2. A frequently overlooked source of pollution in agricultural industries is "odor pollution." Some animals, such as pigs, do not care as much about hygiene as humans and emit an unpleasant odor as a result. For this reason, pig farming can cause a negative externality for those who live near a pig farm. Consider the competitive market for bacon given below. The social marginal benefit of producing a pound of bacon is the private marginal benefit, given by the demand curve. The private marginal cost of producing a pound of bacon is the supply curve. Price Supply = PMC $10 $9 $8 $7 $6 $5 $4 $3 Demand = PMB = SMB $2 $1 4000 s000 12.000 16.000 20,000 24.000 20.00 2.000 36,000 40,000 Pounds of Bacon A. Each pound of bacon produced leads to a $2 negative externality for those who live near the pig farm. Draw the social marginal cost curve. B. What quantity of bacon will the market produce? What is the socially optimal quantity? c. What tax (type of tax and tax rate) should be imposed to move production to the socially optimal quantity? Explain briefly why this tax will lead to the socially optimal quantity being produced.
2. A frequently overlooked source of pollution in agricultural industries is "odor pollution." Some animals, such as pigs, do not care as much about hygiene as humans and emit an unpleasant odor as a result. For this reason, pig farming can cause a negative externality for those who live near a pig farm. Consider the competitive market for bacon given below. The social marginal benefit of producing a pound of bacon is the private marginal benefit, given by the demand curve. The private marginal cost of producing a pound of bacon is the supply curve. Price Supply = PMC $10 $9 $8 $7 $6 $5 $4 $3 Demand = PMB = SMB $2 $1 4000 s000 12.000 16.000 20,000 24.000 20.00 2.000 36,000 40,000 Pounds of Bacon A. Each pound of bacon produced leads to a $2 negative externality for those who live near the pig farm. Draw the social marginal cost curve. B. What quantity of bacon will the market produce? What is the socially optimal quantity? c. What tax (type of tax and tax rate) should be imposed to move production to the socially optimal quantity? Explain briefly why this tax will lead to the socially optimal quantity being produced.
Principles of Microeconomics
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter11: Public Goods And Common Resources
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2PA
Related questions
Question
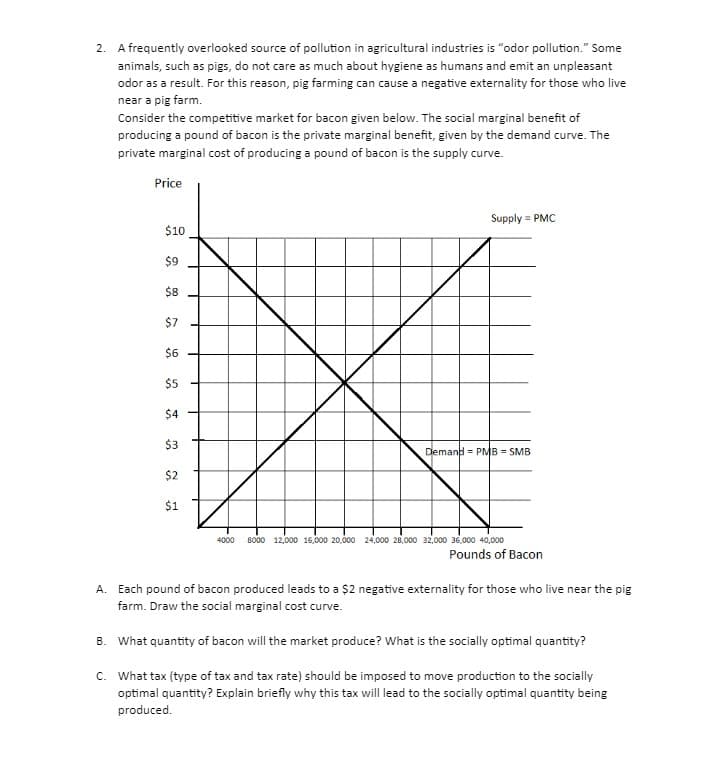
Transcribed Image Text:2. A frequently overlooked source of pollution in agricultural industries is "odor pollution." Some
animals, such as pigs, do not care as much about hygiene as humans and emit an unpleasant
odor as a result. For this reason, pig farming can cause a negative externality for those who live
near a pig farm.
Consider the competitive market for bacon given below. The social marginal benefit of
producing a pound of bacon is the private marginal benefit, given by the demand curve. The
private marginal cost of producing a pound of bacon is the supply curve.
Price
Supply = PMC
$10
$9
$8
$7
$6
$5
$4
$3
Demand = PMB = SMB
$2
$1
4000
8000 12,000 16,000 20,000 24,000 28,000 32,000 36,000 40,000
Pounds of Bacon
A. Each pound of bacon produced leads to a $2 negative externality for those who live near the pig
farm. Draw the social marginal cost curve.
B. What quantity of bacon will the market produce? What is the socially optimal quantity?
C. What tax (type of tax and tax rate) should be imposed to move production to the socially
optimal quantity? Explain briefly why this tax will lead to the socially optimal quantity being
produced.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning