When randomly selecting adults, let M denote the event of randomly selecting a male and let B denote the event of randomly selecting someone with blue eyes. What does P(M|B) represent? Is P(M|B) the same as P(B|M)? What does P(M|B) represent? O A. The probability of getting a male or getting someone with blue eyes. O B. The probability of getting a male and getting someone with blue eyes. OC. The probability of getting a male, given that someone with blue eyes has been selected. O D. The probability of getting someone with blue eyes, given that a male has been selected. Is P(M|B) the same as P(B|M)? O A. No, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting a male, given that someone with blue eyes has been selected. O B. Yes, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting someone with blue eyes, given that a male has been selected. OC. No, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting someone with blue eyes, given that a male has been selected. O D. Yes, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting a male, given that someone with blue eyes has been selected.
When randomly selecting adults, let M denote the event of randomly selecting a male and let B denote the event of randomly selecting someone with blue eyes. What does P(M|B) represent? Is P(M|B) the same as P(B|M)? What does P(M|B) represent? O A. The probability of getting a male or getting someone with blue eyes. O B. The probability of getting a male and getting someone with blue eyes. OC. The probability of getting a male, given that someone with blue eyes has been selected. O D. The probability of getting someone with blue eyes, given that a male has been selected. Is P(M|B) the same as P(B|M)? O A. No, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting a male, given that someone with blue eyes has been selected. O B. Yes, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting someone with blue eyes, given that a male has been selected. OC. No, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting someone with blue eyes, given that a male has been selected. O D. Yes, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting a male, given that someone with blue eyes has been selected.
Chapter8: Sequences, Series,and Probability
Section8.7: Probability
Problem 4ECP: Show that the probability of drawing a club at random from a standard deck of 52 playing cards is...
Related questions
Question
72 and 73 solve both

Transcribed Image Text:When randomly selecting adults, let M denote the event of randomly selecting a male and let B denote the event of randomly selecting someone with blue eyes. What does P(M|B)
represent? Is P(MIB) the same as P(BIM)?
What does P(MIB) represent?
O A. The probability of getting a male or getting someone with blue eyes.
O B. The probability of getting a male and getting someone with blue eyes.
O C. The probability of getting a male, given that someone with blue eyes has been selected.
O D. The probability of getting someone with blue eyes, given that a male has been selected.
Is P(M|B) the same as P(B|M)?
O A. No, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting a male, given that someone with blue eyes has been selected.
O B. Yes, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting someone with blue eyes, given that a male has been selected.
O C. No, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting someone with blue eyes, given that a male has been selected.
O D. Yes, because P(B|M) represents the probability of getting a male, given that someone with blue eyes has been selected.
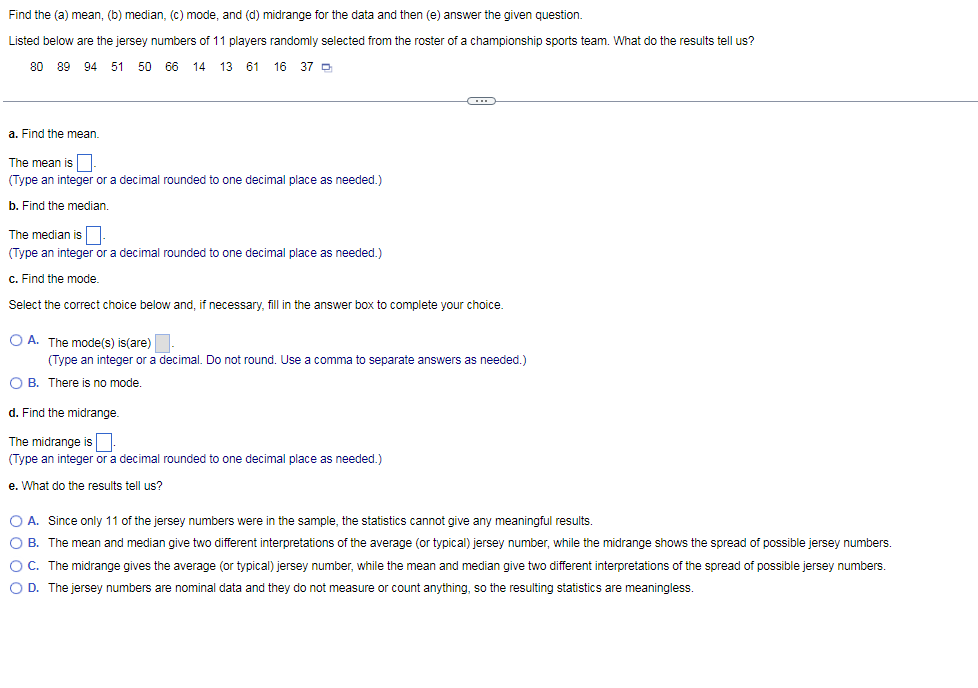
Transcribed Image Text:Find the (a) mean, (b) median, (c) mode, and (d) midrange for the data and then (e) answer the given question.
Listed below are the jersey numbers of 11 players randomly selected from the roster of a championship sports team. What do the results tell us?
80 89 94
51 50 66
14 13
61
16 37 D
a. Find the mean.
The mean is
(Type an integer or a decimal rounded to one decimal place as needed.)
b. Find the median.
The median is||
(Type an integer or a decimal rounded to one decimal place as needed.)
c. Find the mode.
Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
O A. The mode(s) is(are)
(Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round. Use a comma
separate answers as needed.)
O B. There is no mode.
d. Find the midrange.
The midrange is
(Type an integer or a decimal rounded to one decimal place as needed.)
e. What do the results tell us?
O A. Since only 11 of the jersey numbers were in the sample, the statistics cannot give any meaningful results.
O B. The mean and median give two different interpretations of the average (or typical) jersey number, while the midrange shows the spread of possible jersey numbers.
OC. The midrange gives the average (or typical) jersey number, while the mean and median give two different interpretations of the spread of possible jersey numbers.
O D. The jersey numbers are nominal data and they do not measure or count anything, so the resulting statistics are meaningless.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

