Using values from Appendix C of your textbook, calculate the value of AH° for each of the following reactions. (a) 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g) = Fe,03(s) + 3 CO(g) AHO = 26.84 v k) (b) 2 CzHa(g) + 2 H20(g) =2 C2Hg(g) + O2(g) AHO - -288 52 x k) (c) 2 NO(g) + 2 H2(g) =N2(g) + 2 H20(g) AHO (d) CO(g) + H20(g) = co2(g) + H2(g) AHO X kJ
Using values from Appendix C of your textbook, calculate the value of AH° for each of the following reactions. (a) 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g) = Fe,03(s) + 3 CO(g) AHO = 26.84 v k) (b) 2 CzHa(g) + 2 H20(g) =2 C2Hg(g) + O2(g) AHO - -288 52 x k) (c) 2 NO(g) + 2 H2(g) =N2(g) + 2 H20(g) AHO (d) CO(g) + H20(g) = co2(g) + H2(g) AHO X kJ
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter5: Thermochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.61QE: When 7.11 g NH4NO3 is added to 100 mL water, the temperature of the calorimeter contents decreases...
Related questions
Question
12
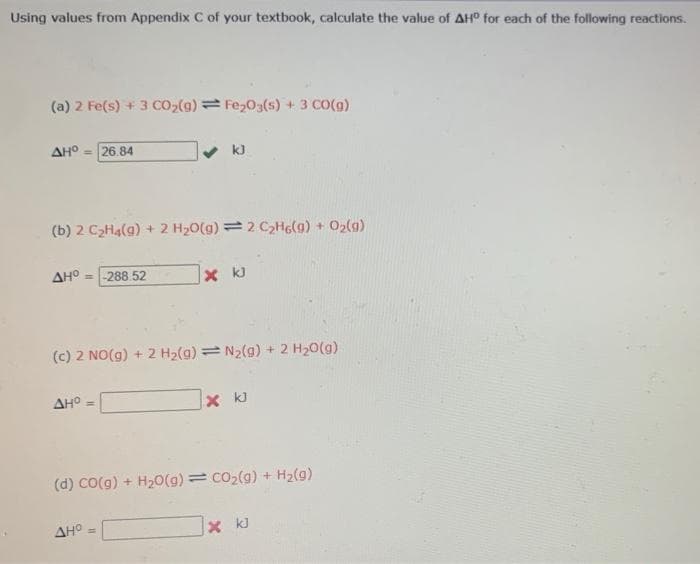
Transcribed Image Text:Using values from Appendix C of your textbook, calculate the value of AH° for each of the following reactions.
(a) 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g)= Fe203(s) + 3 CO(g)
AH° - 26.84
k)
(b) 2 C2H4(g) + 2 H20(g) = 2 C2HG(g) + 02(g)
AHO = -288 52
x k)
(c) 2 NO(g) + 2 H2(g) = N2(g) + 2 H20(g)
AH° =
X kJ
(d) Co(g) + H20(g) = co2(g) + H2(g)
AHO
X kJ
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning