Total Quantity Quantity of heeseburgers Total Benefit of Benefit of Good Cheeseburgers of J Good J 1 $40 1 $30 $70 2 $50 3 $90 3 $65 4 $100 $75 $105 $80 6 $105 $83 has a limited weekly income of $65, and he spends it all on cheeseburgers and Assume the price of each cheeseburger is $10 and the price of Good J is $5 4)
Total Quantity Quantity of heeseburgers Total Benefit of Benefit of Good Cheeseburgers of J Good J 1 $40 1 $30 $70 2 $50 3 $90 3 $65 4 $100 $75 $105 $80 6 $105 $83 has a limited weekly income of $65, and he spends it all on cheeseburgers and Assume the price of each cheeseburger is $10 and the price of Good J is $5 4)
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter6: Consumer Choices
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1SCQ: Jeremy is deeply in love with Jasmine. Jasmine lives where cell phone coverage is poor, so he can...
Related questions
Question
D and E please
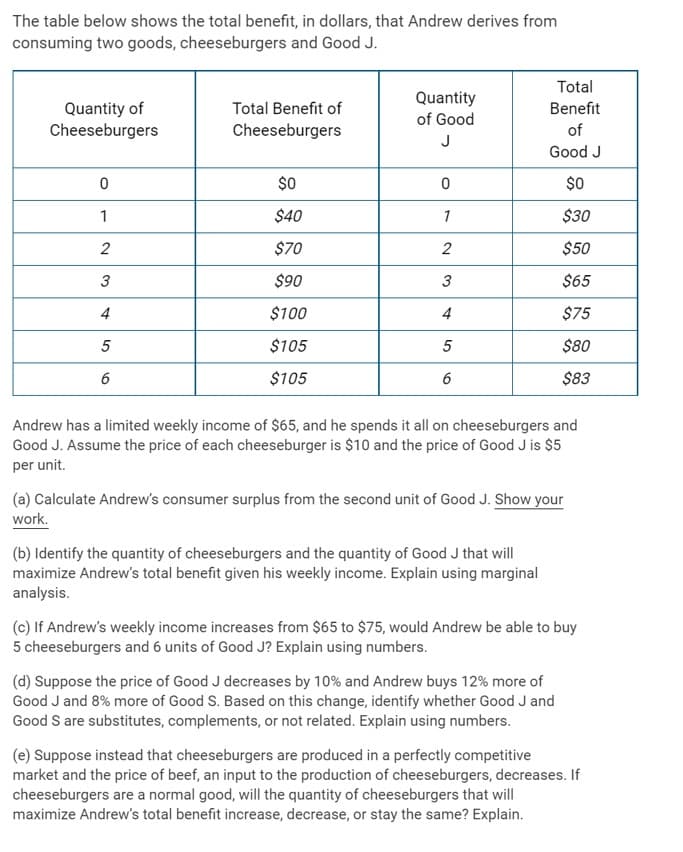
Transcribed Image Text:The table below shows the total benefit, in dollars, that Andrew derives from
consuming two goods, cheeseburgers and Good J.
Total
Quantity of
Cheeseburgers
Quantity
of Good
Total Benefit of
Benefit
Cheeseburgers
of
J
Good J
$0
$0
1
$40
1
$30
2
$70
2
$50
3
$90
3
$65
4
$100
4
$75
$105
$80
$105
$83
Andrew has a limited weekly income of $65, and he spends it all on cheeseburgers and
Good J. Assume the price of each cheeseburger is $10 and the price of Good J is $5
per unit.
(a) Calculate Andrew's consumer surplus from the second unit of Good J. Show your
work.
(b) Identify the quantity of cheeseburgers and the quantity of Good J that will
maximize Andrew's total benefit given his weekly income. Explain using marginal
analysis.
(c) If Andrew's weekly income increases from $65 to $75, would Andrew be able to buy
5 cheeseburgers and 6 units of Good J? Explain using numbers.
(d) Suppose the price of Good J decreases by 10% and Andrew buys 12% more of
Good J and 8% more of Good S. Based on this change, identify whether Good J and
Good S are substitutes, complements, or not related. Explain using numbers.
(e) Suppose instead that cheeseburgers are produced in a perfectly competitive
market and the price of beef, an input to the production of cheeseburgers, decreases. If
cheeseburgers are a normal good, will the quantity of cheeseburgers that will
maximize Andrew's total benefit increase, decrease, or stay the same? Explain.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax


Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax
