You are conducting a study to see if the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is significantly different from 50% at a level of significance of a = 0.01. According to your sample, 39 out of 94 potential voters prefer the Democratic candidate. a. For this study, we should use Select an answer b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Ho: ? ? (please enter a decimal) | (Please enter a decimal) c. The test statistic 2 d. The p-value = e. The p-value is ?▼ a f. Based on this, we should Select an answer the null hypothesis. g. Thus, the final conclusion is that . | (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) O The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly different from 50% at a = 0.01, so there is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is different from 50%. O The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly different from 50% at a = 0.01, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is equal to 50%. The data suggest the populaton proportion is significantly different from 50% at a = 0.01, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is different from 50%
You are conducting a study to see if the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is significantly different from 50% at a level of significance of a = 0.01. According to your sample, 39 out of 94 potential voters prefer the Democratic candidate. a. For this study, we should use Select an answer b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Ho: ? ? (please enter a decimal) | (Please enter a decimal) c. The test statistic 2 d. The p-value = e. The p-value is ?▼ a f. Based on this, we should Select an answer the null hypothesis. g. Thus, the final conclusion is that . | (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) O The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly different from 50% at a = 0.01, so there is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is different from 50%. O The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly different from 50% at a = 0.01, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is equal to 50%. The data suggest the populaton proportion is significantly different from 50% at a = 0.01, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is different from 50%
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
100%
You are conducting a study to see if the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is significantly different from 50% at a level of significance of αα = 0.01. According to your sample, 39 out of 94 potential voters prefer the Democratic candidate.

Transcribed Image Text:h. Interpret the p-value in the context of the study.
There is a 9.88% chance that the percent of all voters who prefer the Democratic candidate differs
from 50%.
There is a 9.88% chance of a Type I error.
If the population proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is 50% and if another 94
voters are surveyed then there would be a 9.88% chance that either fewer than 42% of the 94 voters
surveyed prefer the Democratic candidate or more than 58% of the 94 voters surveyed prefer the
Democratic candidate.
O If the sample proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is 42% and if another 94
voters are surveyed then there would be a 9.88% chance that we would conclude either fewer than
50% of all voters prefer the Democratic candidate or more than 50% of all voters prefer the
Democratic candidate.
i. Interpret the level of significance in the context of the study.
If the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is different from 50% and if another
94 voters are surveyed then there would be a 1% chance that we would end up falsely concuding that
the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is equal to 50%.
O There is a 1% chance that the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is different
from 50%.
O There is a 1% chance that the earth is flat and we never actually sent a man to the moon.
If the population proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is 50% and if another 94
voters are surveyed then there would be a 1% chance that we would end up falsely concuding that the
proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is different from 50%
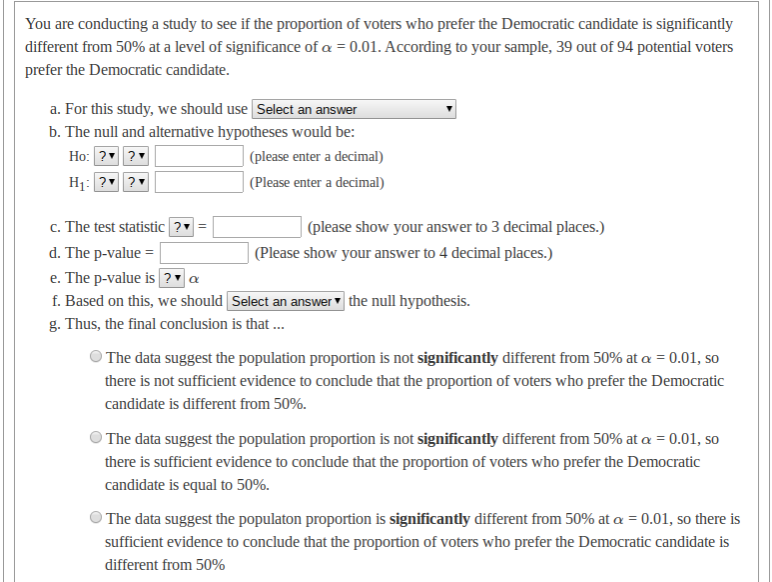
Transcribed Image Text:You are conducting a study to see if the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is significantly
different from 50% at a level of significance of a = 0.01. According to your sample, 39 out of 94 potential voters
prefer the Democratic candidate.
a. For this study, we should use Select an answer
b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be:
Ho: ? ?
H1: ? ?
(please enter a decimal)
| (Please enter a decimal)
c. The test statistic ?
| (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.)
d. The p-value =
(Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.)
e. The p-value is ? a
f. Based on this, we should Select an answer the null hypothesis.
g. Thus, the final conclusion is that ..
O The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly different from 50% at a = 0.01, so
there is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic
candidate is different from 50%.
The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly different from 50% at a = 0.01, so
there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic
candidate is equal to 50%.
The data suggest the populaton proportion is significantly different from 50% at a = 0.01, so there is
sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of voters who prefer the Democratic candidate is
different from 50%
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given that, n=94, x=39,
The sample proportion is,
a) For this study, we should use z-test for population proportion.
b) The null and alternative hypothesis is,
c) The test statistic is given as,
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL