this question. The gas phase decomposition of hydrogen peroxide at 400 °C H202(g)H20(g) + ½ 02(g) is second order in H202 with a rate constant of 0.650 M-1 s-1. If the initial concentration of H202 is 0.178 M, the concentration of H202 will be M after 49.0 seconds have passed
this question. The gas phase decomposition of hydrogen peroxide at 400 °C H202(g)H20(g) + ½ 02(g) is second order in H202 with a rate constant of 0.650 M-1 s-1. If the initial concentration of H202 is 0.178 M, the concentration of H202 will be M after 49.0 seconds have passed
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter14: Chemical Kinetics: The Rates Of Chemical Reactions
Section14.4: Concentration-time Relationships: Integrated Rate Laws
Problem 14.8CYU: The catalyzed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is first-order in [H2O2]. It was found that the...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:values if needed for this question.
The gas phase decomposition of hydrogen peroxide at 400 °C
H202(g)H20(g) + ½ 02(g)
is second order in H,02 with a rate constant of 0.650 M-1 s-1.
If the initial concentration of H202 is 0.178 M, the concentration of H202 will be
M after 49.0 seconds have passed.

Transcribed Image Text:The rearrangement of ammonium cyanate to urea in aqueous solution at 50 °C
NHẠNCO(aq)–→(NH2)2CO(aq)
is second order in NH4NCO.
In one experiment, when the initial concentration of NH4NCO was 0.874 M, the concentration of
NH4NCO dropped to 0.102 M after 506 minutes had passed.
Based on these data, the rate constant for the reaction is
M-1 min-1.
Expert Solution
Step 1
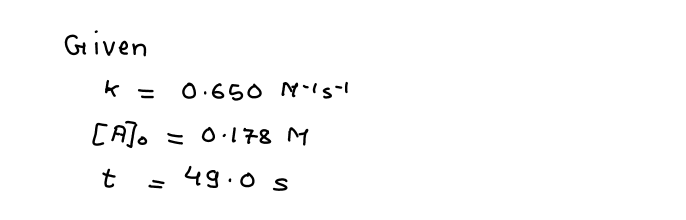
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning