The three diagrams below show a block of mass m being pulled or pushed at constant acceleration a, along a table with a force P. The coefficient of kinetic friction is u,. What is the friction force in each case? Give your answer in terms of the pushing force P, a, m, and the angle 0. (i) (ii) (iii) case (i) Did you draw a free-body diagram for this situation and identify all the forces acting on the object? What is Newton's Second Law for motion in the horizontal direction? case f = uk· (m ·g+P•sin – ) (ii) fk = uk · (m·g - P.sin – ) case (ii) Additional Materials
The three diagrams below show a block of mass m being pulled or pushed at constant acceleration a, along a table with a force P. The coefficient of kinetic friction is u,. What is the friction force in each case? Give your answer in terms of the pushing force P, a, m, and the angle 0. (i) (ii) (iii) case (i) Did you draw a free-body diagram for this situation and identify all the forces acting on the object? What is Newton's Second Law for motion in the horizontal direction? case f = uk· (m ·g+P•sin – ) (ii) fk = uk · (m·g - P.sin – ) case (ii) Additional Materials
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter5: Displacement And Force In Two Dimensions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 80A
Related questions
Question
The three diagrams below show a block of mass m being pulled or pushed at constant acceleration ax along a table with a force P. The coefficient of kinetic friction is μk. What is the friction force in each case? Give your answer in terms of the pushing force P, ax, m, and the angle θ.
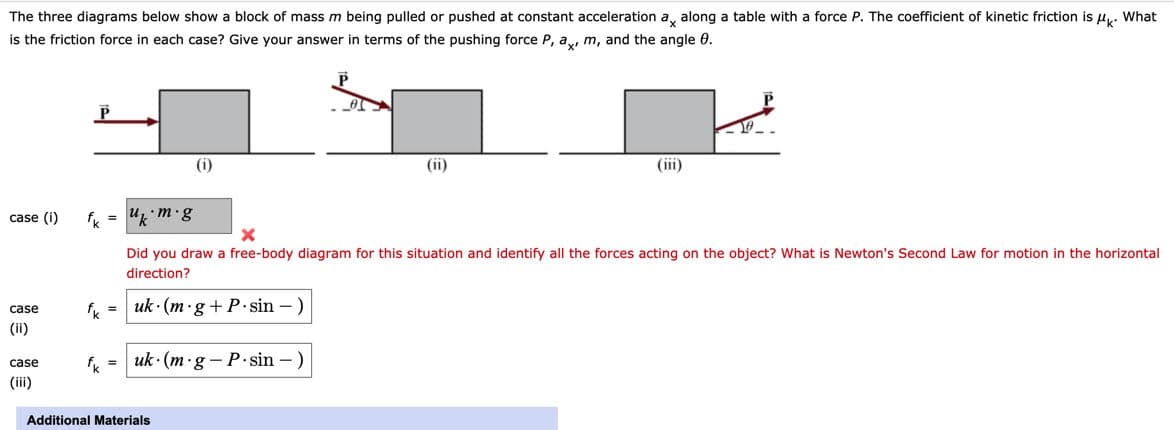
Transcribed Image Text:The three diagrams below show a block of mass m being pulled or pushed at constant acceleration a, along a table with a force P. The coefficient of kinetic friction is u,. What
is the friction force in each case? Give your answer in terms of the pushing force P, a, m, and the angle 0.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
case (i)
Did you draw a free-body diagram for this situation and identify all the forces acting on the object? What is Newton's Second Law for motion in the horizontal
direction?
case
f = uk· (m ·g+P•sin – )
(ii)
fk =
uk · (m·g - P.sin – )
case
(ii)
Additional Materials
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning