The Top Spin Ride can be represented in two dimensions by the following mecnanical system: T L The system consists in two rigid bars linked by a revolute joint. The first bar of mass M and length L rotates around a fixed support at one of its ends, placed at the origin O. It represents the counterweighted arm. The second bar of mass m and length I rotates at one of its ends around the free end of the first bar, it represents the passenger platform. The respective bars' masses are assumed to be distributed uniformly along their lengths. A torque T is applied to the first bar at the origin to represent the action of the motor on the counterweighted arms. The brakes between the counterweighted arms and the passenger platform are represented by a torsional damper with friction coefficient a. The state of the system is given by 0 and ý, which correspond respectively to the angles of the first and second bar with the vertical axis. a). Choose O as the reference point. Determine the potential energy of the system. b). Determine the kinetic energy of the system. c). Derive the mathematical model for the above dynamical system with input T and outputs 0, ý. The solution sliould consist of 2 second order differential equations.
The Top Spin Ride can be represented in two dimensions by the following mecnanical system: T L The system consists in two rigid bars linked by a revolute joint. The first bar of mass M and length L rotates around a fixed support at one of its ends, placed at the origin O. It represents the counterweighted arm. The second bar of mass m and length I rotates at one of its ends around the free end of the first bar, it represents the passenger platform. The respective bars' masses are assumed to be distributed uniformly along their lengths. A torque T is applied to the first bar at the origin to represent the action of the motor on the counterweighted arms. The brakes between the counterweighted arms and the passenger platform are represented by a torsional damper with friction coefficient a. The state of the system is given by 0 and ý, which correspond respectively to the angles of the first and second bar with the vertical axis. a). Choose O as the reference point. Determine the potential energy of the system. b). Determine the kinetic energy of the system. c). Derive the mathematical model for the above dynamical system with input T and outputs 0, ý. The solution sliould consist of 2 second order differential equations.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
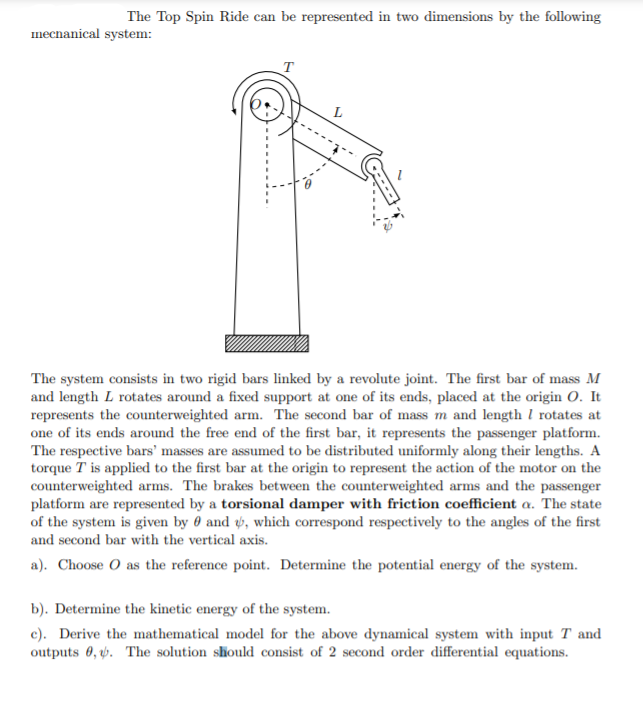
Transcribed Image Text:The Top Spin Ride can be represented in two dimensions by the following
mechanical system:
T
L
The system consists in two rigid bars linked by a revolute joint. The first bar of mass M
and length L rotates around a fixed support at one of its ends, placed at the origin O. It
represents the counterweighted arm. The second bar of mass m and length I rotates at
one of its ends around the free end of the first bar, it represents the passenger platform.
The respective bars' masses are assumed to be distributed uniformly along their lengths. A
torque T is applied to the first bar at the origin to represent the action of the motor on the
counterweighted arms. The brakes between the counterweighted arms and the passenger
platform are represented by a torsional damper with friction coefficient a. The state
of the system is given by 0 and , which correspond respectively to the angles of the first
and second bar with the vertical axis.
a). Choose O as the reference point. Determine the potential energy of the system.
b). Determine the kinetic energy of the system.
c). Derive the mathematical model for the above dynamical system with input T and
outputs 0, tp. The solution should consist of 2 second order differential equations.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY