When comparing two sample proportions with a two-sided alternative hypothesis, all other factors being equal, will you get a smaller p-value if the sample proportions are close together or if they are far apart? Explain. Choose the correct answer below. O A. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are far apart because a larger difference results in a pooled proportion closer to 0.5, and a pooled proportion close to 0.5 results in a smaller standard error, which is the denominator of the test statistic. O B. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are close together because closer proportions results in a smaller standard error, which is the denominator of the test statistic. OC. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are close together because the difference between them is smaller. O D. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are far apart because larger difference results in a larger absolute value of the numerator of the test statistic.
When comparing two sample proportions with a two-sided alternative hypothesis, all other factors being equal, will you get a smaller p-value if the sample proportions are close together or if they are far apart? Explain. Choose the correct answer below. O A. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are far apart because a larger difference results in a pooled proportion closer to 0.5, and a pooled proportion close to 0.5 results in a smaller standard error, which is the denominator of the test statistic. O B. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are close together because closer proportions results in a smaller standard error, which is the denominator of the test statistic. OC. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are close together because the difference between them is smaller. O D. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are far apart because larger difference results in a larger absolute value of the numerator of the test statistic.
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section11.4: Collecting Data
Problem 3E
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Help please.
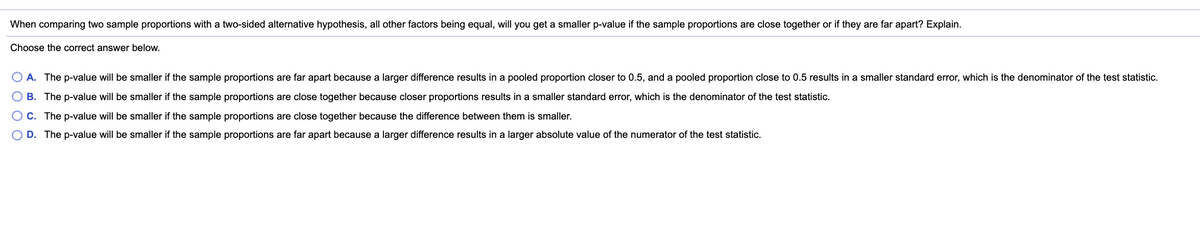
Transcribed Image Text:When comparing two sample proportions with a two-sided alternative hypothesis, all other factors being equal, will you get a smaller p-value if the sample proportions are close together or if they are far apart? Explain.
Choose the correct answer below.
A. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are far apart because a larger difference results in a pooled proportion closer to 0.5, and a pooled proportion close to 0.5 results in a smaller standard error, which is the denominator of the test statistic.
B. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are close together because closer proportions results in a smaller standard error, which is the denominator of the test statistic.
C. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are close together because the difference between them is smaller.
D. The p-value will be smaller if the sample proportions are far apart because a larger difference results in a larger absolute value of the numerator of the test statistic.
O O O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning