y =2 (0,0) u(x,0) = 0 means that in a two-dimensional heat flow, at any point along the x-axis, the temperature equals(4). u( y) = 0 means that any point along the (5) axis, the temperature equals (6) In a one-dimensional heal flow Kving homogeneous boundary conditions, the solution -'at the to the heat equation is u(x, t) = (7) at temp. cond. I 18)
y =2 (0,0) u(x,0) = 0 means that in a two-dimensional heat flow, at any point along the x-axis, the temperature equals(4). u( y) = 0 means that any point along the (5) axis, the temperature equals (6) In a one-dimensional heal flow Kving homogeneous boundary conditions, the solution -'at the to the heat equation is u(x, t) = (7) at temp. cond. I 18)
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
Fill in the blanks
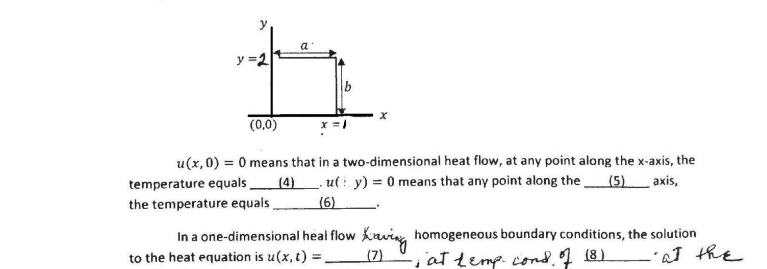
Transcribed Image Text:y
y =2
(0,0)
u(x,0) = 0 means that in a two-dimensional heat flow, at any point along the x-axis, the
temperature equals (4). ut : y) = 0 means that any point along the (5)_ axis,
the temperature equals
(6)
In a one-dimensional heal flow
kaving homogeneous boundary conditions, the solution
-iattemp cond. 18)
L'at the
to the heat equation is u(x, t) :
(7)
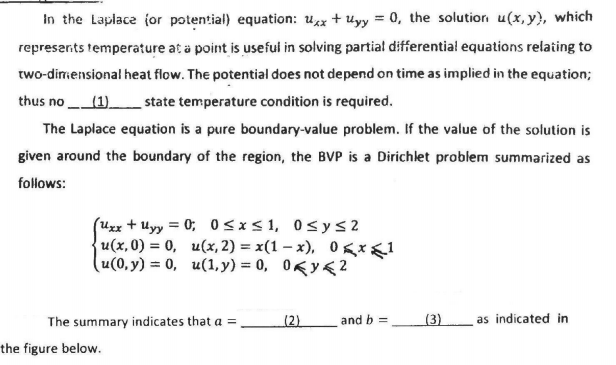
Transcribed Image Text:In the Laplace (or potential) equation: uxx + uyy = 0, the solutior u(x, y), which
represarts temperature at a point is usefui in solving partial differential equations relating to
two-dirmensional heat flow. The potential does not depend on time as implied in the equation;
thus no (1).
_state temperature condition is required.
The Laplace equation is a pure boundary-value problem. If the value of the solution is
given around the boundary of the region, the BVP is a Dirichlet problem summarized as
follows:
(Uxx + uyy = 0; 0<x<1, 0sys2
u(x,0) = 0, u(x, 2) = x(1 – x), 0gx<1
u(0, y) = 0, u(1, y) = 0, 0Ky<2
The summary indicates that a =
(2)
and b =
(3)
as indicated in
the figure below.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

