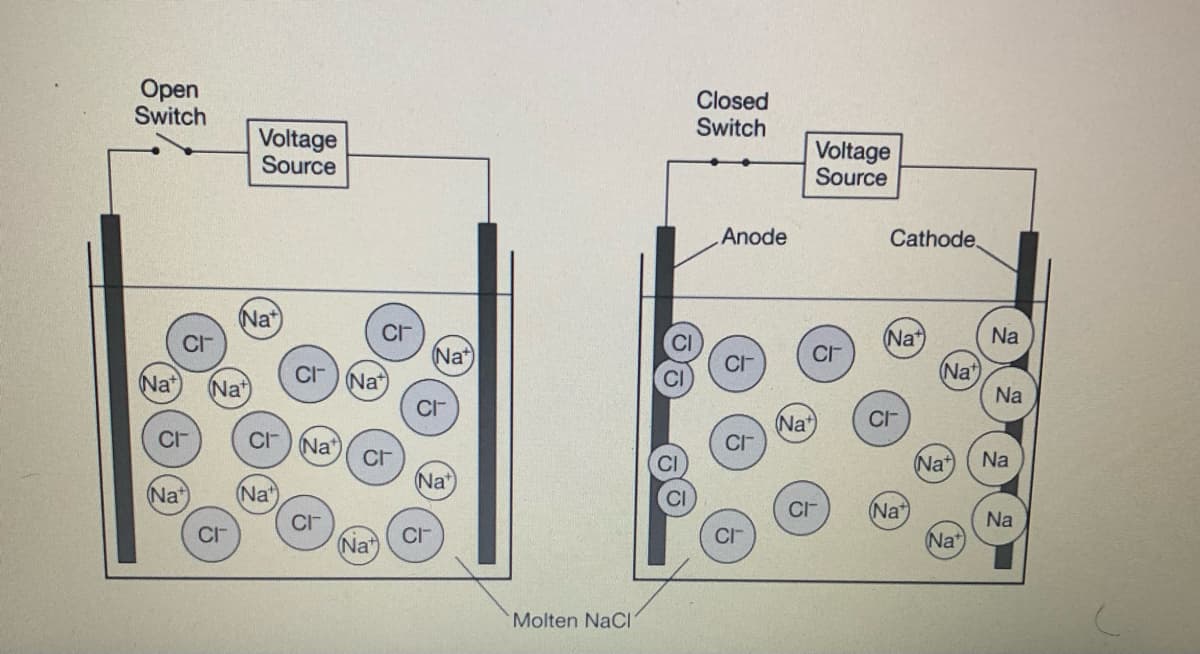
The particle diagrams above represent NaCl(1) and its decomposition into Na(l) and Cl2(g) in an electrochemical cell after voltage is applied. Which of the following statements about the thermodynamic favorability of the decomposition of NaCl(1) is supported by the particle diagrams and why? The decomposition is thermodynamically favored because the transfer of electrons to and from the ions occurs at the electrodes. The decomposition is thermodynamically favored because the formation of a gaseous product results in an increase in entropy. The decomposition is not thermodynamically favored because the pure elements form only after electrical energy is supplied. D The decomposition is not thermodynamically favored because there is a decrease in the number of particles as the reaction proceeds.
The particle diagrams above represent NaCl(1) and its decomposition into Na(l) and Cl2(g) in an electrochemical cell after voltage is applied. Which of the following statements about the thermodynamic favorability of the decomposition of NaCl(1) is supported by the particle diagrams and why? The decomposition is thermodynamically favored because the transfer of electrons to and from the ions occurs at the electrodes. The decomposition is thermodynamically favored because the formation of a gaseous product results in an increase in entropy. The decomposition is not thermodynamically favored because the pure elements form only after electrical energy is supplied. D The decomposition is not thermodynamically favored because there is a decrease in the number of particles as the reaction proceeds.
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter11: Solutions And Colloids
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3E: When KNO3 is dissolved in water, the resulting solution is significantly colder than the water was...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The particle diagrams above represent NaCl(1) and its decomposition into Na(l) and Cl2(g) in an electrochemical cell after voltage is applied. Which of the following statements about the
thermodynamic favorability of the decomposition of NaCl(1) is supported by the particle diagrams and why?
The decomposition is thermodynamically favored because the transfer of electrons to and from the ions occurs at the electrodes.
The decomposition is thermodynamically favored because the formation of a gaseous product results in an increase in entropy.
The decomposition is not thermodynamically favored because the pure elements form only after electrical energy is supplied.
D.
The decomposition is not thermodynamically favored because there is a decrease in the number of particles as the reaction proceeds.
Transcribed Image Text:Open
Switch
Closed
Switch
Voltage
Source
Voltage
Source
Anode
Cathode.
(Na*
CI-
Nat
Na
(Na+
Na*
C)Na*
Nat
Nat
Na
C
(Na*)
CI
CF
Na*
Na*)
Na
Na
(Na+
(Na"
CI-
(Na*
CI
Nat
Na
Na*
CI
CI-
Molten NaCI
of
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning