Thoracic and Abdominal Veins
Thorax is the region that is referred to as the trunk’s superior part and is situated between the region of the abdomen and neck. On the other hand, the abdomen is the region that is situated between the pelvis and thorax. The thoracic veins and veins of the abdomen are responsible for the drainage of deoxygenated blood from the region of the thorax and abdomen in order to return them to the heart. Thus, it plays a significant role in the human body.
Ovarian and Uterine Cycles
Two cycles are engaged with the guideline of a lady's richness: the ovarian cycle and the uterine cycle (additionally called the period). The ovarian cycle is a cycle that controls a lady's fruitfulness. The ovary of the follicle that produces an egg every month addresses the ovarian cycle. The uterine cycle addresses a formation in the uterine coating (endometrium) in light of ovarian chemicals. The follicular phase stages incorporate the menstrual cycle, endometrium reconstruction of the membrane, and groundwork for developing a developing organism. Changes in chemical levels constrain the cycles, including the ovarian cycle and uterine cycle.
Structure and Function of The Vertebral Column
The vertebral column (also known as the backbone or spine) is a tall, thin bone that runs from the base of the spine to the pelvis and is located dorsally. It protects the spinal cord and serves as a vital connection point for a variety of muscle groups.
Axial Versus Appendicular Muscles
Axial muscle is one of the skeletal muscles that are found in the trunk and the head regions of the human body. They include the muscles of the tail and eyeball too. Axial muscles are originated from the axial skeleton that composes the bones in the neck and head. The bones in the skeletal system are arranged in this manner only. The axial muscles are grouped based on their function and location.
Motor Units In Skeletal Muscles
A motor unit is a functional unit of muscle contraction and each muscle in the body includes many motor units. It consists of alpha motor neurons, axons, and muscle fibers. Each motor neuron comes from the anterior horn of the spinal cord and supplies nearly 4-100 muscle fibers. Examples include gastrocnemius muscle that contains 2000 muscle fibers/motor neurons. A collection of motor neurons that supply a muscle is called a motor pool.
Muscle And Nervous Tissues
A tissue is a group of similar cells that are organized to perform one or more specific functions. Tissues are classified into four different types based on their morphology and function: connective tissue, nervous tissue, muscle tissue, and epithelial tissue. A group of tissues forms the organs in the body such as the liver and heart.
Gastroileal Reflex
Gastroileal reflex is a reflexstimulated by the opening of the ileocecal valve, pushing the digested material from the ileum present in the small intestine to the large intestineaccompanied by a desire to defecate. It is the third type of gastrointestinal reflex which is mediated by the vagus nerve and gastrin.
Synaptic Knob
The synaptic knobs (synaptic terminals) are the ends of the neuron that are associated with the signaling of the neuronal impulses. The neurotransmitters enclosed in the vesicle fuse with these synaptic terminals and the chemical within the vesicle is released. The chemical interacts with the postsynaptic end and induces a change in the membrane potential.
Blood Vessels Of The Head And Neck
The carotid arteries are the primary blood vessels that supply the blood to the neck and regions of the neck, brain, and face. Among the carotid arteries, two are positioned on the left and the right. When it comes to the neck, there are two segmental regions of the carotid arteries:
Suspensory Ligament
A suspensory ligament is a group of fibrous membranes or any tissues that puts up or suspends a particular organ or a part of the body.
Receptive Relaxation
Receptive relaxation refers to the relaxation of the muscles in the upper portion of the stomach that occurs before the food particles enter the esophagus. This receptive relaxation helps in the movement of the food. This receptive relaxation is achieved with the help of the peristaltic movement of the stomach. Peristalsis, or the peristaltic movement, is defined as a series of wave-like contractions in the muscle that helps move the food through the gastrointestinal tract.
Structure And Function of the Appendicular Skeleton
In biology, the skeletal system makes up the framework of human bodies structurally and has two main subdivisions-
Structure And Function Of The Axial Skeleton
The skeletal system present in our body is distinguished as the axial and appendicular skeleton. The appendicular skeleton has upper and lower limb bones. The axial skeleton is the bones that are present in the upper part of the body. The axial skeleton is made up of bones found in the head and the trunk region. The bones are the skull bones, ossicles of the ear, hyoid bone (throat bone), rib cage, sternum, and the vertebral column. The ear ossicles consists of the auditory ossicles; the three small bones. The auditory ossicles enable the sound to reach the brain. The axial skeleton helps in attaching the skeletal muscles so that the parts of the body can be moved.
Types Of Joints
A joint is the point where two or more bones are connected. Joints hold the bones together and help in movement of the skeletal system in different directions. It is also called an articular surface. These are present to allow different types of movements. For example, the connection between a tooth and the jawbone is known as a joint. The rib cage is also a type of joint which provides protection to heart, lungs, liver, and spleen.
Dual Innervation
Dual innervation is the instruction that an organ receives from both sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. Most of the organs in our body are innervated by both divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). For example, the vagal parasympathetic innervation slows the heart rate, and sympathetic innervation increases the heart rate.
Circulatory System
The circulatory system serves to deliver oxygen to different regions of the body. The oxygen that is inhaled diffuses through the air sacs into the blood where it binds to the hemoglobin component of the blood and transmitted to different regions of the body. This system is also responsible for the elimination of metabolic wastes like carbon dioxide. Without the circulatory system, the blood would remain static and there will not be a closed system of oxygen transport within the human body and the person will not be alive.
Human Excretory System
The expulsion of nitrogenous wastes (non-gaseous) such as urea, ammonia, uric acid with water, some salts, and pigments out of the body is termed excretion. It helps to maintain the homeostatic conditions (constant internal composition) in the body. Different organisms excrete different types of waste products. Based on the chemical nature of the nitrogenous compounds produced as the waste products, the organisms are divided into the following three types:
Structure And Function Of The Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a network of complex tissues and organs that aid in the expulsion of the toxins and waste materials from the body. The role of this system is to guard the body from foreign invaders and help to maintain the body fluid level.
Interstitial And Appositional Growth
Growth in bones occurs in two ways either longitudinally or increase in the width of bone size. This increase in the length size of the bone is referred as interstitial growth whereas the increase in the preexisting diameter or width size of bones is referred as appositional growth. This growth can be commonly observed after birth of an individual but generally in the first trimester that is around fourth or fifth week the development of bones and stops growing at the age of 21 for males and comparatively in female at lesser age of 18.
Nail Structure And Function
The claw-shaped keratinous plate positioned at the edge of the finger and toes are called the nails. These structures are identified mainly in the primates. The toenails and the fingernails are composed of tough guarding protein known as alpha-keratin, which is found to be a polymer present in the hoof’s claws and hair of the vertebrates. The distal phalanx is found to be protected by the action of the fingernail and it also guards certain soft tissues against various injuries. Various precise movements are found to be enhanced by the presence of the fingernails.
Hair Structure And Function
The hair is considered as the characteristic feature of mammals and it possesses numerous functions including providing protection against external factors and dealing with the production of pheromones, apocrine sweat, and sebum. It is found to have a great impact on sexual and social interactions. It functions in thermoregulation and is found to be a storage site of the stem cells.
Hearing And Equilibrium
The ear is the organ that helps in hearing, which is the modification of sound waves from any source into neural signals that the brain could process. The ears aid in detecting and processing sound and help maintain an overall equilibrium of the being. Equilibrium is the sense of balance and positional awareness. Numerous sensory receptors provide information to the brain about equilibrium. However, unique receptors found in the inner ear play a very critical role in observing equilibrium. To better understand the functioning of the ear and its role in sustaining equilibrium, it is important to learn about its complex structure.
Muscular System
The human body is majorly classified into eleven organ systems. The muscular system is one among them which is specifically responsible for movements. The muscular system is specifically made up of specialized cells termed muscle cells. The significant function of the muscular system is its ability to contract. The muscles attached to bones, blood vessels, and internal organs aid in body movements. Therefore, every movement in the body occurs as a result of muscle contraction.
Structure And Function Of The Pectoral Girdle
A pair of structures that connect the axial skeleton to the upper limbs is known as the pectoral girdle. It forms articulations, or joints, with the upper limbs, each consisting of a clavicle and scapula.
Muscular System Disorders
The human muscular system disorder influences the most important part of the human body- the muscle. It is essential as it provides to and fro movement to the body and nerves. Various types of disorders and illnesses from an irregularity of this movement are observed to be the prime reason.
Human Body Systems
The human body performs various functions with the coordination of several systems. Our heart and lungs are working all the time, even when we are at rest. There is an assortment of different functions that happen inside our bodies. With the advancement of development, life forms started to display progressed attributes and highlights that empowered them to be more productive and flourish in their differentiated climate.
Human Reproductive System
Reproduction defines a biological process that brings new offspring into life from the parents. In humans, reproduction is the process by which gametes from both male and female parents’ gonad fuse to produce a fetus in the female’s body (uterus). The male and female have different mechanisms of producing sex cells or gametes. The male provides sperms, whereas the female provides the egg. Humans have a high degree of sexual differentiation. In addition to reproductive systems, the secondary characteristics also vary in both males and females. The reproductive organ in males is the testis, and the reproductive organ in females is the ovary. Reproduction forms the basis of the existence of life in the world. Every organism has to reproduce to survive. The two methods which prevail universally are asexual and sexual. Sexual methods need two parents’ gametes, usually male and female, to reproduce. An asexual method is usually satisfied by a single parent. In humans, sexual reproduction takes place.
Cephalization of Brain
Cephalization is a steady evolution process through which the mouth, sense organs, nervous, and sensory tissues become concentrated at the anterior part and make the head region. Cephalization word is derived from the Greek word Kephalē, which means head, so in simple words, cephalization means "having a head."
Bone Marrow
The spongy tissue within the bones, like the pelvic and leg bones, is called bone marrow. The bone marrow consists of stem cells. These cells can differentiate into red blood cells that transport oxygen across the body, white blood cells that combat infections, and platelets that aid in blood clotting.
Bones Of The Pelvic Girdle
A single bone, the hip bone or coxal bone (coxal = “hip”), forms the pelvic girdle (hip girdle), which acts as the attachment point for each lower limb. Each hip bone is firmly attached to the axial skeleton through its connection to the sacrum of the vertebral column. Both the right and left hip bones converge anteriorly to connect. The bony pelvis is made up of the two hip bones, the sacrum, and the coccyx, which are attached inferiorly to the sacrum.
Thoracic and Abdominal Arteries
The thoracic artery is also known as the internal mammary artery. It supplies the breasts and the anterior chest wall. There are two internal arteries, the right and left artery, which are situated anterior to the chest wall on either side of the sternum.
The Skeletal Muscle Contraction Cycle
The skeletal muscle contraction cycle is activated by calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The calcium ions bind to the troponin, which reveals the active site on actin by removing tropomyosin. It helps the myosin head to bind the actin. The adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binds to myosin causing the head of the myosin to release from the active site of the actin molecule of the thin filament.
Integumentary System
The integumentary system encompasses a set of organs developing the external most layer of the body, where the skin and the appendages are found to function as a physical barrier for preventing the entry of pathogenic microbes and hazardous substances from the external environment. The structures associated with the integumentary system include scales, hair, nails, hooves, and feathers.
Bone Formation And Development
Bone is the connective tissue that functions to provide support and protection to various organs of the body. It comprises mineral salts and collagen fibers. The formation of new bones is called ossification. The process of ossification is essential for the healing of fractured bones, bone remodeling and for the formation of new bones.
Blood Flow Through The Kidney
Kidneys are the primary organs that eliminate all the waste products from within the body. The acids produced in the cells as a result of metabolism are removed by the kidneys. Kidneys help maintain the salt, water, and minerals like potassium, calcium, and sodium concentration in the blood. Only when the waste is removed, all other organs in the body can function properly.
Body Cavities
The potential spaces detected in the body of the animal is called the body cavity. The structure is found to possess organs and numerous structures and also contain fluid. The dorsal and the ventral body cavities are the largest body cavities found in the human. The embryo of the mammals contains two body cavities called the extraembryonic coelom (lined by extraembryonic mesoderm) and the intraembryonic coelom (lined by somatic and splanchnic lateral plate mesoderm).
Sexual Reproduction
Biology is the study of living organisms. It includes various processes occurring in these organisms, like digestion, reproduction, and excretion. Reproduction is a process of producing offspring or new organisms by single or two parents. When reproduction occurs through one parent, it is called asexual reproduction, but when two parents are usually of the opposite gender, the reproduction is called sexual reproduction.
The Senses
The senses connect an organism to the world. A person can know, both consciously and otherwise, what goes on around him and within him through complex systems that send signals through a maze of brain circuits. These begin with the cells that respond to physical stimuli.
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
Any human body system is composed of a cluster of organs or cells that perform together to execute or maintain homeostasis. For example, the nervous system receives sensory input from the sensory receptors' environment, processes those signals, and directs the muscles and glands to respond to outside stimuli. On the other hand, the endocrine system produces hormones, which influence various functions in the human body like growth, metabolism, reproduction, sensation, etc. Together with the endocrine system, the nervous system maintains homeostasis and is responsible for perception, behavior, and memories, and controls all voluntary movements.
Gustation
Gustation is the perception of the taste or flavors of the food ingested, by the gustatory system. The process of taste occurs when the chemicals present in food or other substances react with the taste receptor cells present in the taste buds. The taste buds are located in the oral cavity, primarily on the tongue. The flavors of food and other substances are determined by the process of taste, along with the olfaction and trigeminal nerve stimulation. Human beings have taste receptor cells on the taste buds, which are located throughout the upper surface of the tongue and also on the epiglottis.
Eye Anatomy And Vision
The eye is the organ that helps in seeing and perceiving the world around. The eye, along with its entire system of muscles and nerves, helps in providing a mental representation of the environment. Thus, the eye contributes in the acuity to navigate properly through physical space, interact with individuals and the objects around.
Respiratory System
It is a process by which living organisms produce energy by the oxidation of complex organic substances, typically with the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide.
The Cardiopulmonary System
The cardiopulmonary system is responsible for the transportation of gases throughout the body. It comprises the heart, blood, and blood vessels. Each component of the cardiopulmonary system plays an important role in maintaining oxygen and carbon dioxide inside the body.
Digestive System
The digestive system consists of the liver and gallbladder, and gastrointestinal tract (also known as the G.I. tract). The G.I. tract is a series of hollow organs connected by a long, twisted tube that runs from the mouth to the anus. The mouth, esophagus, liver, small digestive tract, internal organ, and rear-end are the hollow organs that make up the human digestive system or G.I. tract.
The Digestive and Excretory Systems
The human body consists of several systems that help it to perform several essential life processes. The digestive system and the excretory system are some of the many systems that make the human body fit to its environment.
Hormonal Regulation
The hormones are generated in the body for controlling various biochemical reactions, which are concerned with the maintenance of homeostasis. The hormones regulate the physiological and behavioral processes of the body. The reactions including respiration, metabolism, digestion, reproduction, and movement are found to be regulated by the action of the hormone.
Temporal Summation
The additive effect of multiple electrical impulses on a neuromuscular junction (junction between a nerve cell and a muscle cell), is referred to as summation in physiology. Individually, the stimuli are unable to elicit a response, but when combined, they can. Temporal summation refers to the addition of successive stimuli on a single nerve; spatial summation refers to the addition of simultaneous stimuli from several conducting fibers.
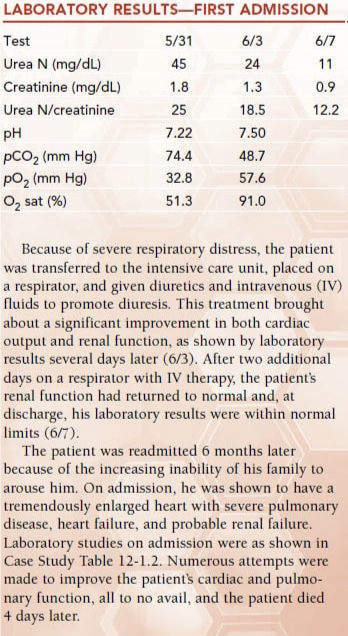
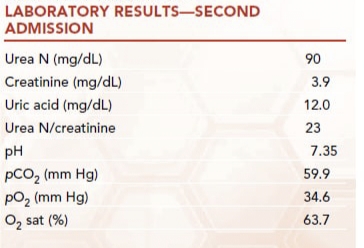
What is the most likely cause of the patient's elevated urea nitrogen? Which data support your conclusion?
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps




