The starting compound was treated with different nucleophiles shown in the table. The reaction was carried out in ethanol (similar to CH3OH) at 25°C. This time the leaving group isn’t a single (halogen) atom; it’s a group of atoms that leaves as a unit. (CH3);COC,H4NO2 + NaNu or HNu (CH3)3CNU + brightly colored compound The byproduct has an intense yellow color, while the starting materials are colorless, so the appearance of a yellow color indicates the reaction is occurring. Reaction Nucleophile (Nu) Compound Relative reactivity Number Color change observed NaOCH3 Yellow after 0.52 sec 1 Very bright yellow immediately НОСН3 2 NaSCH3 Yellow after 0.52 sec 3 Faint bright yellow immediately HSCH3 4 1. Rank the relative reactivity of nucleophiles. The shortest time means fastest reaction, which gets number 1 reactivity. The longest time means slowest reaction, which gets the highest number. There may be some tied scores. 2. The name of the mechanism that best explains all four reactions is 3. True or False: Doubling the concentration of nucleophile in Reaction 4 would double the reaction rate.
The starting compound was treated with different nucleophiles shown in the table. The reaction was carried out in ethanol (similar to CH3OH) at 25°C. This time the leaving group isn’t a single (halogen) atom; it’s a group of atoms that leaves as a unit. (CH3);COC,H4NO2 + NaNu or HNu (CH3)3CNU + brightly colored compound The byproduct has an intense yellow color, while the starting materials are colorless, so the appearance of a yellow color indicates the reaction is occurring. Reaction Nucleophile (Nu) Compound Relative reactivity Number Color change observed NaOCH3 Yellow after 0.52 sec 1 Very bright yellow immediately НОСН3 2 NaSCH3 Yellow after 0.52 sec 3 Faint bright yellow immediately HSCH3 4 1. Rank the relative reactivity of nucleophiles. The shortest time means fastest reaction, which gets number 1 reactivity. The longest time means slowest reaction, which gets the highest number. There may be some tied scores. 2. The name of the mechanism that best explains all four reactions is 3. True or False: Doubling the concentration of nucleophile in Reaction 4 would double the reaction rate.
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Andrei Straumanis
Chapter14: Elimination
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20E
Related questions
Question
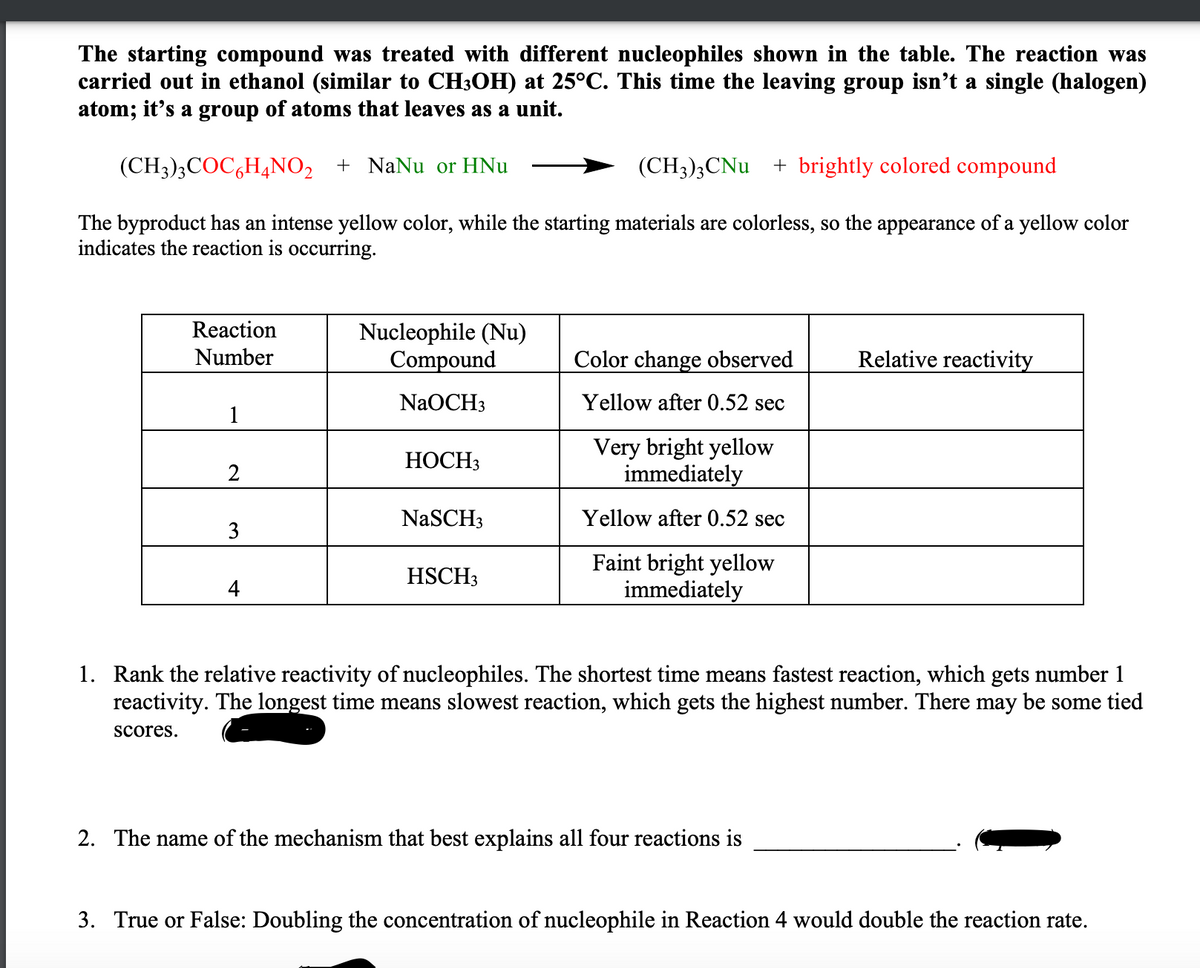
Transcribed Image Text:The starting compound was treated with different nucleophiles shown in the table. The reaction was
carried out in ethanol (similar to CH3OH) at 25°C. This time the leaving group isn’t a single (halogen)
atom; it's a group of atoms that leaves as a unit.
(CH3);COC,H4NO2 + NaNu or HNu
(CH3);CNu + brightly colored compound
The byproduct has an intense yellow color, while the starting materials are colorless, so the appearance of a yellow color
indicates the reaction is occurring.
Reaction
Nucleophile (Nu)
Compound
Relative reactivity
Number
Color change observed
NaOCH3
Yellow after 0.52 sec
1
Very bright yellow
immediately
НОСНЗ
2
NaSCH3
Yellow after 0.52 sec
3
Faint bright yellow
immediately
HSCH3
4
1. Rank the relative reactivity of nucleophiles. The shortest time means fastest reaction, which gets number 1
reactivity. The longest time means slowest reaction, which gets the highest number. There may be some tied
scores.
2. The name of the mechanism that best explains all four reactions is
3. True or False: Doubling the concentration of nucleophile in Reaction 4 would double the reaction rate.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
