1621.56 1243.52 1232.84 815.04 658.50 1572.37 1476.52 1464.39 1339.50 1147.64 778.68 1098.78 1421.27 615.81 1292.55 1054.41 748.47 3456.02 3202.74 1674.07 847.95 3332-25 2542.13 2161.02
1621.56 1243.52 1232.84 815.04 658.50 1572.37 1476.52 1464.39 1339.50 1147.64 778.68 1098.78 1421.27 615.81 1292.55 1054.41 748.47 3456.02 3202.74 1674.07 847.95 3332-25 2542.13 2161.02
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter17: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 45E: If a sample of iron and a sample of zinc come into contact, the zinc corrodes but the iron does not....
Related questions
Question
100%
Please I need help with this question
Based on the experiment- Synthesis of Iodosalicylamide – An Electrophilic Aromatic
Substitution (a derivative of benzene, salicylamide was used and substituted an iodine atom onto the ring; the ring is the nucleophile while the atom/molecule that is being substituted onto the ring has an
electrophilic character)
Please I need help with this QUESTION: Draw the structure of the final product(s) based on the ATTACHED IR analysis. Also label the signals (both the frequency and molecular motion) that help determine the final product(s). Thanks in advance
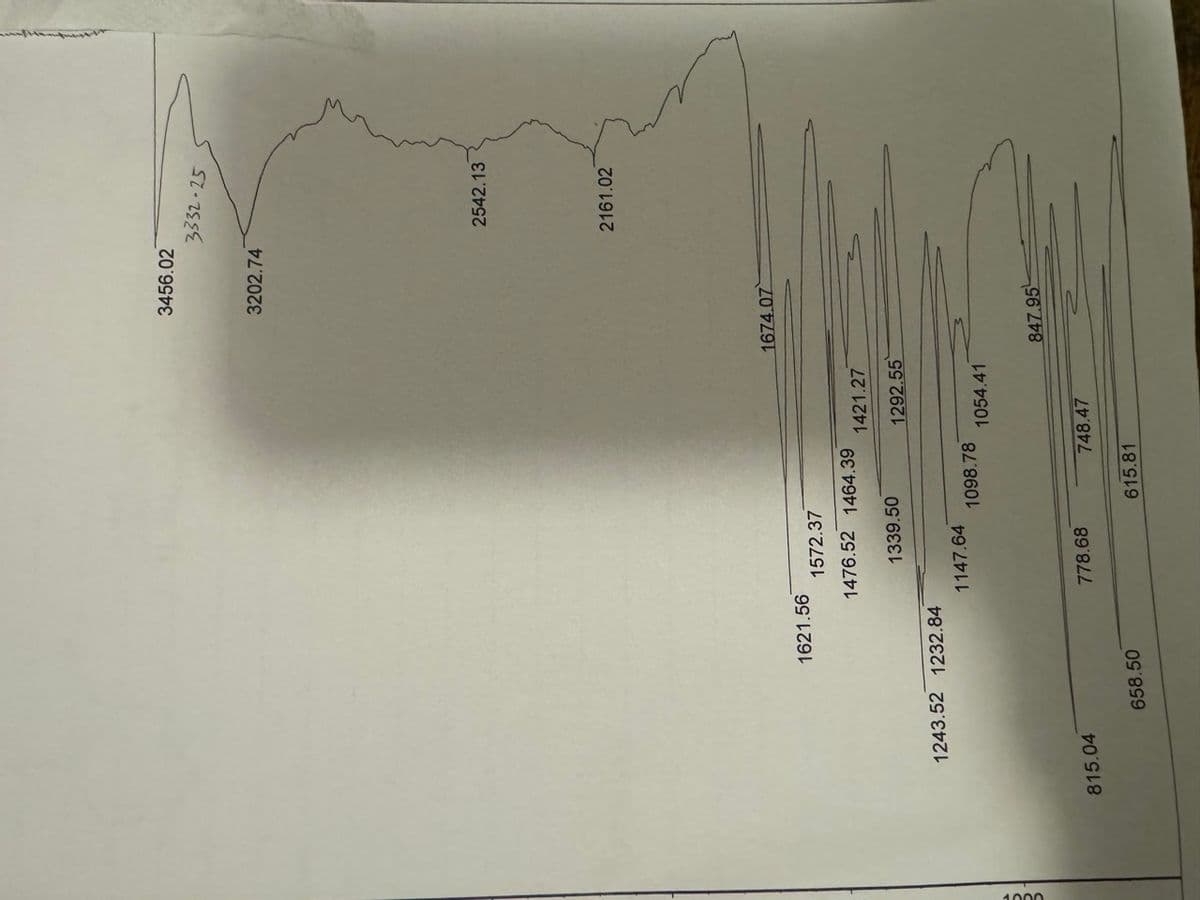
Transcribed Image Text:1000
1621.56
1243.52 1232.84
815.04
658.50
1572.37
1476.52 1464.39
1339.50
1147.64
778.68
1098.78
1421.27
1292.55
615.81
1054.41
748.47
3456.02
3202.74
1674.07
847.95
3332-25
2542.13
2161.02
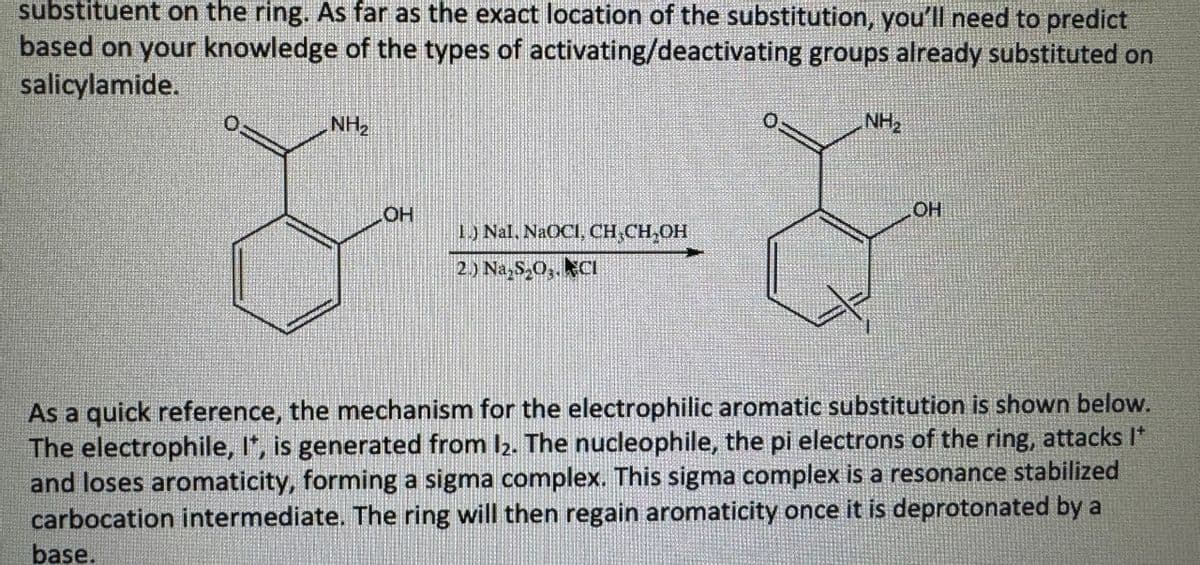
Transcribed Image Text:substituent on the ring. As far as the exact location of the substitution, you'll need to predict
based on your knowledge of the types of activating/deactivating groups already substituted on
salicylamide.
NH₂
OH
1.) Nal, NaOCI, CH₂CH₂OH
2.) Na₂S₂O3. CI
NH₂
OH
As a quick reference, the mechanism for the electrophilic aromatic substitution is shown below.
The electrophile, It, is generated from 12. The nucleophile, the pi electrons of the ring, attacks I*
and loses aromaticity, forming a sigma complex. This sigma complex is a resonance stabilized
carbocation intermediate. The ring will then regain aromaticity once it is deprotonated by a
base.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co