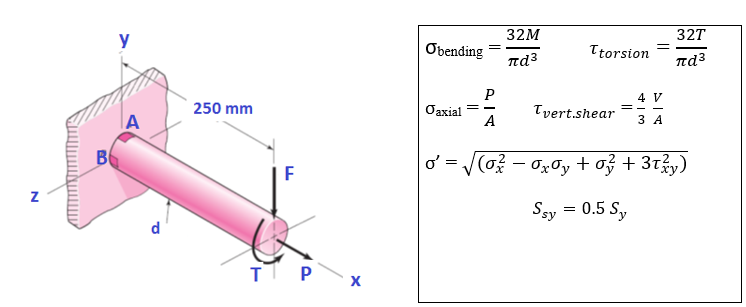
The factor of safety for a machine element depends on the particular point selected for analysis. For the bar and loading, shown in the figure below, we need to have a minimum factor of safety, ηy = 2.5. The bar is to be made of AISI 1050 cold-drawn steel and is loaded by F = 2.65 kN, P = 10.5 kN, and T = 52 N-m. Draw planar stress elements (A and B) showing normal and shear stresses at their proper orientations. Determine a safe diameter d to the nearest mm, based upon the distortion-energy theory, for both stress elements at A and B of the member shown in the figure. Determine the safe diameter, d, based on maximum shear stress theory. You are the designer, and you are to decide on the safe diameter, chosen from one of the diameters obtained from different failure theories used in parts (b) and (c) above, and explain your final decision made on the diameter.
Design Against Fluctuating Loads
Machine elements are subjected to varieties of loads, some components are subjected to static loads, while some machine components are subjected to fluctuating loads, whose load magnitude tends to fluctuate. The components of a machine, when rotating at a high speed, are subjected to a high degree of load, which fluctuates from a high value to a low value. For the machine elements under the action of static loads, static failure theories are applied to know the safe and hazardous working conditions and regions. However, most of the machine elements are subjected to variable or fluctuating stresses, due to the nature of load that fluctuates from high magnitude to low magnitude. Also, the nature of the loads is repetitive. For instance, shafts, bearings, cams and followers, and so on.
Design Against Fluctuating Load
Stress is defined as force per unit area. When there is localization of huge stresses in mechanical components, due to irregularities present in components and sudden changes in cross-section is known as stress concentration. For example, groves, keyways, screw threads, oil holes, splines etc. are irregularities.
The factor of safety for a machine element depends on the particular point selected for analysis. For the bar and loading, shown in the figure below, we need to have a minimum factor of safety, ηy = 2.5. The bar is to be made of AISI 1050 cold-drawn steel and is loaded by F = 2.65 kN, P = 10.5 kN, and T = 52 N-m.
- Draw planar stress elements (A and B) showing normal and shear stresses at their proper orientations.
- Determine a safe diameter d to the nearest mm, based upon the distortion-energy theory, for both stress elements at A and B of the member shown in the figure.
- Determine the safe diameter, d, based on maximum shear stress theory.
- You are the designer, and you are to decide on the safe diameter, chosen from one of the diameters obtained from different failure theories used in parts (b) and (c) above, and explain your final decision made on the diameter.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images









