1. Solve the triangle given below C b Y 6 B 4 A • b = . Based on the length of the sides opposite them, which of the two unknown angles has a lesser measure? What is the degree measure of this angle? What is the degree measure of the remaining angle? 122° α
1. Solve the triangle given below C b Y 6 B 4 A • b = . Based on the length of the sides opposite them, which of the two unknown angles has a lesser measure? What is the degree measure of this angle? What is the degree measure of the remaining angle? 122° α
Mathematics For Machine Technology
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Peterson, John.
Chapter73: Achievement Review—section Seven
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 30AR
Related questions
Question
Sample solution included. Answer each questions.
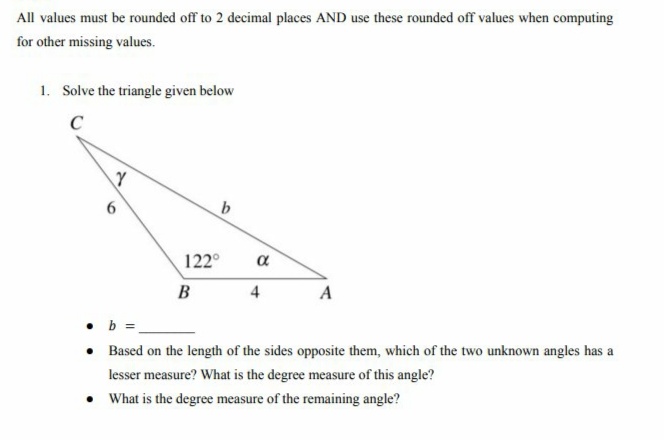
Transcribed Image Text:All values must be rounded off to 2 decimal places AND use these rounded off values when computing
for other missing values.
1. Solve the triangle given below
C
6
b
B
4
A
. b =
• Based on the length of the sides opposite them, which of the two unknown angles has a
lesser measure? What is the degree measure of this angle?
• What is the degree measure of the remaining angle?
Y
122°
α
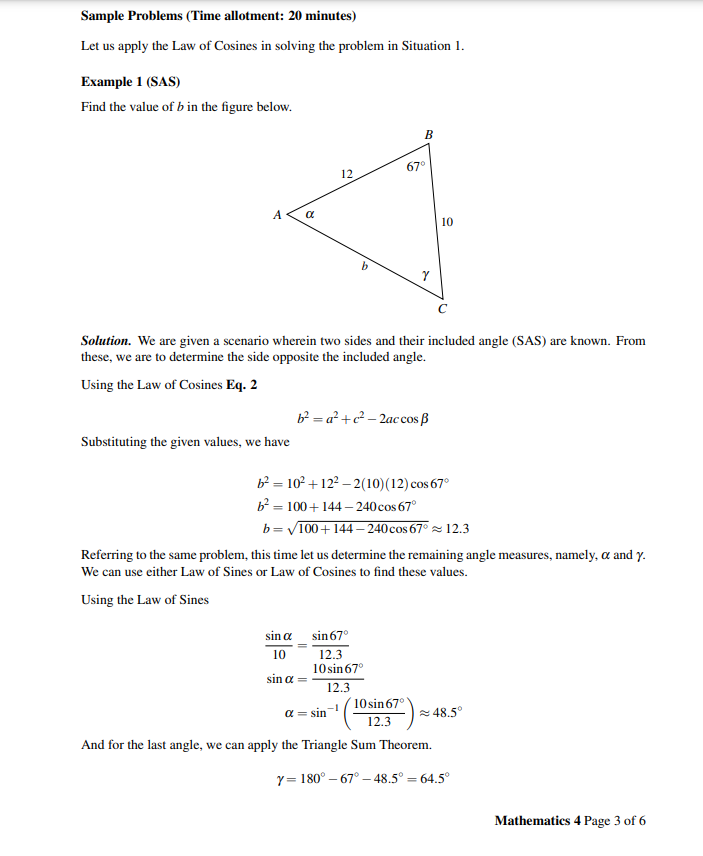
Transcribed Image Text:Sample Problems (Time allotment: 20 minutes)
Let us apply the Law of Cosines in solving the problem in Situation 1.
Example 1 (SAS)
Find the value of b in the figure below.
B
12
A
α
b
Y
Solution. We are given a scenario wherein two sides and their included angle (SAS) are known. From
these, we are to determine the side opposite the included angle.
Using the Law of Cosines Eq. 2
b²=a²+c²-2ac cos B
Substituting the given values, we have
b²
10²+122-2(10)(12) cos 67°
b² 100+144-240 cos 67°
b=√100+144-240 cos 67° 12.3
Referring to the same problem, this time let us determine the remaining angle measures, namely, a and y.
We can use either Law of Sines or Law of Cosines to find these values.
Using the Law of Sines
sin 67°
sin a
10
12.3
10 sin 67°
sin α =
12.3
a=sin 10sin 67°
≈48.5°
12.3
And for the last angle, we can apply the Triangle Sum Theorem.
y=180° -67°-48.5° = 64.5°
Mathematics 4 Page 3 of 6
67°
10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning