The salt magnesium chloride is soluble in water. When 0.530 g of MgCl, is dissolved in 106.00 g of water, the temperature of the solution increases from 25.00 to 26.94 °C. Based on this observation, calculate the enthalpy of dissolution of MgCl, (in kJ/mol). Assume that the specific heat of the solution is 4.184 J/g °C and that the heat absorbed by the calorimeter is negligible. AH dissolution kJ/mol
The salt magnesium chloride is soluble in water. When 0.530 g of MgCl, is dissolved in 106.00 g of water, the temperature of the solution increases from 25.00 to 26.94 °C. Based on this observation, calculate the enthalpy of dissolution of MgCl, (in kJ/mol). Assume that the specific heat of the solution is 4.184 J/g °C and that the heat absorbed by the calorimeter is negligible. AH dissolution kJ/mol
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter5: Thermochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 24E: A 0.500-g sample of KCl is added to 50.0 g of water in a calorimeter (Figure 5.12). If the...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The salt magnesium chloride is soluble in water.
When 0.530 g of MgCl, is dissolved in 106.00 g
of water, the temperature of the solution increases
from 25.00 to 26.94 °C. Based on this
observation, calculate the enthalpy of dissolution
of MgCl, (in kJ/mol).
6.
Assume that the specific heat of the solution is
4.184 J/g °C and that the heat absorbed by the
calorimeter is negligible.
AH dissolution
kJ/mol
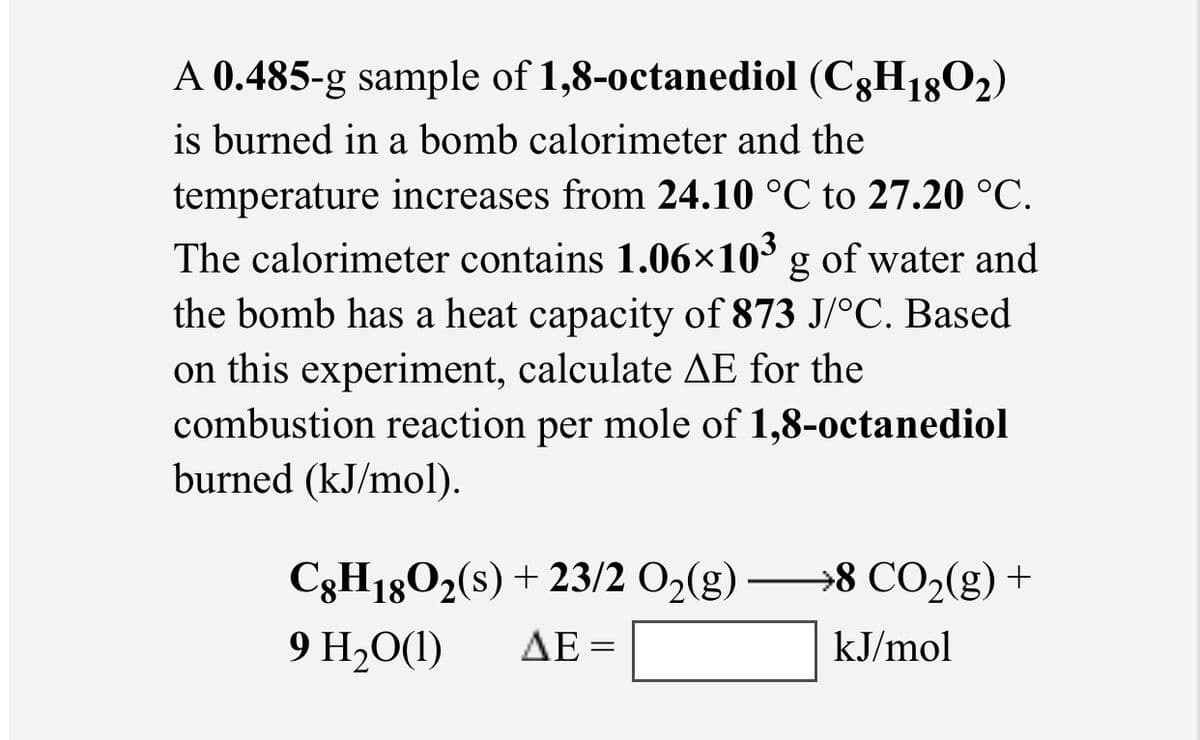
Transcribed Image Text:A 0.485-g sample of 1,8-0ctanediol (C3H1802)
is burned in a bomb calorimeter and the
temperature increases from 24.10 °C to 27.20 °C.
The calorimeter contains 1.06×10³ g of water and
the bomb has a heat capacity of 873 J/°C. Based
on this experiment, calculate AE for the
combustion reaction per mole of 1,8-octanediol
burned (kJ/mol).
C3H1802(s) + 23/2 O2(g) –→8 CO2(g) +
9 H20(1)
ΔΕ-
kJ/mol
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning