Two firms, Firm 1 and Firm 2, compete by simultaneously choosing prices. Both firms sell an identical product for which each of 100 consumers has a maximum willingness to pay of $40. Each consumer will buy at most 1 unit, and will buy it from whichever firm charges the lowest price. If both firms set the same price, they share the market equally. Costs are given by a (g) = 16g. Because of government regulation, firms can only choose prices which are integer numbers, and they cannot price above $40. Answer the following: a) If Firm 1 chooses pn = 27. Firm 2's best response is to set what price? b) If Firm 2 chooses the price determined in the previous question. Firm 1's best response is to choose what price? ) If Firm 1 chooses pi = 5, Firm 2's best response is a range of prices. What is the lowest price in this range? d) Now suppose both firms are capacity-constrained: Firm 1 can produce at most 17 units, and Firm 2 can produce at most 44 units. If firms set different prices, consumers will first buy from the firm charging the lower price. Once that firm's supply is exhausted, consumers will buy from the firm charging the higher price until that firm's supply is exhausted. What is Firm 1's equilibrium profit?
Two firms, Firm 1 and Firm 2, compete by simultaneously choosing prices. Both firms sell an identical product for which each of 100 consumers has a maximum willingness to pay of $40. Each consumer will buy at most 1 unit, and will buy it from whichever firm charges the lowest price. If both firms set the same price, they share the market equally. Costs are given by a (g) = 16g. Because of government regulation, firms can only choose prices which are integer numbers, and they cannot price above $40. Answer the following: a) If Firm 1 chooses pn = 27. Firm 2's best response is to set what price? b) If Firm 2 chooses the price determined in the previous question. Firm 1's best response is to choose what price? ) If Firm 1 chooses pi = 5, Firm 2's best response is a range of prices. What is the lowest price in this range? d) Now suppose both firms are capacity-constrained: Firm 1 can produce at most 17 units, and Firm 2 can produce at most 44 units. If firms set different prices, consumers will first buy from the firm charging the lower price. Once that firm's supply is exhausted, consumers will buy from the firm charging the higher price until that firm's supply is exhausted. What is Firm 1's equilibrium profit?
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter12: Price And Output Determination: Oligopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2E
Related questions
Question
Q3
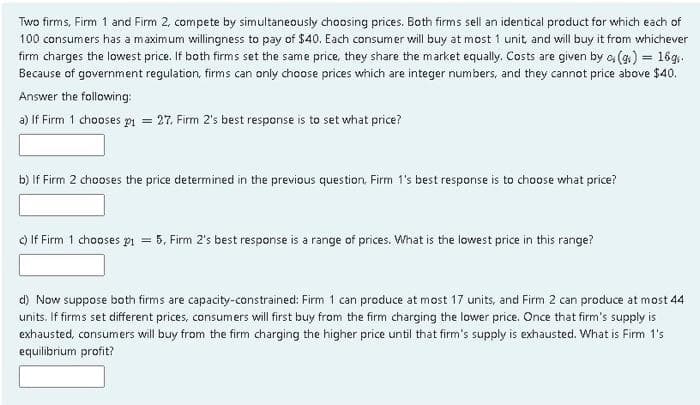
Transcribed Image Text:Two firms, Firm 1 and Firm 2, compete by simultaneously choosing prices. Both firms sell an identical product for which each of
100 consumers has a maximum willingness to pay of $40. Each consumer will buy at most 1 unit, and will buy it from whichever
firm charges the lowest price. If both firms set the same price, they share the market equally. Costs are given by e (g) = 16g:
Because of government regulation, firms can only choose prices which are integer numbers, and they cannot price above $40.
Answer the following:
a) If Firm 1 chooses pn = 27. Firm 2's best response is to set what price?
b) If Firm 2 chooses the price determined in the previous question. Firm 1's best response is to choose what price?
) If Firm 1 chooses pi = 5, Firm 2's best response is a range of prices. What is the lowest price in this range?
d) Now suppose both firms are capacity-constrained: Firm 1 can produce at most 17 units, and Firm 2 can produce at most 44
units. If firms set different prices, consumers will first buy from the firm charging the lower price. Once that firm's supply is
exhausted, consumers will buy from the firm charging the higher price until that firm's supply is exhausted. What is Firm 1's
equilibrium profit?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Survey of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305260948
Author:
Irvin B. Tucker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Survey of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305260948
Author:
Irvin B. Tucker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
