3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantityof consumption Consider the market for paper. Suppose that a paper factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the factory. Producing an additional ton of paper imposes a constant external cost of $315 per ton. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for paper. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $315 per ton.
3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantityof consumption Consider the market for paper. Suppose that a paper factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the factory. Producing an additional ton of paper imposes a constant external cost of $315 per ton. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for paper. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $315 per ton.
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter10: Externalities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2PA
Related questions
Question
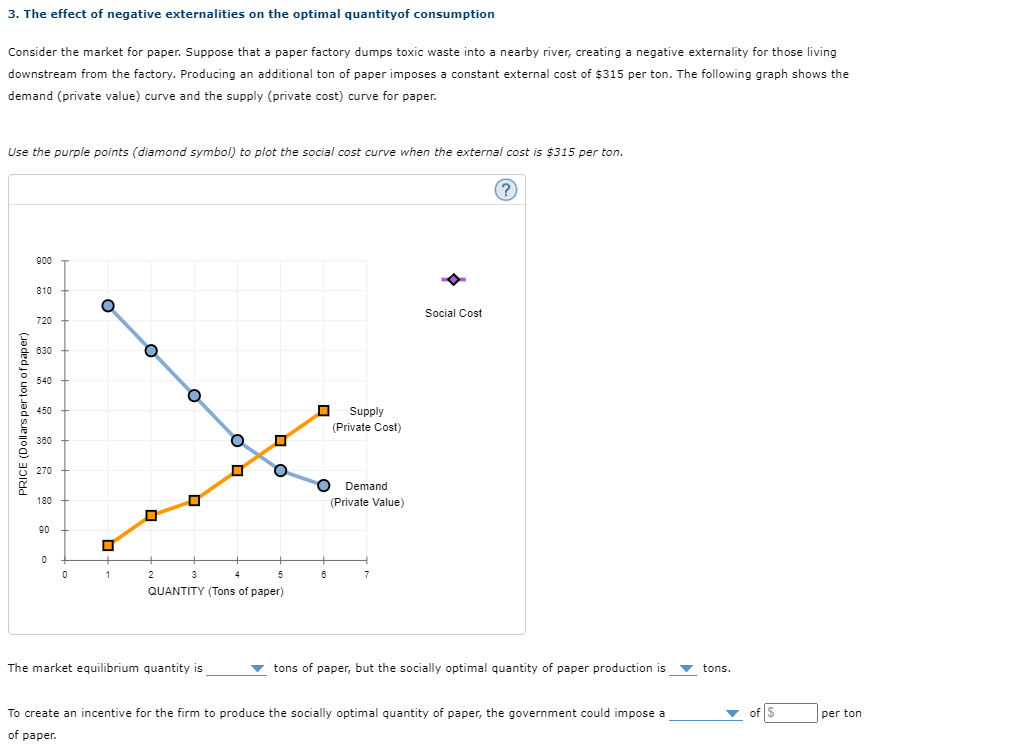
Transcribed Image Text:3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantityof consumption
Consider the market for paper. Suppose that a paper factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living
downstream from the factory. Producing an additional ton of paper imposes a constant external cost of $315 per ton. The following graph shows the
demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for paper.
Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $315 per ton.
(?
900
810
Social Cost
720
630
540
450
Supply
(Private Cost)
360
270
Demand
180
(Private Value)
90
1
2
6
QUANTITY (Tons of paper)
The market equilibrium quantity is
v tons of paper, but the socially optimal quantity of paper production is
v tons.
To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity of paper, the government could impose a
of S
per ton
of paper.
PRICE (Dollars perton of paper)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax


Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax


Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
