The standard enthalpy of formation (AH) is the enthalpy change that occurs when exactly 1 mol of a compound is formed from its constituent elements under standard conditions. The standard conditions are 1 atm pressure, a temperature of 25 °C, and all the species present at a concentration of 1 M.A "standard enthalpies of formation table" containing AH values might look something like this: Part A What is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction used to calculate AH of BaCO3(s)? If fractional coefficients are required, enter them as a fraction (.e. 1/3). Indicate the physical states using te abbreviation (s), 1), or (g) for solid, liquid, or gas, respectively without indicating allotropes. Use (aq) for aqueous solution. Substance AH Express your answer as a chemical equation. H(g) 218 kJ/mol View Available Hint(s) H2(g) O kJ/mol Ba(s) O kJ/mol ΑΣΦ ? Ba2-(aq)-538.4 kJ /mol C(g) 71 kJ/mol C(s) O kJ/mol DA chemical reaction does not occur for this question. N(g) 473 kJ /mol O2(g) O kJ/mol Submit O(g) 249 kJ/mol S2(g) 129 kJ/mol Nex Provide Feedback P Pearson com/myct/itemView?assignmentProblemID=174388861
The standard enthalpy of formation (AH) is the enthalpy change that occurs when exactly 1 mol of a compound is formed from its constituent elements under standard conditions. The standard conditions are 1 atm pressure, a temperature of 25 °C, and all the species present at a concentration of 1 M.A "standard enthalpies of formation table" containing AH values might look something like this: Part A What is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction used to calculate AH of BaCO3(s)? If fractional coefficients are required, enter them as a fraction (.e. 1/3). Indicate the physical states using te abbreviation (s), 1), or (g) for solid, liquid, or gas, respectively without indicating allotropes. Use (aq) for aqueous solution. Substance AH Express your answer as a chemical equation. H(g) 218 kJ/mol View Available Hint(s) H2(g) O kJ/mol Ba(s) O kJ/mol ΑΣΦ ? Ba2-(aq)-538.4 kJ /mol C(g) 71 kJ/mol C(s) O kJ/mol DA chemical reaction does not occur for this question. N(g) 473 kJ /mol O2(g) O kJ/mol Submit O(g) 249 kJ/mol S2(g) 129 kJ/mol Nex Provide Feedback P Pearson com/myct/itemView?assignmentProblemID=174388861
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter5: Thermochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.104QE
Related questions
Question
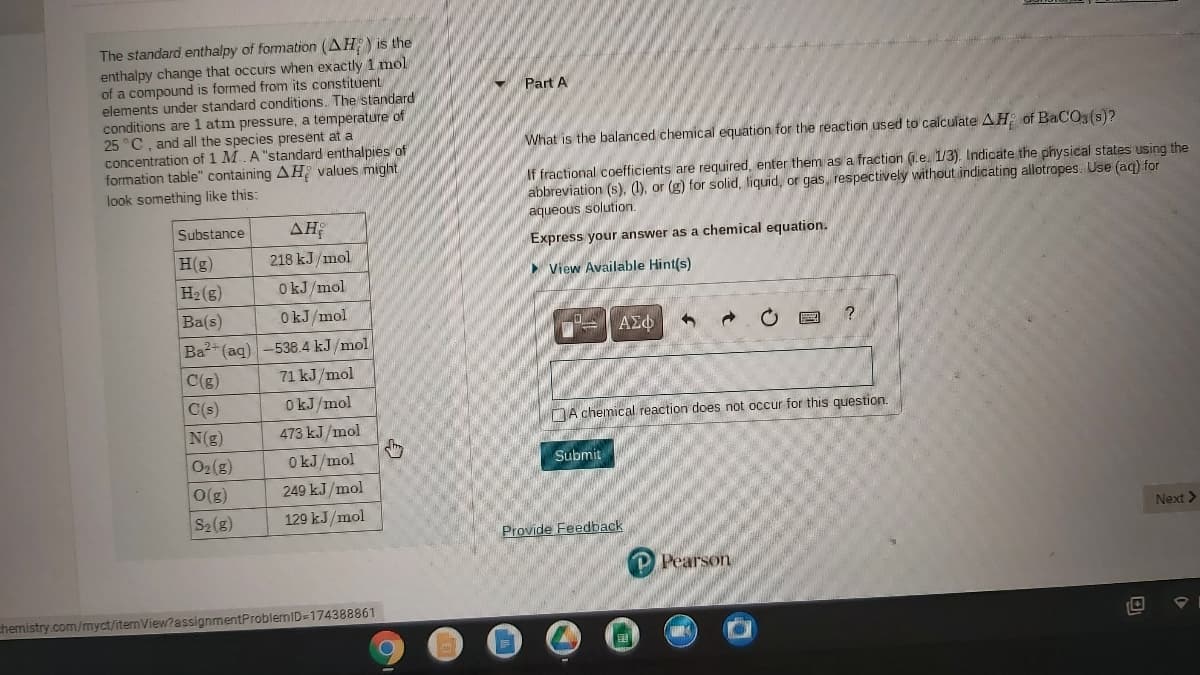
Transcribed Image Text:The standard enthalpy of formation (AH) is the
enthalpy change that occurs when exactly 1 mol
of a compound is formed from its constituent
elements under standard conditions. The standard
conditions are 1 atm pressure, a temperature of
25 °C, and all the species present at a
concentration of 1 M.A "standard enthalpies of
formation table" containing AH values might
look something like this:
Part A
What is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction used to calculate AH of BaCO, (s)?
If fractional coefficients are required, enter them as a fraction (1.e. 1/3). Indicate the physical states using the
abbreviation (s), (1), or (g) for solid, liquid, or gas, respectively without indicating allotrapes. Use (aq) for
aqueous solution.
Substance
AH
Express your answer as a chemical equation.
H(g)
218 kJ/mol
View Available Hint(s)
H2(g)
O kJ/mol
Ba(s)
OkJ/mol
ΑΣφ
Ba2+ (aq) -538.4 kJ /mol
C(g)
71 kJ/mol
C(s)
O kJ/mol
DA chemical reaction does not occur for this question.
N(g)
473 kJ/mol
O2(g)
O kJ/mol
Submit
O(g)
249 kJ /mol
S2(g)
129 kJ/mol
Next >
Provide Feedback
Pearson
chemistry.com/myct/itemView?assignmentProblemID=174388861
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
