Theorem 5.6 (d) Distribution of the Quotient of Two Random Variables. If X and Y are independent continuous random variables, then the p.d.f. of the quotient Z = X/Y, is given by : 81(2) = 8(vz, v) lv I dv = | fx(vz) fy(v) I v I dv (5-33) %3D ... -00
Theorem 5.6 (d) Distribution of the Quotient of Two Random Variables. If X and Y are independent continuous random variables, then the p.d.f. of the quotient Z = X/Y, is given by : 81(2) = 8(vz, v) lv I dv = | fx(vz) fy(v) I v I dv (5-33) %3D ... -00
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 22E
Related questions
Question
100%
Prove the theorem
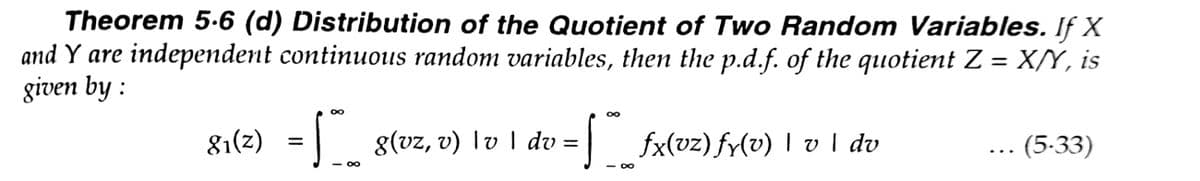
Transcribed Image Text:Theorem 5.6 (d) Distribution of the Quotient of Two Random Variables. If X
and Y are independent continuous random variables, then the p.d.f. of the quotient Z = X/Y, is
given by :
81(2) =| 8(vz, v) lv I dv =
| 8(vz, v) 1v I dv =
| fx(vz) fy(v) lv I dv
.. (5-33)
- D0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning