What is the value of the equilibrium constant at 500 °C for the formation of NH3 according to the following equation? N2(g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) An equilibrium mixture of NH3 (g), H2 (g), and N2 (g) at 500 °C was found to contain 1.35 M H2, 1.15 M N2, and 4.12 ×10^-1 M NH3
What is the value of the equilibrium constant at 500 °C for the formation of NH3 according to the following equation? N2(g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) An equilibrium mixture of NH3 (g), H2 (g), and N2 (g) at 500 °C was found to contain 1.35 M H2, 1.15 M N2, and 4.12 ×10^-1 M NH3
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter14: Acids And Bases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7RQ: Table 13-4 lists the stepwise Ka values for some polyprotic acids. What is the difference between a...
Related questions
Question
100%
What is the value of the equilibrium constant at 500 °C for the formation of NH3 according to the following equation?
N2(g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g)
An equilibrium mixture of NH3 (g), H2 (g), and N2 (g) at 500 °C was found to contain 1.35 M H2, 1.15 M N2, and 4.12 ×10^-1 M NH3
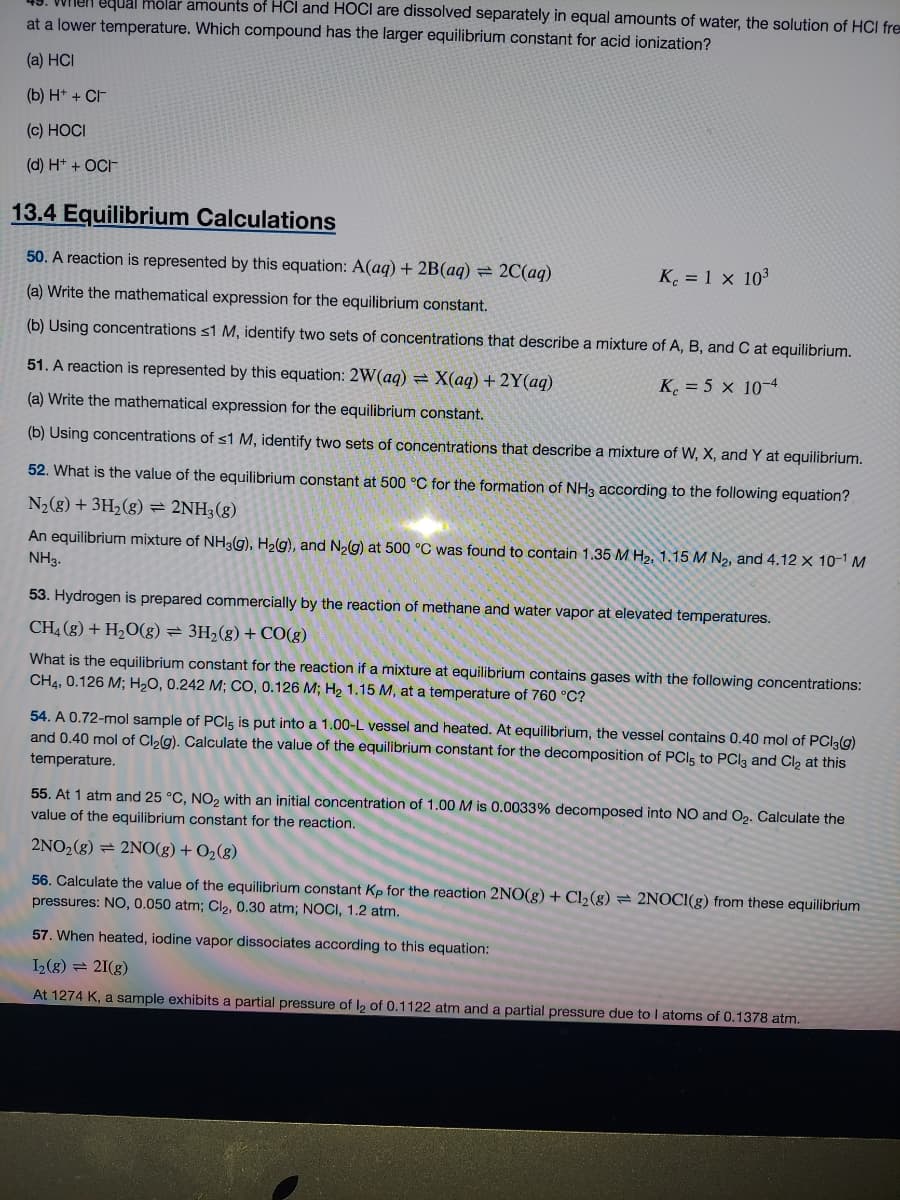
Transcribed Image Text:Vnen equal hôlar amounts of HCl and HOCI are dissolved separately in equal amounts of water, the solution of HCI fre
at a lower temperature. Which compound has the larger equilibrium constant for acid ionization?
(a) HCI
(b) H* + CF
(c) HOCI
(d) H* + OCH
13.4 Equilibrium Calculations
50. A reaction is represented by this equation: A(aq) + 2B(aq) = 2C(aq)
K. = 1 x 103
(a) Write the mathematical expression for the equilibrium constant.
(b) Using concentrations <1 M, identify two sets of concentrations that describe a mixture of A, B, and C at equilibrium.
51. A reaction is represented by this equation: 2W(aq) = X(aq) + 2Y(aq)
K. = 5 × 10-4
(a) Write the mathematical expression for the equilibrium constant.
(b) Using concentrations of <1 M, identify two sets of concentrations that describe a mixture of W, X, and Y at equilibrium.
52. What is the value of the equilibrium constant at 500 °C for the formation of NH3 according to the following equation?
N2(g) + 3H2(g) = 2NH3(g)
An equilibrium mixture of NH39), H2(g), and N2g) at 500 °C was found to contain 1.35 M H2, 1.15 M N2, and 4.12 x 10-1 M
NH3.
53. Hydrogen is prepared commercially by the reaction of methane and water vapor at elevated temperatures.
CH4 (g) + H2O(g) = 3H2(g) + CO(g)
What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction if a mixture at equilibrium contains gases with the following concentrations:
CH4, 0.126 M; H2O, 0.242 M; CO, 0.126 M; H 1.15 M, at a temperature of 760 °C?
54. A 0.72-mol sample of PCIs is put into a 1.00-L vessel and heated. At equilibrium, the vessel contains 0.40 mol of PCI3(g)
and 0.40 mol of Cl2g). Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant for the decomposition of PCI5 to PCI3 and Cl2 at this
temperature.
55. At 1 atm and 25 °C, NO2 with an initial concentration of 1.00 M is 0.0033% decomposed into NO and O2. Calculate the
value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction.
2NO2(g) = 2NO(g) + O2(g)
56. Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) = 2NOCI(g) from these equilibrium
pressures: NO, 0.050 atm; Cl2, 0.30 atm; NOCI, 1.2 atm.
57. When heated, iodine vapor dissociates according to this equation:
I(g) = 21(g)
At 1274 K, a sample exhibits a partial pressure of l, of 0.1122 atm and a partial pressure due to I atoms of 0.1378 atm.
Expert Solution
Step 1

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning