The researchers analyzed the length of hairs from individuals with FT and from unaffected individuals and plotted the length of each hair as shown in Figure 2A. They also determined the ratio of hairs in growth phase to hairs in rest phase as shown in Figure 2B. In a final experiment, the researchers grew human hair in a petri dish with and without adding FGF5 to the dish. The growth of the hair over an 8 day period was measured. The data from this experiment are shown in Figure 3. A. B. Hair Length (mm) Relative Proportions of Plucked Hair Fibers 90 80- 70- 50 40 30- 20- 10 0 100- 75 50 25 Affected Individual 1 Length of an individual hair - Average length of hairs measured Affected Unaffected Unaffected Individual Individual Individual 2 1 2 Percent of hairs in growth phase m Affected Affected Unaffected Unaffected Individual Individual Individual Individual 1 2 2 1 Percent of hairs in rest phase Total Increase in Hair Length (mm) 2.0- No treatment 1.5+ --FGF5 1.0- 0.5 00 + 012 3 4 5 Days in Culture Figure 2A (left). Length of hairs taken from individuals with and without FT. + 6 Figure 2B (left). Proportion of hairs examined that were in growth phase compared with the proportion of examined hairs in rest phase. Figure 3 (above). Human hair growth in culture with and without FGF5 + 7 8 Human hair grows in a cycle that includes a growth phase and a rest phase. A small fraction of the hairs on the scalp are in the rest phase, while the majority of the hairs on the scalp are in the growth phase, which allows the hair on the scalp to grow long. Conversely, the majority of hairs in areas such as the eyelashes are in the rest phase, which keeps those hairs short. Familial trichomegaly (FT) is a genetic condition that results in excessively long eyelashes in affected individuals. In an investigation into the causes of FT, a team of researchers identified mutations in the gene that codes for fibroblast growth factor-5 (FGF5) that are associated with FT. FGF5 is a protein that is secreted by certain cells and functions as a signaling molecule that influences the ratio of growth phase to rest phase in hair. The structure of the FGF5 gene includes 3 exons and 2 introns. Alternate splicing of the pre-mRNA transcribed from the gene creates a long version of the mRNA, FGF5-L, and a short version of the mRNA, FGF5-S (Figure 1). ATG FGF5-L FGF5-S ATG Exon 1 * 355 bp Exon 1 Intron 1 ***** Exon 2,1 104* Intron 2 bp * * Position of E1 delTA mutation Position of E2delG mutation Position of E3subT-C mutation Exon 3 348 bp Stop Codon Stop Codon ***
The researchers analyzed the length of hairs from individuals with FT and from unaffected individuals and plotted the length of each hair as shown in Figure 2A. They also determined the ratio of hairs in growth phase to hairs in rest phase as shown in Figure 2B. In a final experiment, the researchers grew human hair in a petri dish with and without adding FGF5 to the dish. The growth of the hair over an 8 day period was measured. The data from this experiment are shown in Figure 3. A. B. Hair Length (mm) Relative Proportions of Plucked Hair Fibers 90 80- 70- 50 40 30- 20- 10 0 100- 75 50 25 Affected Individual 1 Length of an individual hair - Average length of hairs measured Affected Unaffected Unaffected Individual Individual Individual 2 1 2 Percent of hairs in growth phase m Affected Affected Unaffected Unaffected Individual Individual Individual Individual 1 2 2 1 Percent of hairs in rest phase Total Increase in Hair Length (mm) 2.0- No treatment 1.5+ --FGF5 1.0- 0.5 00 + 012 3 4 5 Days in Culture Figure 2A (left). Length of hairs taken from individuals with and without FT. + 6 Figure 2B (left). Proportion of hairs examined that were in growth phase compared with the proportion of examined hairs in rest phase. Figure 3 (above). Human hair growth in culture with and without FGF5 + 7 8 Human hair grows in a cycle that includes a growth phase and a rest phase. A small fraction of the hairs on the scalp are in the rest phase, while the majority of the hairs on the scalp are in the growth phase, which allows the hair on the scalp to grow long. Conversely, the majority of hairs in areas such as the eyelashes are in the rest phase, which keeps those hairs short. Familial trichomegaly (FT) is a genetic condition that results in excessively long eyelashes in affected individuals. In an investigation into the causes of FT, a team of researchers identified mutations in the gene that codes for fibroblast growth factor-5 (FGF5) that are associated with FT. FGF5 is a protein that is secreted by certain cells and functions as a signaling molecule that influences the ratio of growth phase to rest phase in hair. The structure of the FGF5 gene includes 3 exons and 2 introns. Alternate splicing of the pre-mRNA transcribed from the gene creates a long version of the mRNA, FGF5-L, and a short version of the mRNA, FGF5-S (Figure 1). ATG FGF5-L FGF5-S ATG Exon 1 * 355 bp Exon 1 Intron 1 ***** Exon 2,1 104* Intron 2 bp * * Position of E1 delTA mutation Position of E2delG mutation Position of E3subT-C mutation Exon 3 348 bp Stop Codon Stop Codon ***
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Chapter17: Biotechnology And Genomics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3VCQ: Figure 17.15 In 2011, the United States Preventative Services Task Force recommended against using...
Related questions
Question
Researchers isolated a mutation that results in an FGF5 receptor that can bind the FGF5 protein but cannot stimulate production of second messengers in the cell. Based on the data provided in Figure 3, predict the effect of the new mutation on hair growth, regardless of hair type.
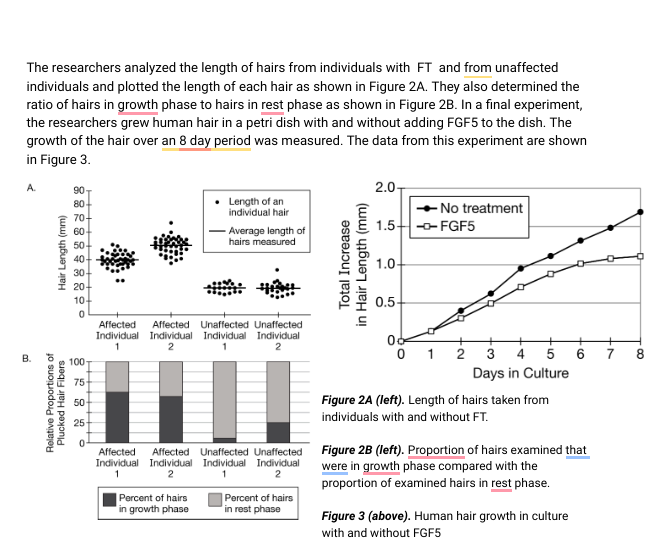
Transcribed Image Text:The researchers analyzed the length of hairs from individuals with FT and from unaffected
individuals and plotted the length of each hair as shown in Figure 2A. They also determined the
ratio of hairs in growth phase to hairs in rest phase as shown in Figure 2B. In a final experiment,
the researchers grew human hair in a petri dish with and without adding FGF5 to the dish. The
growth of the hair over an 8 day period was measured. The data from this experiment are shown
in Figure 3.
A.
B.
Hair Length (mm)
Relative Proportions of
Plucked Hair Fibers
90
80-
70-
50
40
30-
20-
10
0
100-
75
50
25
Affected
Individual
1
Length of an
individual hair
- Average length of
hairs measured
Affected Unaffected Unaffected
Individual Individual Individual
2
1
2
Percent of hairs
in growth phase
m
Affected
Affected Unaffected Unaffected
Individual Individual Individual Individual
1
2
2
1
Percent of hairs
in rest phase
Total Increase
in Hair Length (mm)
2.0-
No treatment
1.5+ --FGF5
1.0-
0.5
00
+
012 3 4 5
Days in Culture
Figure 2A (left). Length of hairs taken from
individuals with and without FT.
+
6
Figure 2B (left). Proportion of hairs examined that
were in growth phase compared with the
proportion of examined hairs in rest phase.
Figure 3 (above). Human hair growth in culture
with and without FGF5
+
7
8
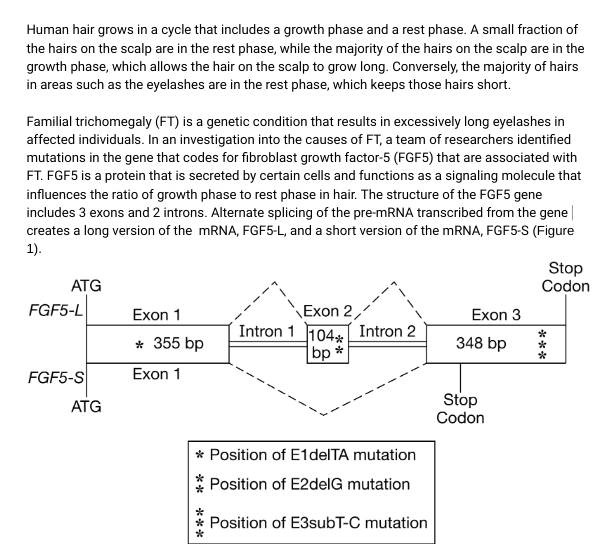
Transcribed Image Text:Human hair grows in a cycle that includes a growth phase and a rest phase. A small fraction of
the hairs on the scalp are in the rest phase, while the majority of the hairs on the scalp are in the
growth phase, which allows the hair on the scalp to grow long. Conversely, the majority of hairs
in areas such as the eyelashes are in the rest phase, which keeps those hairs short.
Familial trichomegaly (FT) is a genetic condition that results in excessively long eyelashes in
affected individuals. In an investigation into the causes of FT, a team of researchers identified
mutations in the gene that codes for fibroblast growth factor-5 (FGF5) that are associated with
FT. FGF5 is a protein that is secreted by certain cells and functions as a signaling molecule that
influences the ratio of growth phase to rest phase in hair. The structure of the FGF5 gene
includes 3 exons and 2 introns. Alternate splicing of the pre-mRNA transcribed from the gene
creates a long version of the mRNA, FGF5-L, and a short version of the mRNA, FGF5-S (Figure
1).
ATG
FGF5-L
FGF5-S
ATG
Exon 1
* 355 bp
Exon 1
Intron 1
*****
Exon 2,1
104* Intron 2
bp *
* Position of E1 delTA mutation
Position of E2delG mutation
Position of E3subT-C mutation
Exon 3
348 bp
Stop
Codon
Stop
Codon
***
AI-Generated Solution
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning