Use this mRNA coding sequence as your starting point. This sequence begins with a start codon and ends with a stop codon, so it is only looking at the region of DNA that directly encodes a protein sequence. 5’-AUGCACAAAUUAGAGUACCCCCCAGGAAGGUAG-3’ Make the following mutation in this sequence by changing/adding/removing only one nucleotide. Make the mutation easy to see (a different color, circled, something like that) 1) A silent mutation that is also a transition
Use this mRNA coding sequence as your starting point. This sequence begins with a start codon and ends with a stop codon, so it is only looking at the region of DNA that directly encodes a protein sequence. 5’-AUGCACAAAUUAGAGUACCCCCCAGGAAGGUAG-3’ Make the following mutation in this sequence by changing/adding/removing only one nucleotide. Make the mutation easy to see (a different color, circled, something like that) 1) A silent mutation that is also a transition
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter30: Protein Synthesis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6P
Related questions
Question
Use this mRNA coding sequence as your starting point. This sequence begins with a start codon and ends with a stop codon, so it is only looking at the region of DNA that directly encodes a protein sequence.
5’-AUGCACAAAUUAGAGUACCCCCCAGGAAGGUAG-3’
Make the following mutation in this sequence by changing/adding/removing only one
1) A silent mutation that is also a transition
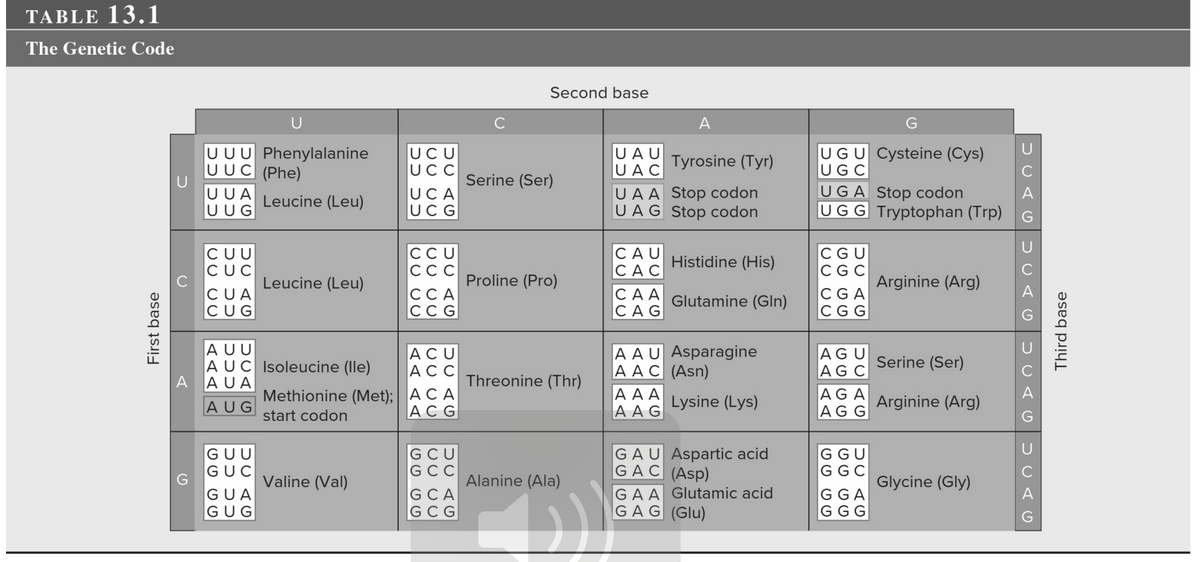
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 13.1
The Genetic Code
First base
U
UUU Phenylalanine
UUC (Phe)
UUA
UUG
CUU
CUC
CUA
CUG
A AUA
AUG
AUU
AUC Isoleucine (lle)
GUU
GUC
Leucine (Leu)
GUA
GUG
Leucine (Leu)
Methionine (Met);
start codon
Valine (Val)
UCU
UCC
UCA
UCG
CU CU
UU UU
UC AG
CCA
CCG
ACU
ACC
A CA
ACG
GGGG
UU UU
UUAG
Second base
Serine (Ser)
Proline (Pro)
Threonine (Thr)
Alanine (Ala)
(_))
UAU
UAC
UAA Stop codon
UAG Stop codon
CAU
CAC
A
Tyrosine (Tyr)
Histidine (His)
CAA Glutamine (Gln)
CAG
AAA
AAG
A A U Asparagine
AAC (Asn)
Lysine (Lys)
GAU Aspartic acid
GAC (Asp)
GAA Glutamic acid
GAG (Glu)
UGU Cysteine (Cys)
UGC
UGA Stop codon
UGG Tryptophan (Trp)
UU UU
SSSS
AGU
AG C
AGA
AGG
SU G
Arginine (Arg)
Serine
Arginine (Arg)
(Ser)
Glycine (Gly)
DUAG
C
UCAG
DUAG DUAG
Third base
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning