[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Sweeten Company had no jobs in progress at the beginning of the year and no beginning inventories. It started, completed, and sold only two jobs during the year-Job P and Job Q. The company uses a plantwide predetermined overhead rate based on machine-hours. At the beginning of the year, it estimated that 4,000 machine-hours would be required for the period's estimated level of production. Sweeten also estimated $31,000 of fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the coming period and variable manufacturing overhead of $3.20 per machine-hour. Because Sweeten has two manufacturing departments-Molding and Fabrication-it is considering replacing its plantwide overhead rate with departmental rates that would also be based on machine-hours. The company gathered the following additional information to enable calculating departmental overhead rates: Molding 2,500 $ 13,750 $ 2.90 Fabrication 1,500 $ 17,250 $ 3.70 Total 4,000 $ 31,000 Estimated total machine-hours used Estimated total fixed manufacturing overhead Estimated variable manufacturing overhead per machine-hour The direct materials cost, direct labor cost, and machine-hours used for Jobs P and Q are as follows: Direct materials Direct labor cost Job P $ 28,000 $ 33,000 Job Q $ 15,500 $ 13,500 Actual machine-hours used: Molding Fabrication 3,200 2,100 5,300 2,300 2,400 4,700 Total Sweeten Company had no overapplied or underapplied manufacturing overhead costs during the year.
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Sweeten Company had no jobs in progress at the beginning of the year and no beginning inventories. It started, completed, and sold only two jobs during the year-Job P and Job Q. The company uses a plantwide predetermined overhead rate based on machine-hours. At the beginning of the year, it estimated that 4,000 machine-hours would be required for the period's estimated level of production. Sweeten also estimated $31,000 of fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the coming period and variable manufacturing overhead of $3.20 per machine-hour. Because Sweeten has two manufacturing departments-Molding and Fabrication-it is considering replacing its plantwide overhead rate with departmental rates that would also be based on machine-hours. The company gathered the following additional information to enable calculating departmental overhead rates: Molding 2,500 $ 13,750 $ 2.90 Fabrication 1,500 $ 17,250 $ 3.70 Total 4,000 $ 31,000 Estimated total machine-hours used Estimated total fixed manufacturing overhead Estimated variable manufacturing overhead per machine-hour The direct materials cost, direct labor cost, and machine-hours used for Jobs P and Q are as follows: Direct materials Direct labor cost Job P $ 28,000 $ 33,000 Job Q $ 15,500 $ 13,500 Actual machine-hours used: Molding Fabrication 3,200 2,100 5,300 2,300 2,400 4,700 Total Sweeten Company had no overapplied or underapplied manufacturing overhead costs during the year.
Principles of Cost Accounting
17th Edition
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Chapter5: Process Cost Accounting—general Procedures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8E: Argo Manufacturing Co. had 500 units, three-fifths completed, in process at the beginning of the...
Related questions
Question
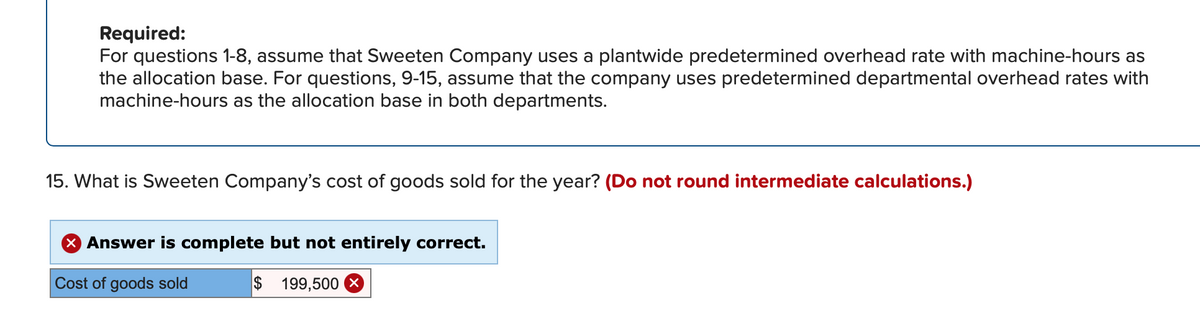
Transcribed Image Text:Required:
For questions 1-8, assume that Sweeten Company uses a plantwide predetermined overhead rate with machine-hours as
the allocation base. For questions, 9-15, assume that the company uses predetermined departmental overhead rates with
machine-hours as the allocation base in both departments.
15. What is Sweeten Company's cost of goods sold for the year? (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
X Answer is complete but not entirely correct.
Cost of goods sold
$
199,500 X
![Required information
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Sweeten Company had no jobs in progress at the beginning of the year and no beginning inventories. It started,
completed, and sold only two jobs during the year-Job P and Job Q. The company uses a plantwide predetermined
overhead rate based on machine-hours. At the beginning of the year, it estimated that 4,000 machine-hours would be
required for the period's estimated level of production. Sweeten also estimated $31,000 of fixed manufacturing overhead
cost for the coming period and variable manufacturing overhead of $3.20 per machine-hour.
Because Sweeten has two manufacturing departments-Molding and Fabrication-it is considering replacing its plantwide
overhead rate with departmental rates that would also be based on machine-hours. The company gathered the following
additional information to enable calculating departmental overhead rates:
Molding
2,500
$ 13,750
$ 2.90
Fabrication
1,500
$ 17,250
$ 3.70
Total
Estimated total machine-hours used
4,000
Estimated total fixed manufacturing overhead
Estimated variable manufacturing overhead per machine-hour
$ 31,000
The direct materials cost, direct labor cost, and machine-hours used for Jobs P and Q are as follows:
Job Q
$ 15,500
$ 13,500
Job P
Direct materials
Direct labor cost
Actual machine-hours used:
$ 28,000
$ 33,000
Molding
Fabrication
3,200
2,100
5,300
2,300
2,400
4,700
Total
Sweeten Company had no overapplied or underapplied manufacturing overhead costs during the year.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fe545fd09-eb77-4890-bcfb-29db8d122cdd%2Fea284f84-da97-4689-91a9-e88235fa4a6c%2F2v51pco_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Sweeten Company had no jobs in progress at the beginning of the year and no beginning inventories. It started,
completed, and sold only two jobs during the year-Job P and Job Q. The company uses a plantwide predetermined
overhead rate based on machine-hours. At the beginning of the year, it estimated that 4,000 machine-hours would be
required for the period's estimated level of production. Sweeten also estimated $31,000 of fixed manufacturing overhead
cost for the coming period and variable manufacturing overhead of $3.20 per machine-hour.
Because Sweeten has two manufacturing departments-Molding and Fabrication-it is considering replacing its plantwide
overhead rate with departmental rates that would also be based on machine-hours. The company gathered the following
additional information to enable calculating departmental overhead rates:
Molding
2,500
$ 13,750
$ 2.90
Fabrication
1,500
$ 17,250
$ 3.70
Total
Estimated total machine-hours used
4,000
Estimated total fixed manufacturing overhead
Estimated variable manufacturing overhead per machine-hour
$ 31,000
The direct materials cost, direct labor cost, and machine-hours used for Jobs P and Q are as follows:
Job Q
$ 15,500
$ 13,500
Job P
Direct materials
Direct labor cost
Actual machine-hours used:
$ 28,000
$ 33,000
Molding
Fabrication
3,200
2,100
5,300
2,300
2,400
4,700
Total
Sweeten Company had no overapplied or underapplied manufacturing overhead costs during the year.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College