The velocity of a particle moving along the x-axis varies according to the expression v, = (39 - 0.8t) m/s, where v, is in meters per second and t is in seconds. ", (m/s) t (s) 4 The velocity-time graph for a particle moving along the x-axis. Think about what the particle doing from the mathematical representation. Is it moving at t= 0? O Yes O No In which direction? O in the positive direction O in the negative direction O the particle is not moving As the particle moves from A to B, does speed up or slow down? O It speeds up. O It slows down. The figure is a v-t graph that was created from the velocity versus time expression given in the problem statement. Because the slope of the entire v, - t curve is negative, we expect the acceleration to be -Select--V. (a) Find the average acceleration in the time interval t-0 to t- 2.0 s. SOLUTION Find the velocities (in m/s) at t, - t, and t,- t- 2.0 s by substituting these values of t into the expression for the velocity: m/s m/s VA Vx8 =
The velocity of a particle moving along the x-axis varies according to the expression v, = (39 - 0.8t) m/s, where v, is in meters per second and t is in seconds. ", (m/s) t (s) 4 The velocity-time graph for a particle moving along the x-axis. Think about what the particle doing from the mathematical representation. Is it moving at t= 0? O Yes O No In which direction? O in the positive direction O in the negative direction O the particle is not moving As the particle moves from A to B, does speed up or slow down? O It speeds up. O It slows down. The figure is a v-t graph that was created from the velocity versus time expression given in the problem statement. Because the slope of the entire v, - t curve is negative, we expect the acceleration to be -Select--V. (a) Find the average acceleration in the time interval t-0 to t- 2.0 s. SOLUTION Find the velocities (in m/s) at t, - t, and t,- t- 2.0 s by substituting these values of t into the expression for the velocity: m/s m/s VA Vx8 =
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The velocity of a particle moving along the x-axis varies according to the expression v, =
(39 – 0.8t2) m/s, where v, is in meters per second and t is in seconds.
-
Vz (m/s)
B
t (s)
1
4
The velocity-time graph for a particle moving
along the x-axis.
Think about what the particle is doing from the mathematical representation.
Is it moving at t = 0?
Yes
O No
In which direction?
O in the positive direction
O in the negative direction
O the particle is not moving
As the particle moves from A to B, does it speed up or slow down?
O It speeds up.
O It slows down.
The figure is a vy
- t graph that was created from the velocity versus time expression given in the problem statement. Because the slope of the entire v,
- t curve is negative, we expect the acceleration to be --Select--- V
(a) Find the average acceleration in the time interval t = 0 to t = 2.0 s.
SOLUTION
Find the velocities (in m/s) at t, = t, and t, = t, = 2.0 s by substituting these values of t into the expression for the velocity:
%3D
VXA
m/s
V,
XB
m/s
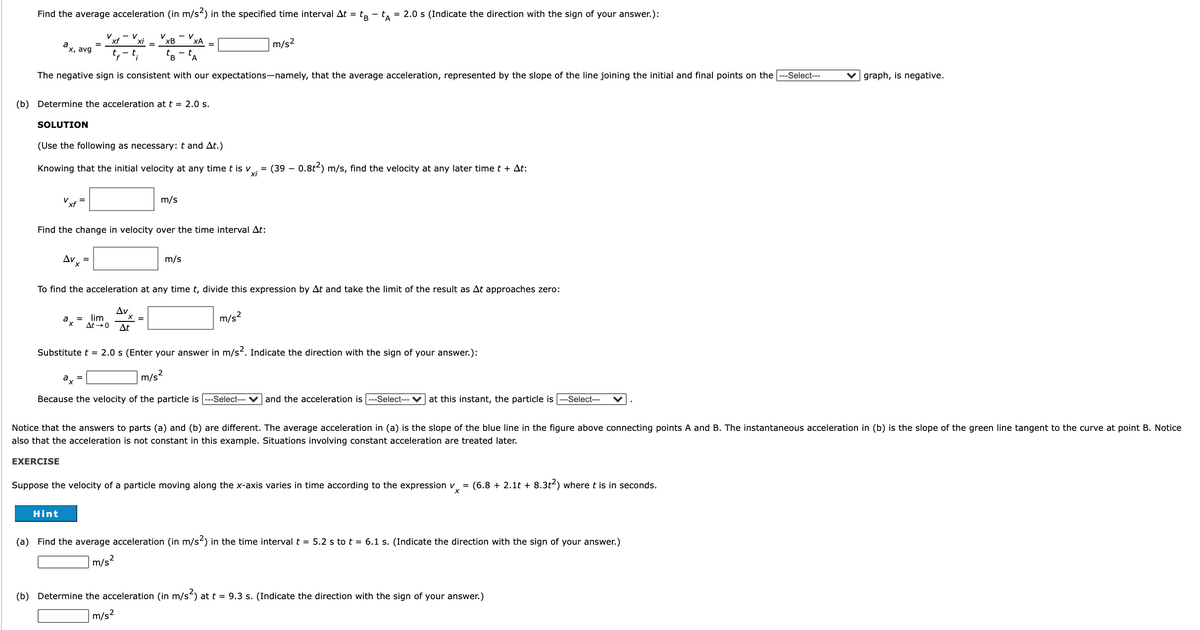
Transcribed Image Text:Find the average acceleration (in m/s) in the specified time interval At = tp - t, = 2.0 s (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.):
- V
xB
ХА
xf
a
"x, avg
m/s2
В
A
The negative sign is consistent with our expectations-namely, that the average acceleration, represented by the slope of the line joining the initial and final points on the
--Select---
V graph, is negative.
(b) Determine the acceleration at t = 2.0 s.
SOLUTION
(Use the following as necessary: t and At.)
Knowing that the initial velocity at any time t is v
(39 – 0.8t2) m/s, find the velocity at any later time t + At:
=
xi
Vxf
m/s
=
Find the change in velocity over the time interval At:
m/s
=
To find the acceleration at any time t, divide this expression by At and take the limit of the result as At approaches zero:
Av
= lim
At0
m/s2
a,
At
Substitute t = 2.0 s (Enter your answer in m/s2. Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.):
ax
m/s?
Because the velocity of the particle is
-Select---
and the acceleration is
-Select--- V at this instant, the particle is
--Select---
Notice that the answers to parts (a) and (b) are different. The average acceleration in (a) is the slope of the blue line in the figure above connecting points A and B. The instantaneous acceleration in (b) is the slope of the green line tangent to the curve at point B. Notice
also that the acceleration is not constant in this example. Situations involving constant acceleration are treated later.
EXERCISE
Suppose the velocity of a particle moving along the x-axis varies in time according to the expression v
= (6.8 + 2.1t + 8.3t2) where t is in seconds.
Hint
(a) Find the average acceleration (in m/s2) in the time interval t = 5.2 s to t = 6.1 s. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)
m/s?
(b) Determine the acceleration (in m/s) at t = 9.3 s. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)
m/s2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON