The quantity demanded of salt decreases when the price of pepper increases. This is an example of * O own-price elasticity. O supply elasticity. O income elasticity. O rubber band elasticity. cross-price elasticity. If the government wants to put a per unit tax on a product so that it can raise revenue to support local schools, it would most likely accomplish this goal by doing which of the following? * O placing a tax on a good with an elastic demand. O placing a tax on a good that has many substitutes. O placing a tax on a good with an inelastic demand. O placing a tax on a good with a perfectly elastic demand. O relying of the goodness of mankind and simply ask for donations.
The quantity demanded of salt decreases when the price of pepper increases. This is an example of * O own-price elasticity. O supply elasticity. O income elasticity. O rubber band elasticity. cross-price elasticity. If the government wants to put a per unit tax on a product so that it can raise revenue to support local schools, it would most likely accomplish this goal by doing which of the following? * O placing a tax on a good with an elastic demand. O placing a tax on a good that has many substitutes. O placing a tax on a good with an inelastic demand. O placing a tax on a good with a perfectly elastic demand. O relying of the goodness of mankind and simply ask for donations.
Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
14th Edition
ISBN:9781337794992
Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Chapter6: Demand And Elasticity
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3TY
Related questions
Question
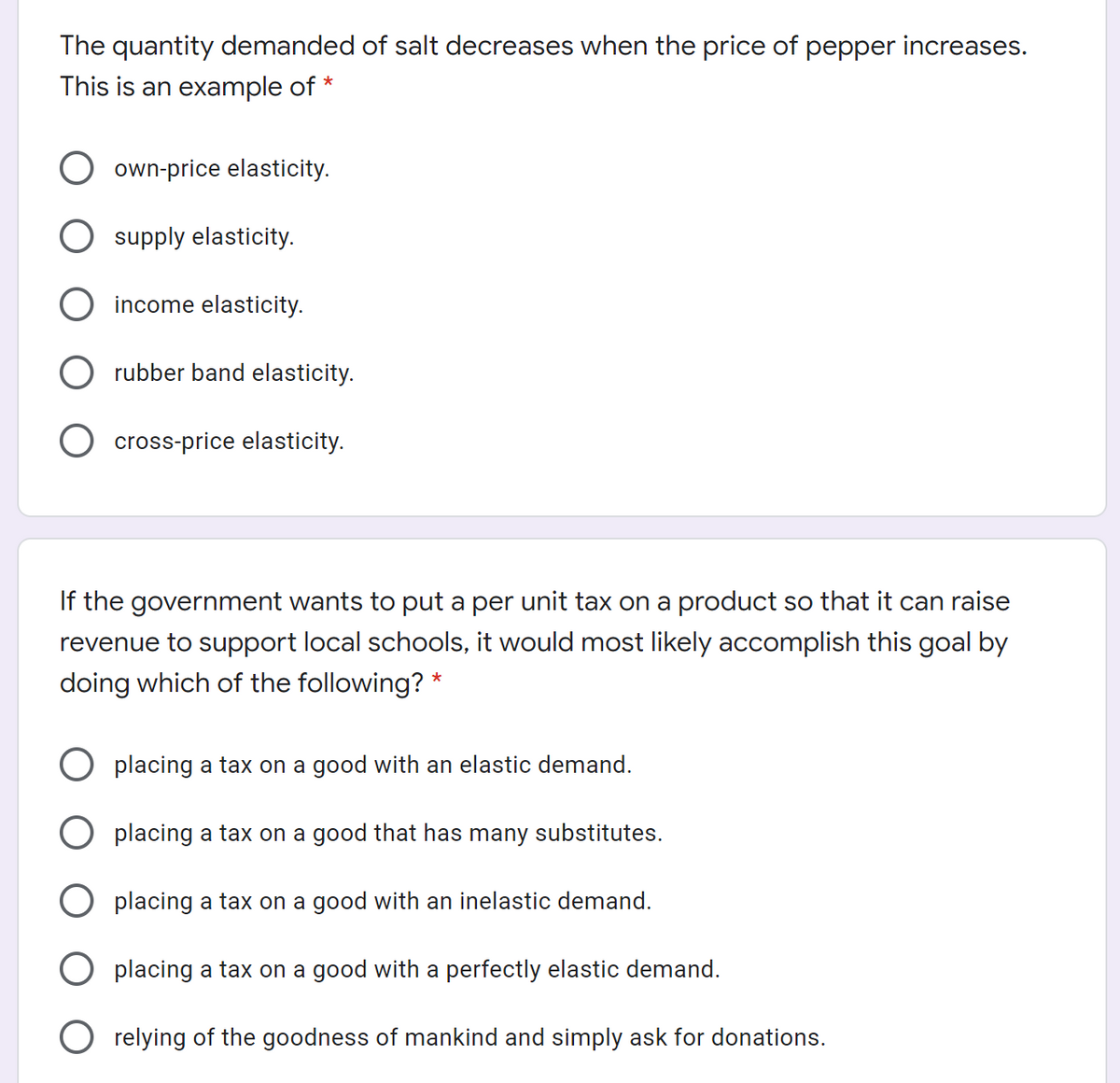
Transcribed Image Text:The quantity demanded of salt decreases when the price of pepper increases.
This is an example of *
own-price elasticity.
supply elasticity.
income elasticity.
O rubber band elasticity.
cross-price elasticity.
If the government wants to put a per unit tax on a product so that it can raise
revenue to support local schools, it would most likely accomplish this goal by
doing which of the following? *
O placing a tax on a good with an elastic demand.
placing a tax on a good that has many substitutes.
placing a tax on a good with an inelastic demand.
placing a tax on a good with a perfectly elastic demand.
O relying of the goodness of mankind and simply ask for donations.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
