10. Customers arrive an average of 8 per hour and an average of 12 customers can be served in an hour. Assume this is an M/M/1 model. (Noteshaper Quick Start #18 - #20) what is the system utilization? what is the average length of the line? what is the average number of customers in the system? what is the average amount of time spent waiting in the line? what is the average amount of time a customer spends in the system? what is the probability of no customers in the system?
10. Customers arrive an average of 8 per hour and an average of 12 customers can be served in an hour. Assume this is an M/M/1 model. (Noteshaper Quick Start #18 - #20) what is the system utilization? what is the average length of the line? what is the average number of customers in the system? what is the average amount of time spent waiting in the line? what is the average amount of time a customer spends in the system? what is the probability of no customers in the system?
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter12: Queueing Models
Section12.5: Analytic Steady-state Queueing Models
Problem 9P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:10. Customers arrive an average of 8 per hour and an average of 12 customers can be
served in an hour. Assume this is an M/M/1 model. (Noteshaper Quick Start #18 - #20)
what is the system utilization?
what is the average length of the line?
what is the average number of customers in the system?
what is the average amount of time spent waiting in the line?
what is the average amount of time a customer spends in the system?
what is the probability of no customers in the system?
11. Customers arrive at a ferry ticket office at the rate of 18 per hour on Monday mornings.
This can be described as a M/M/1 model. Selling the tickets and providing general
information takes an average of 2 minutes per customer. One ticket agent is on duty on
Mondays. (Noteshaper Scenario #34)
a. What is the average length of the line on Monday mornings?
b. On average, how long does a customer wait to buy a ticket on Monday mornings
(in minutes)?
c. How long does it take to successfully buy a ticket on Monday mornings (in
minutes)? (This includes time waiting in line and purchasing from the agent.)
d. What is the probability that an arriving customer has to wait to buy a ferry ticket
on Monday morning?
e. What is the probability of exactly four customers in the ferry ticket office? This
includes both customers waiting in line and those being served.
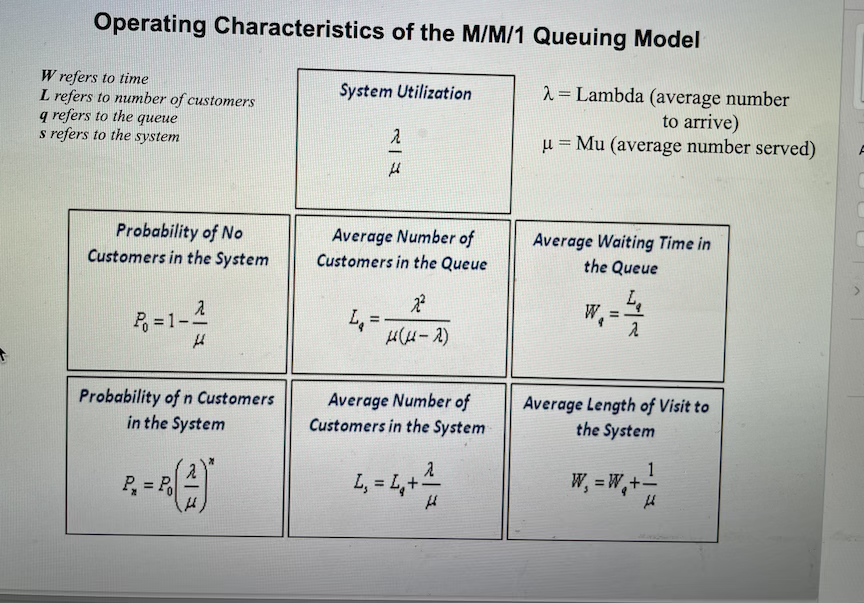
Transcribed Image Text:Operating Characteristics of the M/M/1 Queuing Model
W refers to time
L refers to number of customers
q refers to the queue
s refers to the system
2= Lambda (average number
to arrive)
u = Mu (average number served)
System Utilization
Probability of No
Customers in the System
Average Number of
Customers in the Queue
Average Waiting Time in
the Queue
W, =
%3D
る=1-2
Hu-ス)
Probability of n Customers
in the System
Average Number of
Customers in the System
Average Length of Visit to
the System
W, = W,+-
%3!
P, = P
%3!
ペ|さ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,