1.) The fragrance industry uses volatile molecules to add scent to perfumes. A strategy shown below is used to prolong the longevity of a fragrance: the volatile molecule, hexanal, is covalently linked to a non-volatile substrate, such as cyclodextrin. a. Show a mechanism for the reaction between hexanal and cyclodextrin to form the abivah ajoye covalently linked complex. Simplified Cyclodextrin Structure NH₂ H Hexanal s CH3 CH3 Hydrolysis H₂O cat. H-A b. Under specific chemical conditions, a reaction will occur to release the volatile substance. For instance, as exposure to water increases, the complex shown in part a undergoes hydrolysis. The rate of the addition of water to the imine is found to be faster under acidic conditions. Explain why. Covalently-Linked Complex CH3 Volatile Fragrance Released CH3 NH₂ noites
1.) The fragrance industry uses volatile molecules to add scent to perfumes. A strategy shown below is used to prolong the longevity of a fragrance: the volatile molecule, hexanal, is covalently linked to a non-volatile substrate, such as cyclodextrin. a. Show a mechanism for the reaction between hexanal and cyclodextrin to form the abivah ajoye covalently linked complex. Simplified Cyclodextrin Structure NH₂ H Hexanal s CH3 CH3 Hydrolysis H₂O cat. H-A b. Under specific chemical conditions, a reaction will occur to release the volatile substance. For instance, as exposure to water increases, the complex shown in part a undergoes hydrolysis. The rate of the addition of water to the imine is found to be faster under acidic conditions. Explain why. Covalently-Linked Complex CH3 Volatile Fragrance Released CH3 NH₂ noites
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Chapter24: Catalytic Carbon-carbon Bond Formation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 24.21P
Related questions
Question
please explain w steps and answer a and b
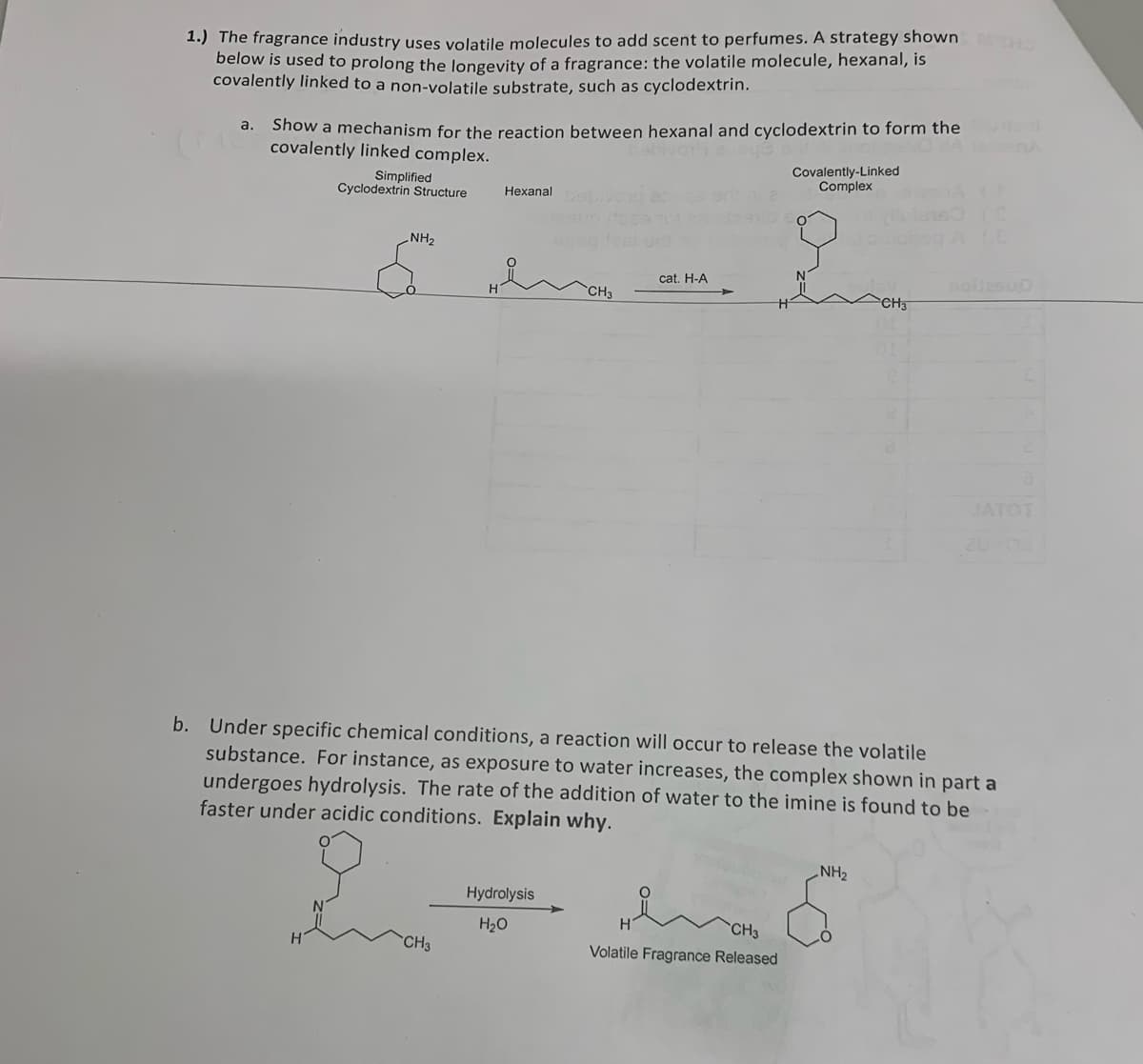
Transcribed Image Text:1.) The fragrance industry uses volatile molecules to add scent to perfumes. A strategy shown MOHO
below is used to prolong the longevity of a fragrance: the volatile molecule, hexanal, is
covalently linked to a non-volatile substrate, such as cyclodextrin.
a.
Show a mechanism for the reaction between hexanal and cyclodextrin to form the
covalently linked complex.
Simplified
Cyclodextrin Structure
NH₂
Hexanal
CH3
CH3
Hydrolysis
H₂O
cat. H-A
Covalently-Linked
Complex
b. Under specific chemical conditions, a reaction will occur to release the volatile
substance. For instance, as exposure to water increases, the complex shown in part a
undergoes hydrolysis. The rate of the addition of water to the imine is found to be
faster under acidic conditions. Explain why.
HenCHO
CH3
Volatile Fragrance Released
CH3
NH₂
(E
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning