15. Does learning a second language change brain structure? Mechelli et al. (2004) tested 22 native Italian speakers who had learned English as a second language. Proficiencies in reading, writ- ing, and speech were assessed using a number of tests whose results were summarized by a profi- ciency score. Gray-matter density was measured in the left inferior parietal region of the brain using a neuroimaging technique, as mm³ of gray matter per voxel. (A voxel is a picture element, or "pixel," in three dimensions.) The data are listed in the accompanying table. a. Display the association between the two variables in a scatter plot. b. Calculate the correlation between second language proficiency and gray-matter density. c. Test the null hypothesis of zero correlation. d. What are your assumptions in part (c)? e. Does the scatter plot support these assump- tions? Explain. Proficiency score for Gray-matter second density language (mm³/voxel) 0.26 0.44 0.89 1.26 1.69 1.97 1.98 2.24 2.24 2.58 2.50 -0.070 -0.080 -0.008 -0.009 -0.023 -0.009 -0.036 -0.029 -0.008 -0.023 -0.006 Proficiency score for Gray-matter second density language (mm³/voxel) 2.75 3.25 3.85 3.04 2.55 2.50 3.11 3.18 3.52 3.59 3.40 -0.008 -0.006 0.022 0.018 0.023 0.022 0.036 0.059 0.062 0.049 0.033
15. Does learning a second language change brain structure? Mechelli et al. (2004) tested 22 native Italian speakers who had learned English as a second language. Proficiencies in reading, writ- ing, and speech were assessed using a number of tests whose results were summarized by a profi- ciency score. Gray-matter density was measured in the left inferior parietal region of the brain using a neuroimaging technique, as mm³ of gray matter per voxel. (A voxel is a picture element, or "pixel," in three dimensions.) The data are listed in the accompanying table. a. Display the association between the two variables in a scatter plot. b. Calculate the correlation between second language proficiency and gray-matter density. c. Test the null hypothesis of zero correlation. d. What are your assumptions in part (c)? e. Does the scatter plot support these assump- tions? Explain. Proficiency score for Gray-matter second density language (mm³/voxel) 0.26 0.44 0.89 1.26 1.69 1.97 1.98 2.24 2.24 2.58 2.50 -0.070 -0.080 -0.008 -0.009 -0.023 -0.009 -0.036 -0.029 -0.008 -0.023 -0.006 Proficiency score for Gray-matter second density language (mm³/voxel) 2.75 3.25 3.85 3.04 2.55 2.50 3.11 3.18 3.52 3.59 3.40 -0.008 -0.006 0.022 0.018 0.023 0.022 0.036 0.059 0.062 0.049 0.033
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.3: Measures Of Spread
Problem 1GP
Related questions
Question
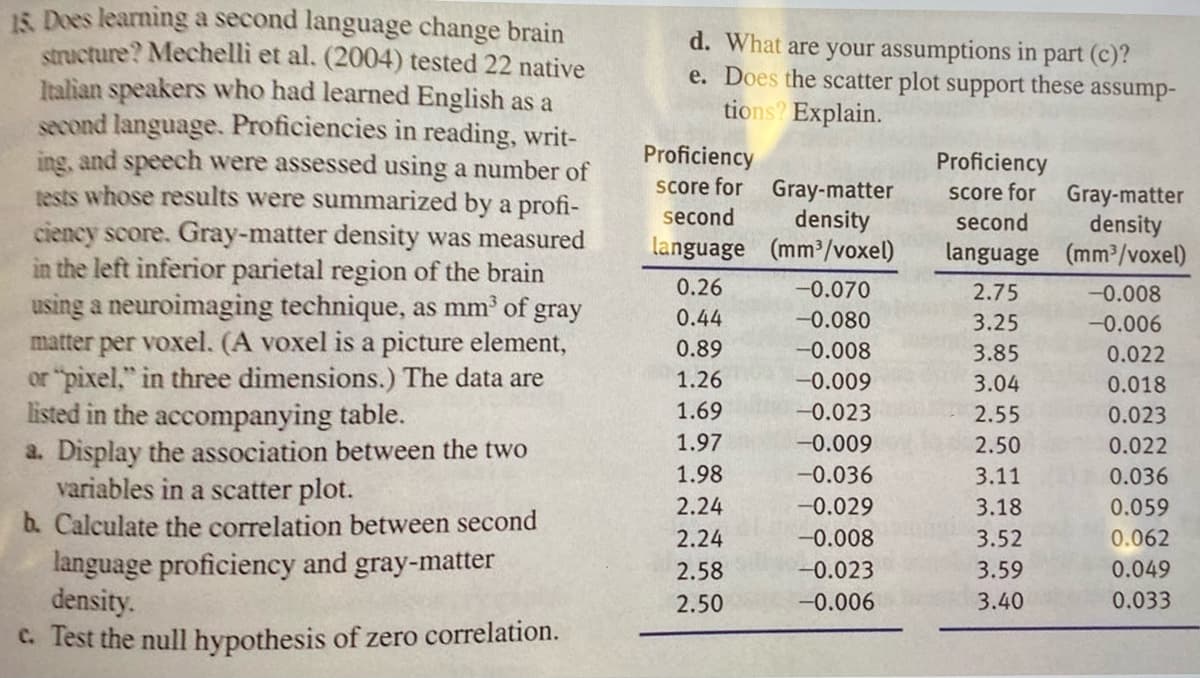
Transcribed Image Text:15. Does learning a second language change brain
structure? Mechelli et al. (2004) tested 22 native
Italian speakers who had learned English as a
second language. Proficiencies in reading, writ-
ing, and speech were assessed using a number of
tests whose results were summarized by a profi-
ciency score. Gray-matter density was measured
in the left inferior parietal region of the brain
using a neuroimaging technique, as mm³ of gray
matter per voxel. (A voxel is a picture element,
or "pixel," in three dimensions.) The data are
listed in the accompanying table.
a. Display the association between the two
variables in a scatter plot.
b. Calculate the correlation between second
language proficiency and gray-matter
density.
c. Test the null hypothesis of zero correlation.
d. What are your assumptions in part (c)?
e. Does the scatter plot support these assump-
tions? Explain.
Proficiency
score for Gray-matter
second density
language (mm³/voxel)
0.26
0.44
0.89
1.26
1.69
1.97
1.98
2.24
2.24
2.58
2.50
-0.070
-0.080
-0.008
-0.009
-0.023
-0.009
-0.036
-0.029
-0.008
-0.023
-0.006
Proficiency
score for Gray-matter
second
density
language
(mm³/voxel)
2.75
3.25
3.85
3.04
2.55
2.50
3.11
3.18
3.52
3.59
3.40
-0.008
-0.006
0.022
0.018
0.023
0.022
0.036
0.059
0.062
0.049
0.033

Transcribed Image Text:f. Do the results demonstrate that second lan-
guage proficiency affects gray-matter density
in the brain? Why or why not?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill