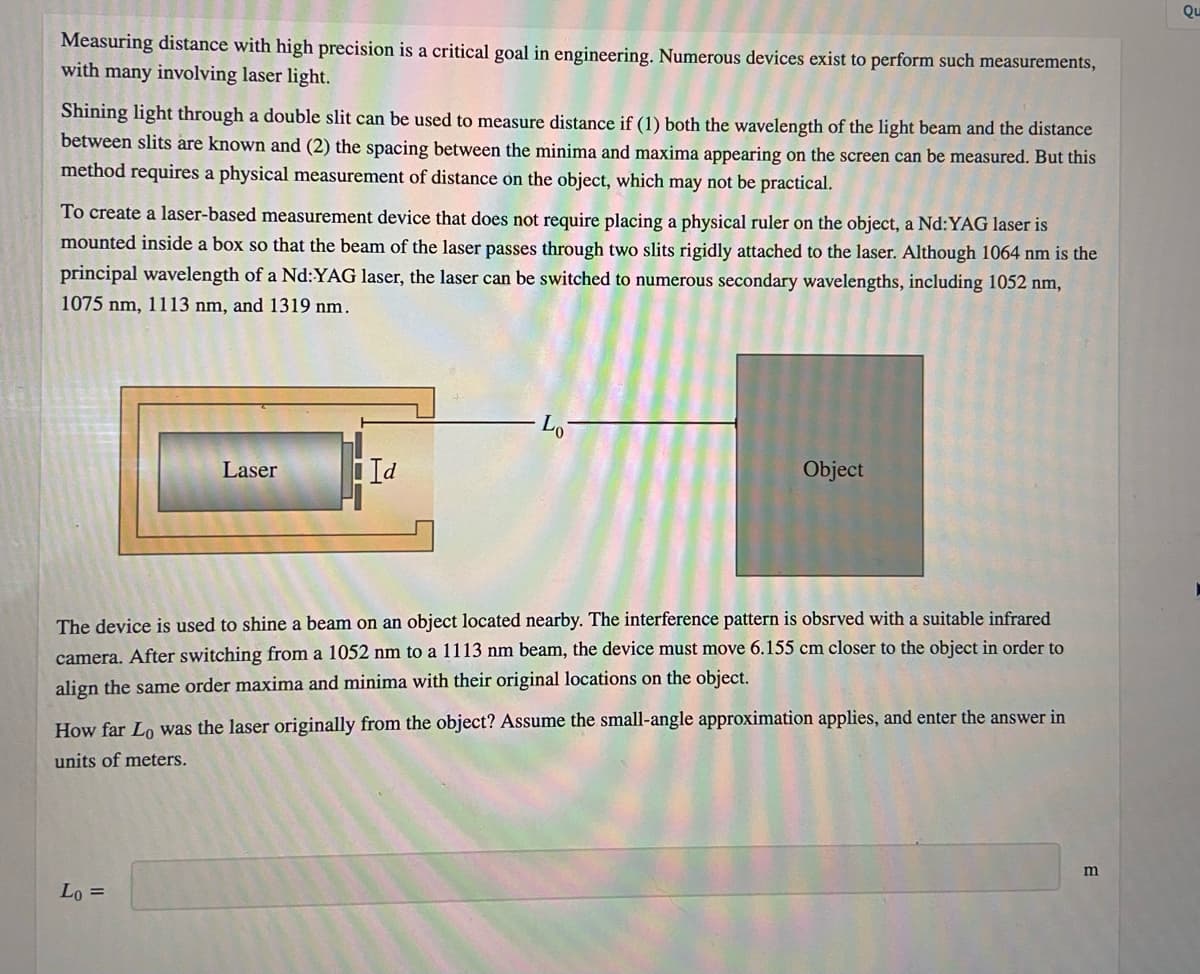
Transcribed Image Text:Measuring distance with high precision is a critical goal in engineering. Numerous devices exist to perform such measurements,
with many involving laser light.
Shining light through a double slit can be used to measure distance if (1) both the wavelength of the light beam and the distance
between slits are known and (2) the spacing between the minima and maxima appearing on the screen can be measured. But this
method requires a physical measurement of distance on the object, which may not be practical.
To create a laser-based measurement device that does not require placing a physical ruler on the object, a Nd:YAG laser is
mounted inside a box so that the beam of the laser passes through two slits rigidly attached to the laser. Although 1064 nm is the
principal wavelength of a Nd:YAG laser, the laser can be switched to numerous secondary wavelengths, including 1052 nm,
1075 nm, 1113 nm, and 1319 nm.
Laser
Id
Object
The device is used to shine a beam on an object located nearby. The interference pattern is obsrved with a suitable infrared
camera. After switching from a 1052 nm to a 1113 nm beam, the device must move 6.155 cm closer to the object in order to
align the same order maxima and minima with their original locations on the object.
How far Lo was the laser originally from the object? Assume the small-angle approximation applies, and enter the answer in
units of meters.
m
Lo =
Qu
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill