2 NH3(g) → N2(g) + 3 H2(g) the average rate of disappearance of NH3 over the time period from t = 0 s to t = 5.07x103 s is found to be 1.50x10-6 M/s. What is the average rate of appearance of H2 over the same time period? M/s. Submit Examine the balanced chemical eguation, Is the rate of formation of Ha faster than or slower than the rate of disappearance of NHa?
2 NH3(g) → N2(g) + 3 H2(g) the average rate of disappearance of NH3 over the time period from t = 0 s to t = 5.07x103 s is found to be 1.50x10-6 M/s. What is the average rate of appearance of H2 over the same time period? M/s. Submit Examine the balanced chemical eguation, Is the rate of formation of Ha faster than or slower than the rate of disappearance of NHa?
Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305264434
Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Chapter20: Rates Of Chemical Reactions, I. The Iodination Of Acetone
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3ASA
Related questions
Question
100%
help me asap pls less than 30 mins with shortcuts only
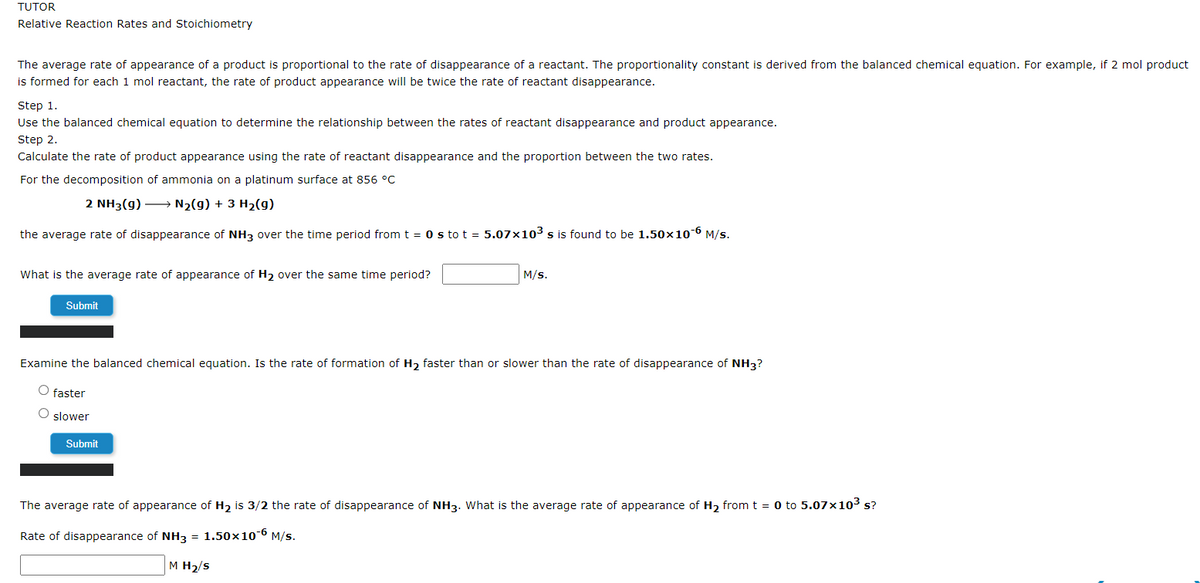
Transcribed Image Text:TUTOR
Relative Reaction Rates and Stoichiometry
The average rate of appearance of a product is proportional to the rate of disappearance of a reactant. The proportionality constant is derived from the balanced chemical equation. For example, if 2 mol product
is formed for each 1 mol reactant, the rate of product appearance will be twice the rate of reactant disappearance.
Step 1.
Use the balanced chemical equation to determine the relationship between the rates of reactant disappearance and product appearance.
Step 2.
Calculate the rate of product appearance using the rate of reactant disappearance and the proportion between the two rates.
For the decomposition of ammonia on a platinum surface at 856 °C
2 NH3(g) → N2(g) + 3 H2(g)
the average rate of disappearance of NH3 over the time period from t = 0 s to t = 5.07x103 s is found to be 1.50×10-6 M/s.
What is the average rate of appearance of H2 over the same time period?
M/s.
Submit
Examine the balanced chemical equation. Is the rate of formation of H2 faster than or slower than the rate of disappearance of NH3?
O faster
O slower
Submit
The average rate of appearance of H2 is 3/2 the rate of disappearance of NH3. What is the average rate of appearance of H2 from t = 0 to 5.07x103 s?
Rate of disappearance of NH3 = 1.50×10-6 M/s.
M H2/s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305264434
Author:
Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:
Brooks Cole


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305264434
Author:
Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:
Brooks Cole


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning