The rigid object shown below consists of three balls and three connecting rods, with M 1.6 kg, L 0.6 m and 0 = 30°. The balls may be treated as particles, and the connecting rods have negligible mass. Determine the rotational kinetic energy of the object if it has an angular speed of w = 1.2 rad/s about (a) an axis that passes through point P and is perpendicular to the plane of the figure, coming out towards your eyes and (b) an axis that passes through point P and lies on the rod of length 2L in the plane of the figure. (Hint: the distance from a particle to the axis of rotation is the length of the line connecting the particle to the axis that is perpendicular to the axis.) 2M L M 2L 2М
The rigid object shown below consists of three balls and three connecting rods, with M 1.6 kg, L 0.6 m and 0 = 30°. The balls may be treated as particles, and the connecting rods have negligible mass. Determine the rotational kinetic energy of the object if it has an angular speed of w = 1.2 rad/s about (a) an axis that passes through point P and is perpendicular to the plane of the figure, coming out towards your eyes and (b) an axis that passes through point P and lies on the rod of length 2L in the plane of the figure. (Hint: the distance from a particle to the axis of rotation is the length of the line connecting the particle to the axis that is perpendicular to the axis.) 2M L M 2L 2М
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter13: Rotation Ii: A Conservation Approach
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 32PQ
Related questions
Question
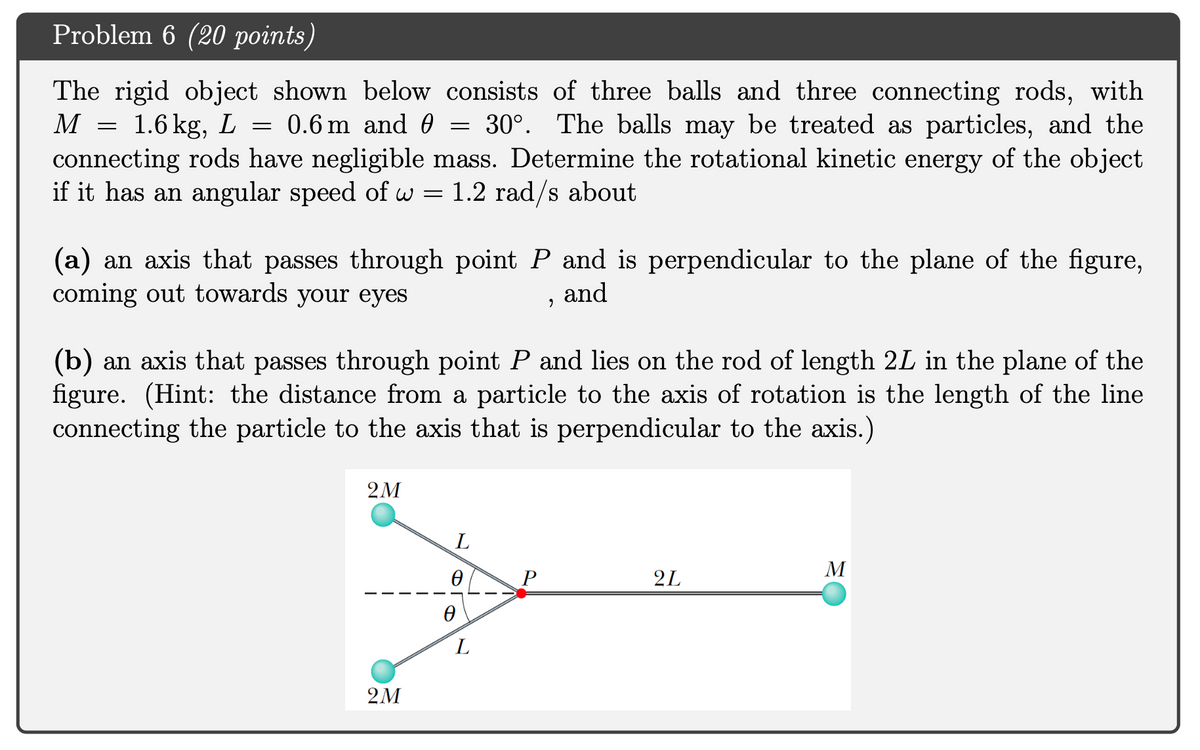
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 6 (20 points)
The rigid object shown below consists of three balls and three connecting rods, with
M
1.6 kg,
0.6 m and 0
30°. The balls may be treated as particles, and the
connecting rods have negligible mass. Determine the rotational kinetic energy of the object
if it has an angular speed of w = 1.2 rad/s about
(a) an axis that passes through point P and is perpendicular to the plane of the figure,
coming out towards your eyes
and
(b) an axis that passes through point P and lies on the rod of length 2L in the plane of the
figure. (Hint: the distance from a particle to the axis of rotation is the length of the line
connecting the particle to the axis that is perpendicular to the axis.)
2M
M
P
2L
L
2M
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning