The figure below shows a two-stage vapor-compression refrigeration system with ammonia as the working fluid. The system uses a direct-contact heat exchanger to achieve intercooling. The evaporator has a refrigerating capacity of 40 tons and produces -30°F saturated vapor at its exit. In the first compressor stage, the refrigerant is compressed adiabatically to 140 lbf/in.², which is the pressure in the direct contact heat exchanger. Saturated vapor at 140 lbf/in² enters the second compressor stage and is compressed adiabatically to 250 lbf/in.2 Each compressor stage has an isentropic efficiency of 85%. There are no significant pressure drops as the refrigerant passes through the heat exchangers. Saturated liquid enters each expansion valve.
The figure below shows a two-stage vapor-compression refrigeration system with ammonia as the working fluid. The system uses a direct-contact heat exchanger to achieve intercooling. The evaporator has a refrigerating capacity of 40 tons and produces -30°F saturated vapor at its exit. In the first compressor stage, the refrigerant is compressed adiabatically to 140 lbf/in.², which is the pressure in the direct contact heat exchanger. Saturated vapor at 140 lbf/in² enters the second compressor stage and is compressed adiabatically to 250 lbf/in.2 Each compressor stage has an isentropic efficiency of 85%. There are no significant pressure drops as the refrigerant passes through the heat exchangers. Saturated liquid enters each expansion valve.
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Chapter22: Condensers
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7RQ: When a standard-efficiency air-cooled condenser is used, the condensing refrigerant will normally be...
Related questions
Question
100%
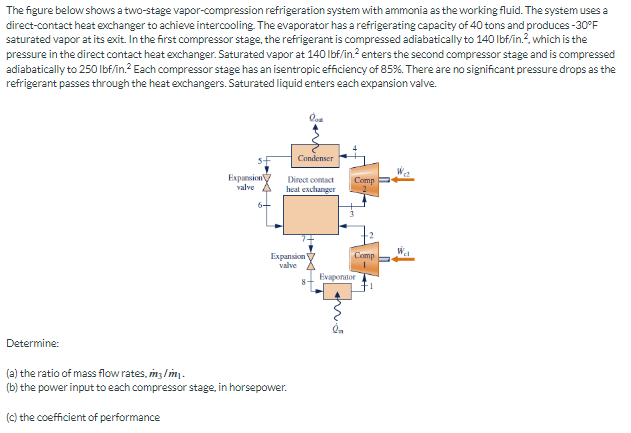
Transcribed Image Text:The figure below shows a two-stage vapor-compression refrigeration system with ammonia as the working fluid. The system uses a
direct-contact heat exchanger to achieve intercooling. The evaporator has a refrigerating capacity of 40 tons and produces -30°F
saturated vapor at its exit. In the first compressor stage, the refrigerant is compressed adiabatically to 140 lbf/in.², which is the
pressure in the direct contact heat exchanger. Saturated vapor at 140 lbf/in.² enters the second compressor stage and is compressed
adiabatically to 250 lbf/in.² Each compressor stage has an isentropic efficiency of 85%. There are no significant pressure drops as the
refrigerant passes through the heat exchangers. Saturated liquid enters each expansion valve.
Determine:
Expansion
valve
6-
Condenser
Direct contact
heat exchanger
Expansion
valve
(a) the ratio of mass flow rates, m3/my.
(b) the power input to each compressor stage, in horsepower.
(c) the coefficient of performance
Comp
Comp
Evaporator
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning