What is the curent read by the ammeter in the circuit below? Let R1 = 1 kiloohm, R2 = 2 kiloohm, R3 = 3 kiloohm, and the emf of the ideal source is 5 volts. Input R1, R2, and R3 for resistors R1, R2, and R3 respectively. Input E for the emf E, Use context clues to figure out if you need to input a numerical value, variable, word, etc. AN numerical answers should be in three significant figures. R| R2 R3 First we calculate the current across each resistor. From Ohm's law, we arrive at a general formula for current: Plugging in values, the current across the resistor R1 is equal to: (Piease note that the curent is in miliamperes) mA Similarly the current across R2 is: 12 = mA And the current across R3 is: 13 = mA The current read by the ammeter is the sum of the ourrents across each resistor: |=l1 +12+l3 Alternatively, we can solve for the current across the ammeter by first calculating the equivalent resistance and then applying Ohm's law. The equivalent resistance of the three resistors in parallel is: 1/Req =/R1 + 1/R2 +1/ Thus. Reg=
What is the curent read by the ammeter in the circuit below? Let R1 = 1 kiloohm, R2 = 2 kiloohm, R3 = 3 kiloohm, and the emf of the ideal source is 5 volts. Input R1, R2, and R3 for resistors R1, R2, and R3 respectively. Input E for the emf E, Use context clues to figure out if you need to input a numerical value, variable, word, etc. AN numerical answers should be in three significant figures. R| R2 R3 First we calculate the current across each resistor. From Ohm's law, we arrive at a general formula for current: Plugging in values, the current across the resistor R1 is equal to: (Piease note that the curent is in miliamperes) mA Similarly the current across R2 is: 12 = mA And the current across R3 is: 13 = mA The current read by the ammeter is the sum of the ourrents across each resistor: |=l1 +12+l3 Alternatively, we can solve for the current across the ammeter by first calculating the equivalent resistance and then applying Ohm's law. The equivalent resistance of the three resistors in parallel is: 1/Req =/R1 + 1/R2 +1/ Thus. Reg=
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter24: Magnetic Fields
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 75A
Related questions
Question
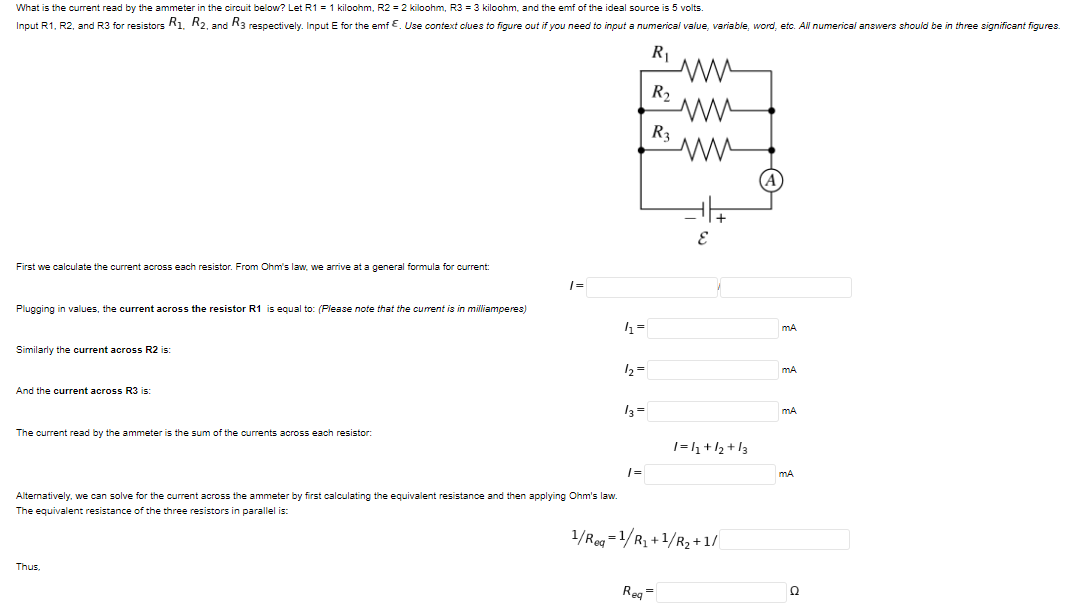
Transcribed Image Text:What is the current read by the ammeter in the circuit below? Let R1 = 1 kiloohm, R2 = 2 kiloohm, R3 = 3 kiloohm, and the emf of the ideal source is 5 volts.
Input R1, R2, and R3 for resistors R1. R2, and R3 respectively. Input E for the emf E. Use context clues to figure out if you need to input a numerical value, variable, word, etc. All numerical answers should be in three significant figures.
R|
R2
R3
First we calculate the current across each resistor. From Ohm's law, we arrive at a general formula for current:
Plugging in values, the current across the resistor R1 is equal to: (Please note that the current is
milliamperes)
Similarly the current across R2 is:
12=
mA
And the current across R3 is:
13 =
mA
The current read by the ammeter is the sum of the currents across each resistor:
1=h+/2 +13
|=
Alternatively, we can solve for the current across the ammeter by first calculating the equivalent resistance and then applying Ohm's law.
The equivalent resistance of the three resistors in parallel is:
1/Re =1/R, +1/R2 +1/
Thus,
Reg=
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill