Use the given sum or difference identity to find sin(a + B) exactly, given that cos a = such that 6. a terminates in quadrant IIl and cos B 1 such that B terminates in quadrant II then: %3D sin(a + B) = sin(a)cos(8) + cos(a)sin(8) sin(a + B) sin(a + B) =
Use the given sum or difference identity to find sin(a + B) exactly, given that cos a = such that 6. a terminates in quadrant IIl and cos B 1 such that B terminates in quadrant II then: %3D sin(a + B) = sin(a)cos(8) + cos(a)sin(8) sin(a + B) sin(a + B) =
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.3: The Addition And Subtraction Formulas
Problem 50E
Related questions
Concept explainers
Ratios
A ratio is a comparison between two numbers of the same kind. It represents how many times one number contains another. It also represents how small or large one number is compared to the other.
Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometric ratios give values of trigonometric functions. It always deals with triangles that have one angle measuring 90 degrees. These triangles are right-angled. We take the ratio of sides of these triangles.
Question
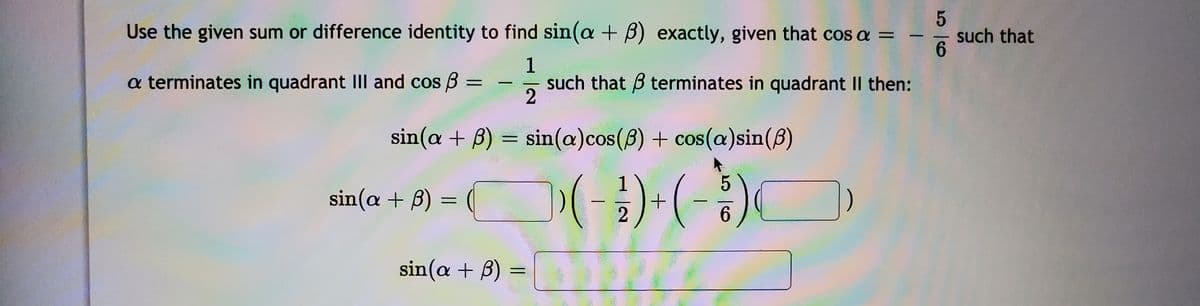
Transcribed Image Text:Use the given sum or difference identity to find sin(a + B) exactly, given that cos a =
such that
6.
1
a terminates in quadrant III and cos B :
such that B terminates in quadrant II then:
2
|
sin(a + B) = sin(a)cos(8) + cos(a)sin(8)
(-)-(-)
sin(a + B) =
2
6.
sin(a + B) =
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, trigonometry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage