Using the table showing partial pressures for the formation of ammonia and corresponding equilibrium constants, show that at 101 bar, apparent equilibrium constants equals 0.0072 and the thermodynamic equilibrium constant equals 0.0064.
Using the table showing partial pressures for the formation of ammonia and corresponding equilibrium constants, show that at 101 bar, apparent equilibrium constants equals 0.0072 and the thermodynamic equilibrium constant equals 0.0064.
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter13: Fundamental Equilibrium Concepts
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 101E: A 0.010 M solution of the weak acid HA has an osmotic pressure (see chapter on solutions and...
Related questions
Question
Using the table showing partial pressures for the formation of ammonia and corresponding equilibrium constants, show that at 101 bar, apparent equilibrium constants equals 0.0072 and the
please help me. thank you
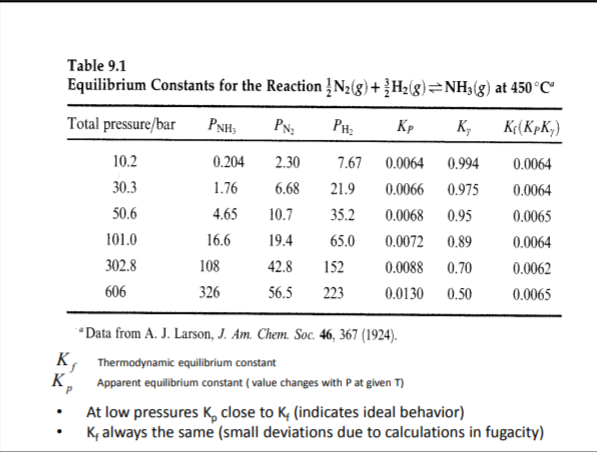
Transcribed Image Text:Table 9.1
Equilibrium Constants for the Reaction !N2(g)+ {H2(g)=NH3(g) at 450°C
Total pressure/bar
PNH,
PH:
Kp
K,
K¢(KpK;)
10.2
0.204
2.30
7.67
0.0064
0.994
0.0064
30.3
1.76
6.68
21.9
0.0066
0.975
0.0064
50.6
4.65
10.7
35.2
0.0068
0.95
0.0065
101.0
16.6
19.4
65.0
0.0072
0.89
0.0064
302.8
108
42.8
152
0.0088
0.70
0.0062
606
326
56.5
223
0.0130
0.50
0.0065
*Data from A. J. Larson, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 46, 367 (1924).
K, Thermodynamic equilibrium constant
K, Apparent equilibrium constant ( value changes with P at given T)
At low pressures K, close to K, (indicates ideal behavior)
K, always the same (small deviations due to calculations in fugacity)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning