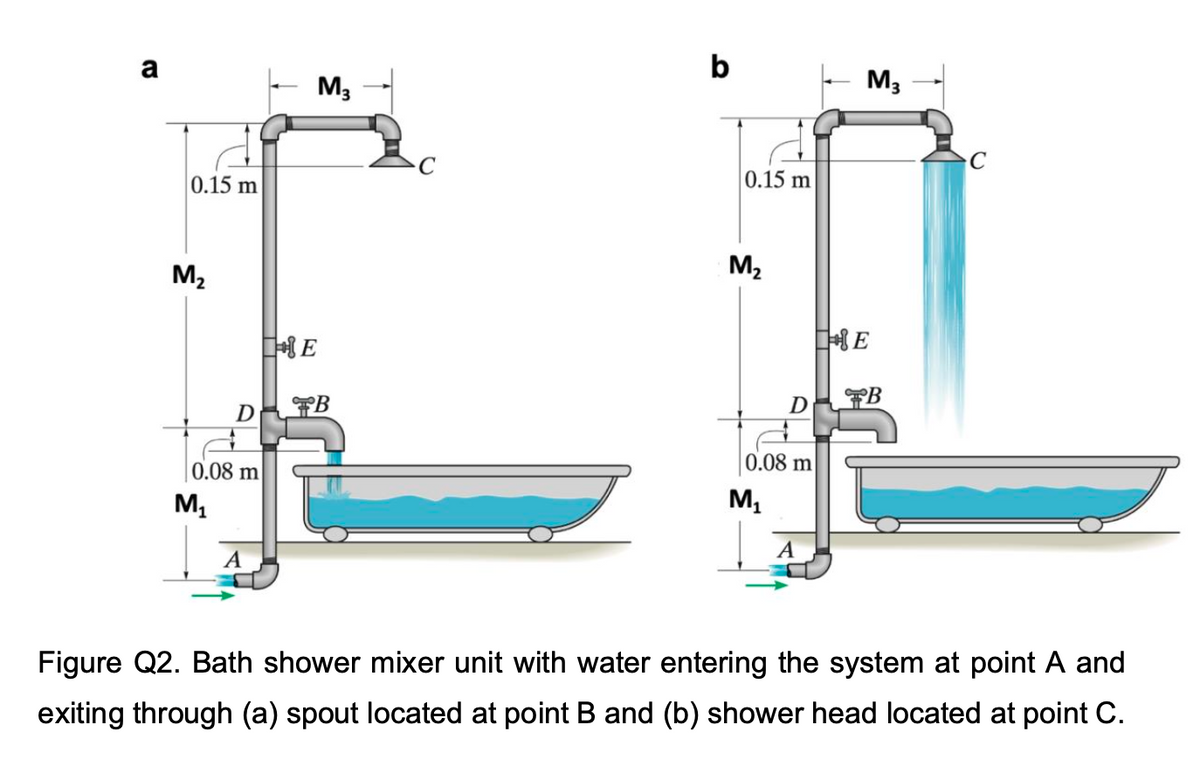
Water at 40 °C (? = 992.3 ?? ??? ? = 0.664 × 10−6 ?2/?) flows at a velocity of 2 m/s through a pipe with a diameter of 20 mm and a friction factor of f = 0.004. The water enters the pipe at point A (Figure Q2) into a bath shower mixer unit out of which, the water can exit through the spout via a gate valve (Figure Q2a) or through the showerhead (Figure Q2b). a. If the water exits through the spout (Figure Q2a) via a fully opened gate valve at B, with a diameter of 12 mm, determine the water pressure at point A. The minor loss coefficient is Kspout = 0.6 for the spout at B. Account for the minor loss in the elbow, the tee, and the gate valve. The gate valve at E is closed. b. If the water emerges through the showerhead (Figure Q2b, point C) that consists of 100 identical holes, each with a diameter of 1.5 mm. Determine the pressure of the water at A if the minor loss coefficient is Kshowerhead = 0.45 for the showerhead. The gate valve at B is closed. Account for the minor loss in the three elbows, the fully opened gate valve at E, and the tee. M1 = 1.330m M2 = 2.330m M3 = 1.015m Table of Loss Coeffcients Loss Coeffcients KL Gate Valve - Fully Open 0.19 90° Bend 0.9 45° Bend 0.4 Tee for Valve along Branch 1.8
Water at 40 °C (? = 992.3 ?? ??? ? = 0.664 × 10−6 ?2/?) flows at a velocity of 2 m/s through a pipe with a diameter of 20 mm and a friction factor of f = 0.004. The water enters the pipe at point A (Figure Q2) into a bath shower mixer unit out of which, the water can exit through the spout via a gate valve (Figure Q2a) or through the showerhead (Figure Q2b).
a. If the water exits through the spout (Figure Q2a) via a fully opened gate valve at B, with a diameter of 12 mm, determine the water pressure at point A. The minor loss coefficient is Kspout = 0.6 for the spout at B. Account for the minor loss in the elbow, the tee, and the gate valve. The gate valve at E is closed.
b. If the water emerges through the showerhead (Figure Q2b, point C) that consists of 100 identical holes, each with a diameter of 1.5 mm. Determine the pressure of the water at A if the minor loss coefficient is Kshowerhead = 0.45 for the showerhead. The gate valve at B is closed. Account for the minor loss in the three elbows, the fully opened gate valve at E, and the tee.
M1 = 1.330m
M2 = 2.330m
M3 = 1.015m
Table of Loss Coeffcients
| Loss Coeffcients | KL |
| Gate Valve - Fully Open | 0.19 |
| 90° Bend | 0.9 |
| 45° Bend | 0.4 |
| Tee for Valve along Branch | 1.8 |
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps


