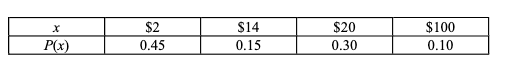
While playing Monopoly, Andi estimated the probabilities of the non-zero rents according to the following probability distribution: x P(x) $2 0.45 $14 0.15 $20 0.30 $100 0.10. (picture attached) Consider the random variable x = dollar amount in rent collected in a Monopoly roll. a) If the table above specifies the probability distribution of x, what is the mean of the random variable x? b) If the probabilities are associated with the outcomes as in the table above, what is the standard deviation of the random variable x?
Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
While playing Monopoly, Andi estimated the probabilities of the non-zero rents according to the following
probability distribution:
x
P(x)
$2
0.45
$14
0.15
$20
0.30
$100
0.10. (picture attached)
Consider the random variable x = dollar amount in rent collected in a Monopoly roll.
a) If the table above specifies the probability distribution of x, what is the mean of the random
variable x?
b) If the probabilities are associated with the outcomes as in the table above, what is the
standard deviation of the random variable x?
Random Variable: A random variable is a real valued function that assign a real number to each outcome (i.e., sample point) of a random experiment. Random variable divided into two types they are
- Discrete random variable - A random variable say "x", which can take finite number of values in the interval of domain
- Continuous random variable - A random variable say "x", which can take any value in its domain or in an interval.
The Mean (expected value) of the random variable x is denoted by E[X]
i.e., E[X] =
The Variance of the random variable x is denoted by Var[X]
i.e., Var[X] = E[X2] - (E[X])2
Here E[X2] =
and Standard deviation =
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









