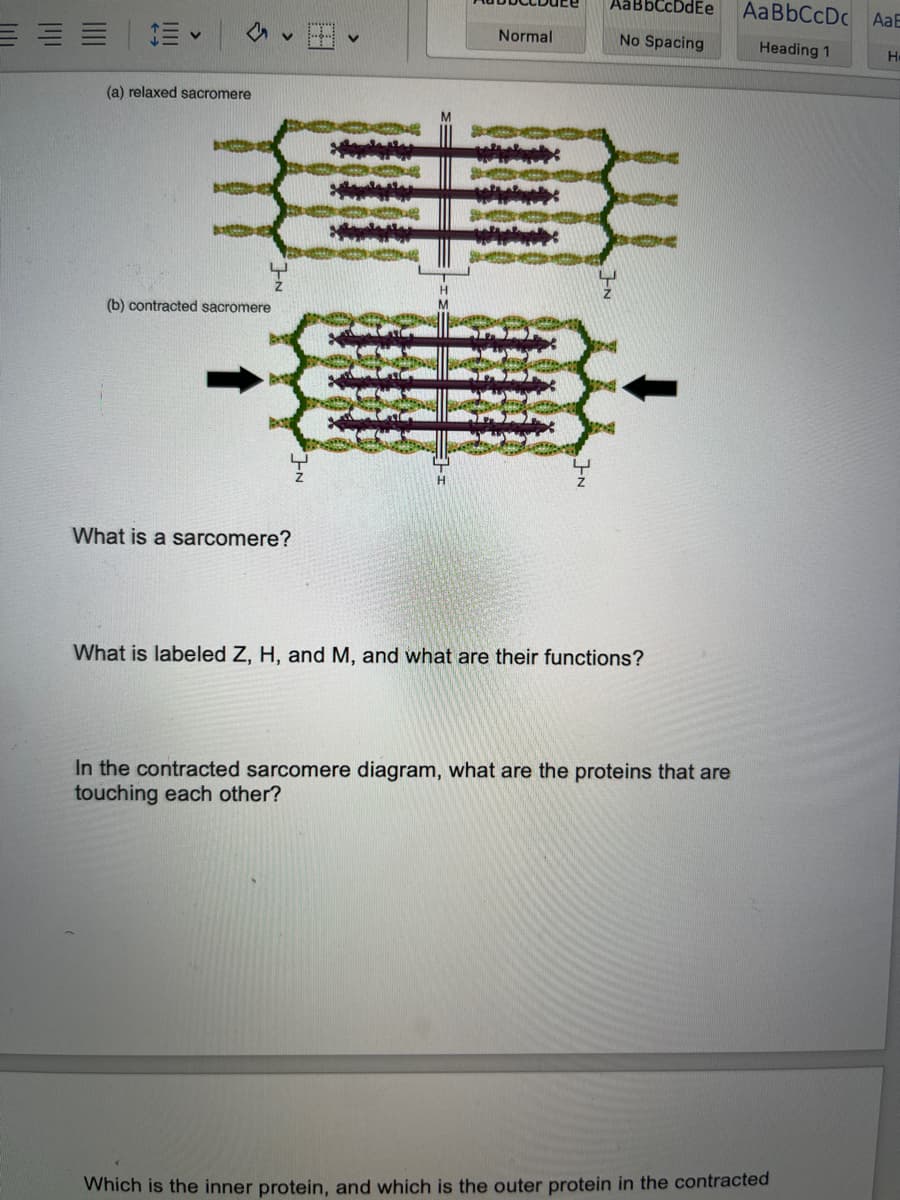
What is a sarcomere? What is labeled Z,H, and M, and what are their functions? In the contracted sarcomere diagram, what are the proteins that are touching each other
introduction:-
Muscle fibres are specialised cells that make up the muscular system. Its ability to contract is their main characteristic. Movement is caused by muscles that are connected to blood vessels, internal organs, or bones. Muscle contraction is the primary cause of almost all bodily movement. Cilia, the flagellum on sperm cells, and certain white blood cell amoeboid movement are examples of exceptions to this rule.
Walking and running are two examples of visible movements that are produced by the coordinated action of joints, bones, and skeletal muscles. Skeletal muscles can also make softer motions that influence different facial expressions, eye movements, and breathing.
In addition to facilitating mobility, muscle contraction also contributes to the body's posture, joint stability, and heat production. Muscle contraction is responsible for maintaining posture, such as standing and sitting. The body's immobile positions are maintained by the skeletal muscles' ongoing minute modifications. Many muscles' tendons extend over joints, which helps to stabilise the joints. This is especially clear in the knee and shoulder joints, where muscle tendons play a significant role in maintaining joint stability. A crucial byproduct of muscle metabolism is the creation of heat, which helps to keep the body temperature stable. Muscle contraction is the cause of around 85% of the heat generated by the body.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps






