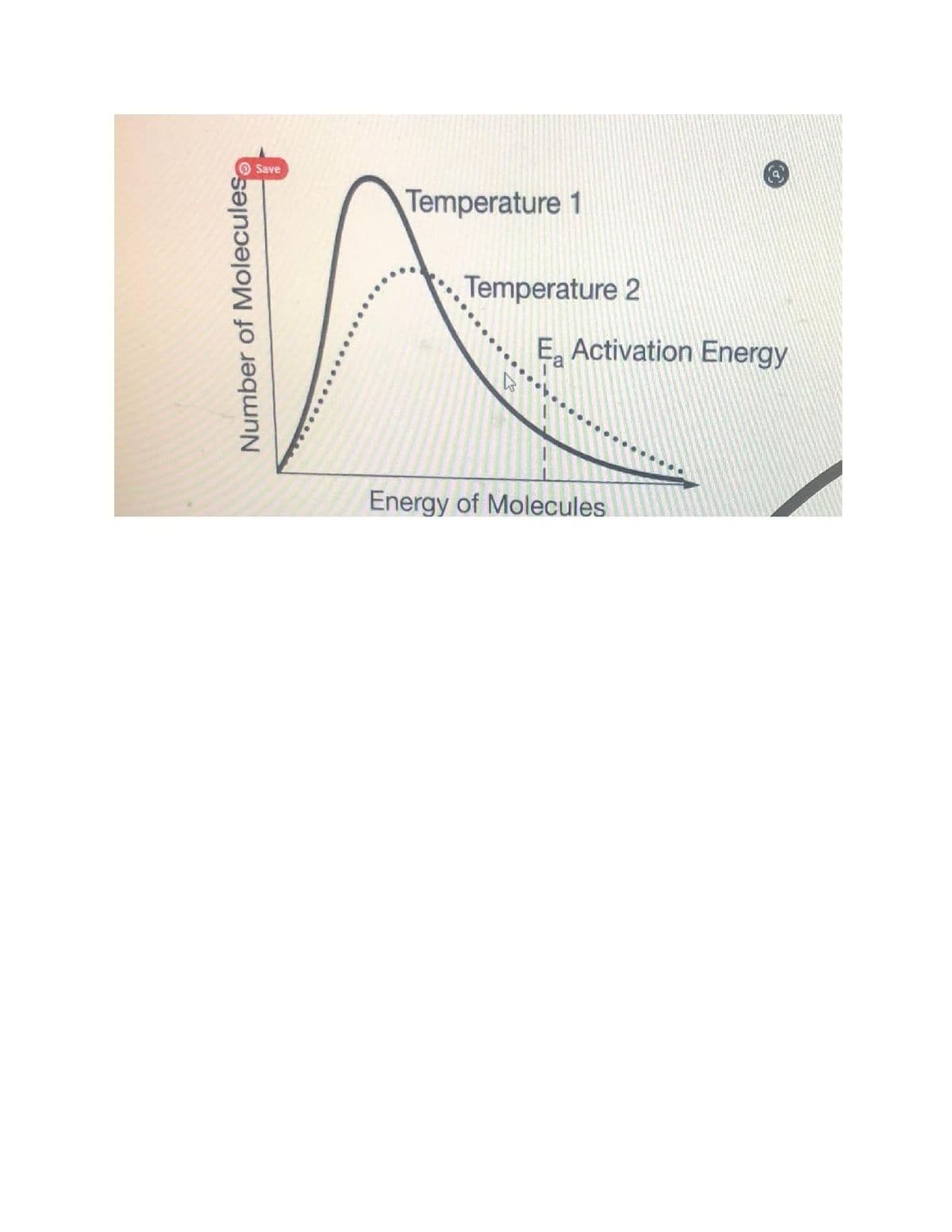
The proposed rate-determining step for a reaction is 2 NO2(g)→NO3(g)+NO(g)2 . The graph above shows the distribution of energies for NO2(g) molecules at two temperatures. Based on the graph, which of the following statements best explains why the rates of disappearance of NO2(g) are different at temperature 2 and temperature 1? (see attached image) a.) NO2(g) is consumed at a faster rate at temperature 2 because more molecules possess energies at or above the minimum energy required for a collision to lead to a reaction compared to temperature 1. b.) NO2(g) is consumed at a faster rate at temperature 2 because the molecules have a wider range of energies allowing for a better orientation during a collision compared to temperature 1. c.) Fewer NO2(g) molecules have a relatively high energy at temperature 1, which favors collisions between molecules rather than between the molecules and the container, leading to a faster rate of disappearance compared to temperature 2. d.) More NO2(g) molecules have a relatively low energy at temperature 1, which increases the number of effective collisions taking place and the rate of disappearance compared to temperature 2.
The proposed rate-determining step for a reaction is 2 NO2(g)→NO3(g)+NO(g)2 . The graph above shows the distribution of energies for NO2(g) molecules at two temperatures. Based on the graph, which of the following statements best explains why the rates of disappearance of NO2(g) are different at temperature 2 and temperature 1? (see attached image) a.) NO2(g) is consumed at a faster rate at temperature 2 because more molecules possess energies at or above the minimum energy required for a collision to lead to a reaction compared to temperature 1. b.) NO2(g) is consumed at a faster rate at temperature 2 because the molecules have a wider range of energies allowing for a better orientation during a collision compared to temperature 1. c.) Fewer NO2(g) molecules have a relatively high energy at temperature 1, which favors collisions between molecules rather than between the molecules and the container, leading to a faster rate of disappearance compared to temperature 2. d.) More NO2(g) molecules have a relatively low energy at temperature 1, which increases the number of effective collisions taking place and the rate of disappearance compared to temperature 2.
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter17: Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 94AP
Related questions
Question
The proposed rate-determining step for a reaction is 2 NO2(g)→NO3(g)+NO(g)2 . The graph above shows the distribution of energies for NO2(g) molecules at two temperatures. Based on the graph, which of the following statements best explains why the rates of disappearance of NO2(g) are different at temperature 2 and temperature 1? (see attached image)
a.) NO2(g) is consumed at a faster rate at temperature 2 because more molecules possess energies at or above the minimum energy required for a collision to lead to a reaction compared to temperature 1.
b.) NO2(g) is consumed at a faster rate at temperature 2 because the molecules have a wider range of energies allowing for a better orientation during a collision compared to temperature 1.
c.) Fewer NO2(g) molecules have a relatively high energy at temperature 1, which favors collisions between molecules rather than between the molecules and the container, leading to a faster rate of disappearance compared to temperature 2.
d.) More NO2(g) molecules have a relatively low energy at temperature 1, which increases the number of effective collisions taking place and the rate of disappearance compared to temperature 2.
Transcribed Image Text:O Save
Temperature 1
Temperature 2
E, Activation Energy
Energy of Molecules
Number of Molecules
Expert Solution
Step 1
Activation energy:
When the reactant molecule converts into the products, they required the minimum amount of excess energy known as activation energy. The highest energy state between the reactant and the product is known as the transition state.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305960060
Author:
Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning