AUU ACU AAU AGU U TABLE 15-2 The Codons of mRNA Isoleucine Threonine Asparagine Serine First Second Base Third AUC АСС AAC AGC Base U Base A Isoleucine Threonine Asparagine Serine A UUU UCU UAU UGU U AUA ACA AAA AGA A Phenylalanine Serine Tyrosine Cysteine Isoleucine Threonine Lysine Arginine UUC UCC UAC UGC AUG ACG AAG AGG G Phenylalanine Serine Tyrosine Cysteine (START) Threonine Lysine Arginine U Methionine UUA UCA UAA UGA A Leucine Serine STOP STOP GUU GCU GAU GGU Valine Alanine Aspartic Glycine UUG UCG UAG UGG acid Leucine Serine STOP Tryptophan GUC GCC GAC GGC CUU CCU CAU CGU U Valine Alanine Aspartic Glycine Leucine Proline Histidine Arginine acid CỤC C CAC CGC GUA GCA GAA GGA A Leucine Proline Histidine Arginine Valine Alanine Glutamic Glycine acid CỦA CCA CAA CGA A Leucine Proline Glutamine Arginine GUG GCG GAG GGG G Valine Alanine Glutamic Glycine CUG CCG CAG CGG G acid Leucine Proline Glutamine Arginine The triplets in MRNA are codons; the DNA triplets in the gene itself are their complements. The first base of the codon is listed on the left and the second base at the top. Within each large box are the four possible third bases and the amino acid specified by each.
Nucleotides
It is an organic molecule made up of three basic components- a nitrogenous base, phosphate,and pentose sugar. The nucleotides are important for metabolic reactions andthe formation of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are essential biomolecules present in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and viruses. They carry the genetic information for the synthesis of proteins and cellular replication. The nucleic acids are of two types: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The structure of all proteins and ultimately every biomolecule and cellular component is a product of information encoded in the sequence of nucleic acids. Parts of a DNA molecule containing the information needed to synthesize a protein or an RNA are genes. Nucleic acids can store and transmit genetic information from one generation to the next, fundamental to any life form.
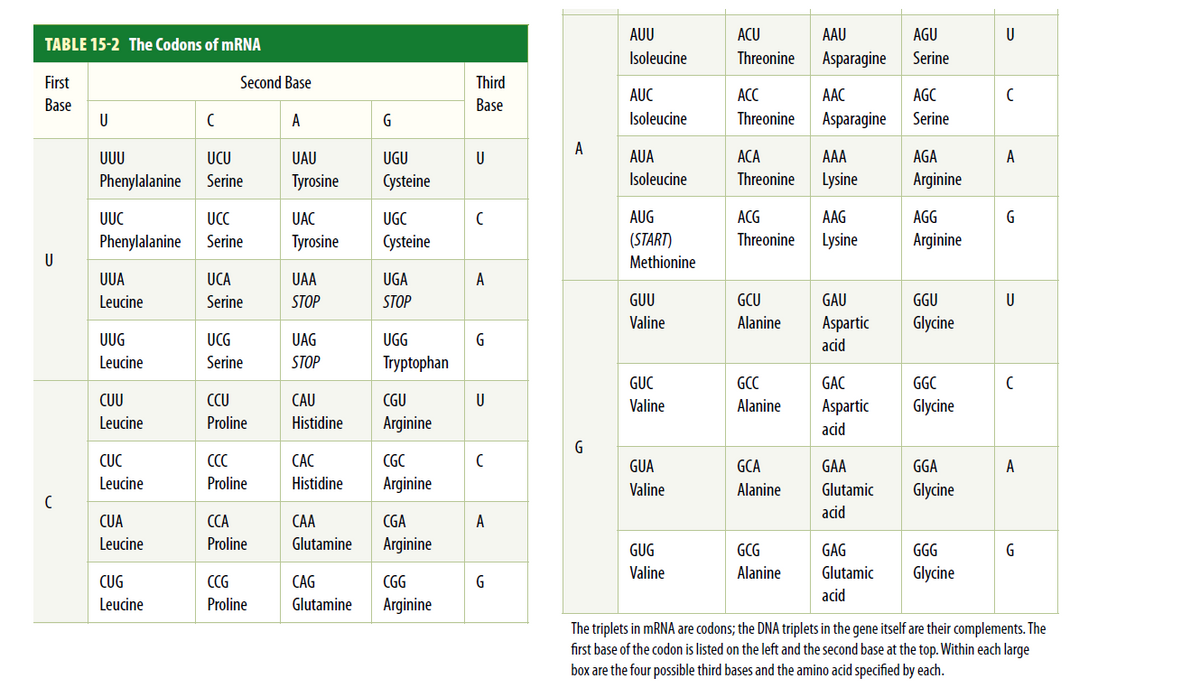
Examine Table 15-2. Which amino acids are coded by the following codons? (Hint: For the first base [letter] in each of the codons listed below, look at the leftmost column of the table labeled “First Base.” For the second
base in each codon, look at the top row of bases, and for the third base, look at the column on the right-hand side
of the page).
a. UUU
b. UCU
c. UAU
d. UGC
e. CUU
f. CGA
g. CGG
h. AAA
i. AAG
j. GAG
k. GGU
l. GGC
m. GGA
n. GGG
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps







