11.153 and 11.154 A satellite will travel indefinitely in a circular orbit around a planet if the normal component of the acceleration of the satellite is equal to g(R/r), where g is the acceleration of gravity at the surface of the planet, R is the radius of the planet, and r is the distance from the center of the planet to the satellite. Knowing that the diameter of the sun is 1.39 Gm and that the acceleration of gravity at its surface is 274 m/s?, determine the radius of the orbit of the indicated planet around the sun assuming that the orbit is circular. 11.153 Earth: (vmean)orbit 11.154 Saturn: (vmean)orbit 107 Mm/h. 34.7 Mm/h.
11.153 and 11.154 A satellite will travel indefinitely in a circular orbit around a planet if the normal component of the acceleration of the satellite is equal to g(R/r), where g is the acceleration of gravity at the surface of the planet, R is the radius of the planet, and r is the distance from the center of the planet to the satellite. Knowing that the diameter of the sun is 1.39 Gm and that the acceleration of gravity at its surface is 274 m/s?, determine the radius of the orbit of the indicated planet around the sun assuming that the orbit is circular. 11.153 Earth: (vmean)orbit 11.154 Saturn: (vmean)orbit 107 Mm/h. 34.7 Mm/h.
Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
5th Edition
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Chapter10: Motion In A Noninertial Reference Frame
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.20P: Calculate the effective gravitational field vector g at Earths surface at the poles and the equator....
Related questions
Question
Knowing that the radius of the earth is 6370 km, determine the time of one orbit of the Hubble Space Telescope if the telescope travels in a circular orbit 590 km above the surface of the earth. (See information given in Probs. 11.153–11.154.)
Reference to Problem 11.153-11.154:
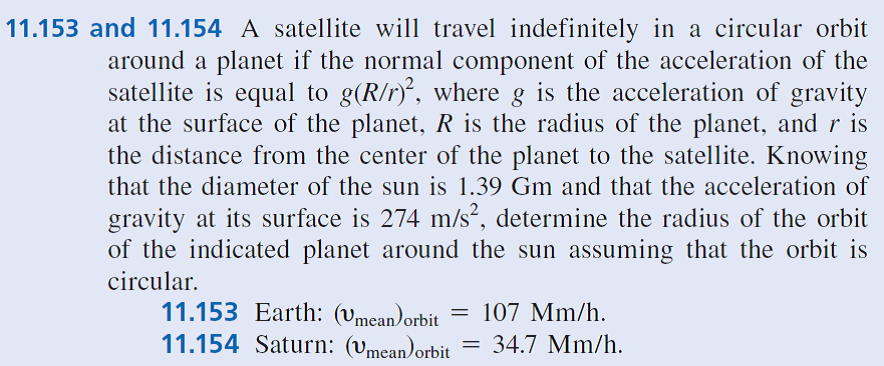
Transcribed Image Text:11.153 and 11.154 A satellite will travel indefinitely in a circular orbit
around a planet if the normal component of the acceleration of the
satellite is equal to g(R/r), where g is the acceleration of gravity
at the surface of the planet, R is the radius of the planet, and r is
the distance from the center of the planet to the satellite. Knowing
that the diameter of the sun is 1.39 Gm and that the acceleration of
gravity at its surface is 274 m/s?, determine the radius of the orbit
of the indicated planet around the sun assuming that the orbit is
circular.
11.153 Earth: (vmean)orbit
11.154 Saturn: (vmean)orbit
107 Mm/h.
34.7 Mm/h.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning