Calculate the expected ΔHrxn using the ΔHf values for the reactants and products in the Reaction. (Hint: this is actually much easier if you write the net reaction first and then calculate ΔHrxn for the net.) HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) -> H2O(l) + NaCl(aq) i attached the table for the problem and my work up to this point. plz only solve for trial one. i am wondering how delta H will change when the concentration of HCl changes. Note the lab question is How does the concentration of acid affect the heat of reaction (ΔHrxn)between a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base(NaOH)?
Calculate the expected ΔHrxn using the ΔHf values for the reactants and products in the Reaction. (Hint: this is actually much easier if you write the net reaction first and then calculate ΔHrxn for the net.) HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) -> H2O(l) + NaCl(aq) i attached the table for the problem and my work up to this point. plz only solve for trial one. i am wondering how delta H will change when the concentration of HCl changes. Note the lab question is How does the concentration of acid affect the heat of reaction (ΔHrxn)between a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base(NaOH)?
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter10: Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8A
Related questions
Question
Calculate the expected ΔHrxn using the ΔHf values for the reactants and
products in the Reaction. (Hint: this is actually much easier if you write
the net reaction first and then calculate ΔHrxn for the net.)
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) -> H2O(l) + NaCl(aq)
i attached the table for the problem and my work up to this point. plz only solve for trial one. i am wondering how delta H will change when the concentration of HCl changes. Note the lab question is
How does the concentration of acid affect the heat of reaction (ΔHrxn)between a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base(NaOH)?
this is for reference
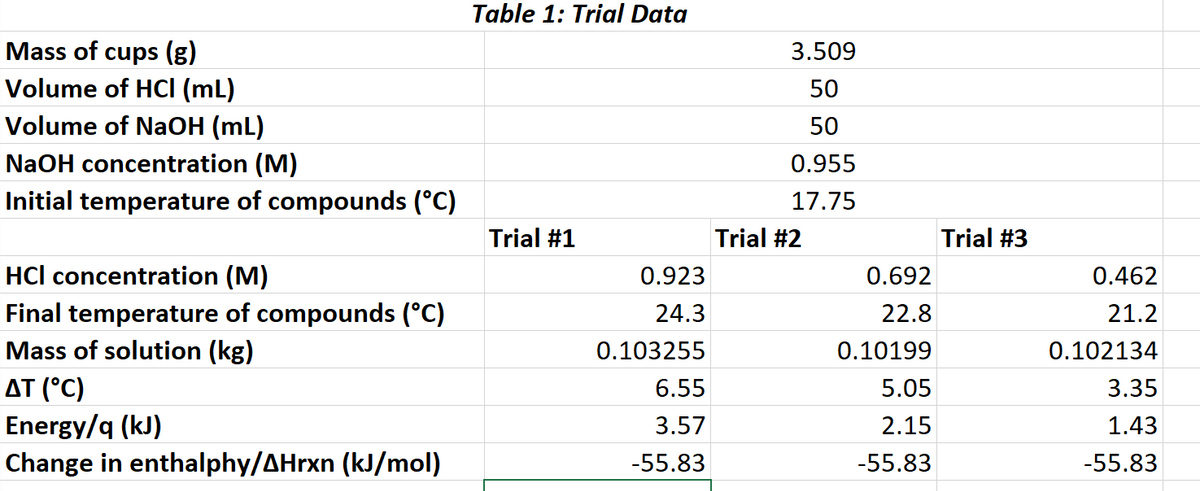
Transcribed Image Text:Table 1: Trial Data
Mass of cups (g)
Volume of HCI (mL)
Volume of NaOH (mL)
3.509
50
50
NaOH concentration (M)
0.955
Initial temperature of compounds (°C)
17.75
Trial #1
Trial #2
Trial #3
HCl concentration (M)
0.923
0.692
0.462
Final temperature of compounds (°C)
Mass of solution (kg)
24.3
22.8
21.2
0.103255
0.10199
0.102134
AT (°C)
6.55
5.05
3.35
Energy/q (kJ)
Change in enthalphy/AHrxn (kJ/mol)
3.57
2.15
1.43
-55.83
-55.83
-55.83

Transcribed Image Text:a) (msolution) = total mass
(msolution) = 106.764g – 3.509g = 103.255g
b) AT = Tt - Ti
AT = 24.30°C – 17.75°C = 6.550°C
c) q = m*Cs* AT
q = 0.103255kg * 4.184kJ/K*6.550°C = 3.56966kJ
d) n(HCI) = (0.923mol/L)(50mL)(1L/1000mL) = 0.046mol
n(NaOH) = (0.955mol/L)(50mL)(1L/1000OmL) = 0.048mol
According to the balanced equation: HCI(aq)+NaOH(aq)→NaCI(aq)+H
20(1), the stoichiometric ratio between the moles of HCl and the product
moles of H20 produced is of a 1:1 ratio, thus 0.046mol of HCI will react
with 0.048mol of NaOH to produce 0.046mol of H2O
mass of cups
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning