To evaluate this integral we substitute x = a sin(0). Then dx = d0. To change the limits of integration we note that when x = 0, sin(0) = 0, so 0 0; when x = a, sin(0) = 1, so 0 = Also Va? - x2 = Va? – a? sin²(0) Va?(cos²(0)) alcos(0)| = a cos(0) = since 0 < 0 < T/2. Therefore a 4 a dx A = T/2 4 a a cos(0) · do T/2 cos?(0) d0 • T/2 + cos(20)) d0 %D | T/2 2ab 0 + 2ab + 0 - 0 %3D We have shown that the area of an ellipse with semiaxes a and b is nab. In particular, taking a = b = r, we have proved the famous formula that the area of a circle with radius r is ar2.
To evaluate this integral we substitute x = a sin(0). Then dx = d0. To change the limits of integration we note that when x = 0, sin(0) = 0, so 0 0; when x = a, sin(0) = 1, so 0 = Also Va? - x2 = Va? – a? sin²(0) Va?(cos²(0)) alcos(0)| = a cos(0) = since 0 < 0 < T/2. Therefore a 4 a dx A = T/2 4 a a cos(0) · do T/2 cos?(0) d0 • T/2 + cos(20)) d0 %D | T/2 2ab 0 + 2ab + 0 - 0 %3D We have shown that the area of an ellipse with semiaxes a and b is nab. In particular, taking a = b = r, we have proved the famous formula that the area of a circle with radius r is ar2.
Chapter4: Rational Functions And Conics
Section4.3: Conics
Problem 89E: Area of an Ellipse Consider the ellipse x2a2+y2b2=1,a+b=20 (a) The area of the ellipse is given by...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:To evaluate this integral we substitute x = a sin(0). Then
dx =
de. To change the limits of integration we note that when
x = 0, sin(0) = 0, so 0 = 0; when x = a, sin(0) = 1, so
%3D
Also
Va? – x2
Va?
- a² sin?(0) = Va²(cos?(0)) = alcos(0)|
= a cos(0)
since 0 < 0 < T/2. Therefore
a
A =
dx
a
T/2
4
a
a cos(0) ·
de
• T/2
cos?(0) d0
• T/2
| (1 + cos(20)) do
T/2
2ab 0 +
2ab
+ 0 - 0
We have shown that the area of an ellipse with semiaxes a and b is rab. In
particular, taking a = b = r, we have proved the famous formula that the area
of a circle with radius r is tr².
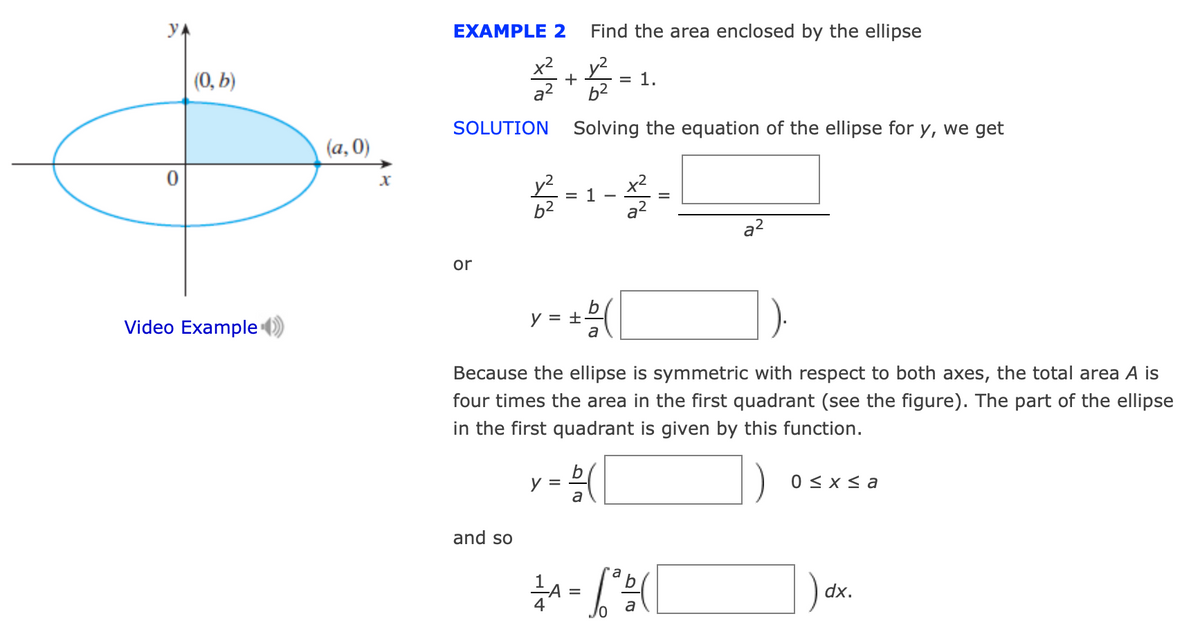
Transcribed Image Text:YA
EXAMPLE 2
Find the area enclosed by the ellipse
(0, b)
x2
+
y²
= 1.
a?
b2
SOLUTION
Solving the equation of the ellipse for y, we get
(a, 0)
= 1
b2
x2
a?
a2
or
Video Example
y = +
a
Because the ellipse is symmetric with respect to both axes, the total area A is
four times the area in the first quadrant (see the figure). The part of the ellipse
in the first quadrant is given by this function.
y =
a
0 < x s a
and so
) dx.
=
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning