The following table gives the mean velocity of planets in their orbits versus their mean distance from the sun. Note that 1 AU (astronomical unit) is the mean distance from Earth to the sun, about 93 million miles. Planet d = distance (AU) V = velocity (km/sec) Mercury Venus 0.39 47.4 0.72 35.0 Earth 1 29.8 Mars 1.52 24.1 Jupiter Saturn 5.20 13.1 9.58 9.7 Uranus 19.20 6.8 Neptune 30.05 5.4 Astronomers tell us that it is reasonable to model these data with a power function. (a) Use power regression to express velocity as a power function of distance from the sun. (Round regression parameters to two decimal places.) v= 21.41 x d-0.50 V = 21.41 x d-0.29 ov = 29.73 x d-0.50 v = 29.73 x d0.73 v = 29.73 x d0.50 (b) Plot the data along with the regression equation. 50 50 50 50 40 40 40 40 30 30 30 30 20 20 20 20 10 10 10 10 d 5 10 15 20 25 30 5 10 15 20 25 30 5 10 15 20 25 30 5 10 15 20 25 30 (c) An asteroid orbits at a mean distance of 3 AU from the sun. According to the power model you found in part (a), what is the mean orbital velocity of the asteroid? (Round your answer to two decimal places.) | km/sec
The following table gives the mean velocity of planets in their orbits versus their mean distance from the sun. Note that 1 AU (astronomical unit) is the mean distance from Earth to the sun, about 93 million miles. Planet d = distance (AU) V = velocity (km/sec) Mercury Venus 0.39 47.4 0.72 35.0 Earth 1 29.8 Mars 1.52 24.1 Jupiter Saturn 5.20 13.1 9.58 9.7 Uranus 19.20 6.8 Neptune 30.05 5.4 Astronomers tell us that it is reasonable to model these data with a power function. (a) Use power regression to express velocity as a power function of distance from the sun. (Round regression parameters to two decimal places.) v= 21.41 x d-0.50 V = 21.41 x d-0.29 ov = 29.73 x d-0.50 v = 29.73 x d0.73 v = 29.73 x d0.50 (b) Plot the data along with the regression equation. 50 50 50 50 40 40 40 40 30 30 30 30 20 20 20 20 10 10 10 10 d 5 10 15 20 25 30 5 10 15 20 25 30 5 10 15 20 25 30 5 10 15 20 25 30 (c) An asteroid orbits at a mean distance of 3 AU from the sun. According to the power model you found in part (a), what is the mean orbital velocity of the asteroid? (Round your answer to two decimal places.) | km/sec
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Chapter5: A Survey Of Other Common Functions
Section5.3: Modeling Data With Power Functions
Problem 2E: Planetary Velocity The following table gives the mean velocity of planets in their orbits versus...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
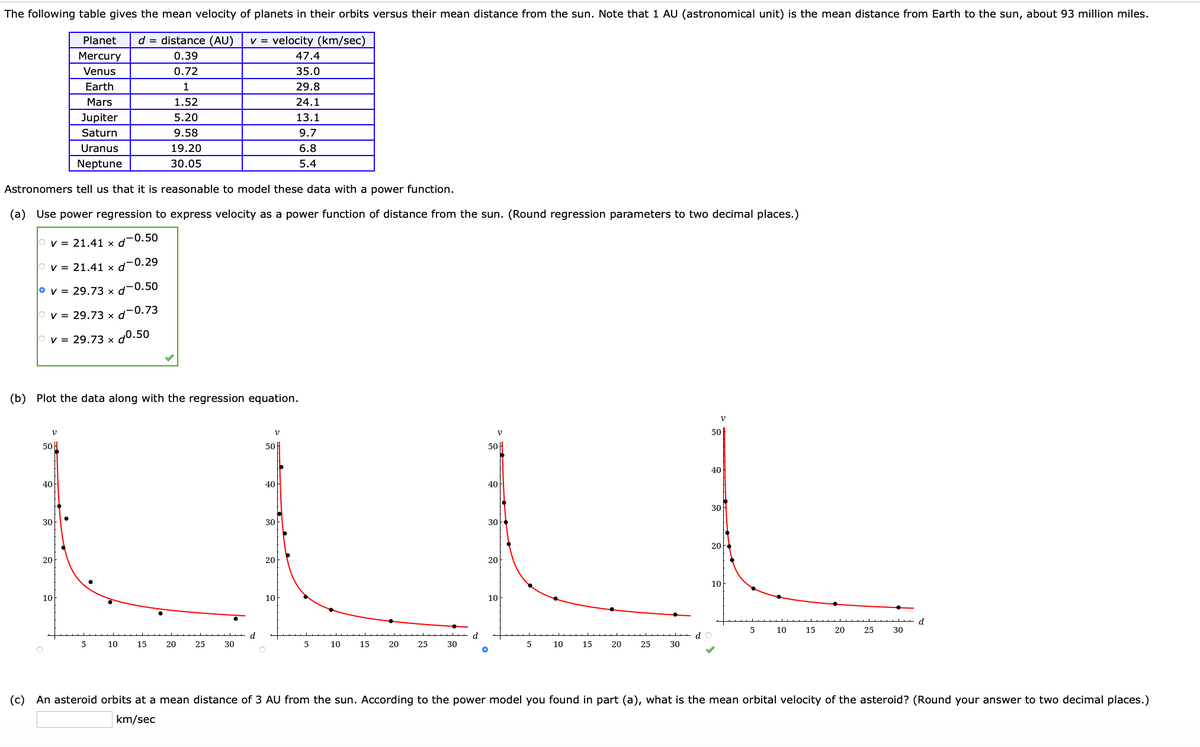
Transcribed Image Text:The following table gives the mean velocity of planets in their orbits versus their mean distance from the sun. Note that 1 AU (astronomical unit) is the mean distance from Earth to the sun, about 93 million miles.
Planet
d = distance (AU)
v = velocity (km/sec)
Mercury
0.39
47.4
Venus
0.72
35.0
Earth
1
29.8
Mars
1.52
24.1
Jupiter
5.20
13.1
Saturn
9.58
9.7
Uranus
19.20
6.8
Neptune
30.05
5.4
Astronomers tell us that it is reasonable to model these data with a power function.
(a) Use power regression to express velocity as a power function of distance from the sun. (Round regression parameters to two decimal places.)
V = 21.41 x d
-0.50
V = 21.41 x d-0.29
° v = 29.73 x d¬0.50
V = 29.73 x d-0.73
v = 29.73 x d0.50
(b) Plot the data along with the regression equation.
v
V
50
50 H
50
50H
40
40
40
40
30
30
30
30
20
20
20
20-
10
10
10
10
d
10
15
20
25
30
d
d
5
10
15
20
25
30
5
10
15
20
25
30
5
10
15
20
25
30
(c) An asteroid orbits at a mean distance of 3 AU from the sun. According to the power model you found in part (a), what is the mean orbital velocity of the asteroid? (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
km/sec
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt