2. Consider the model of labor pooling, with each firm locating either in an isolated site or in a cluster with other fi rms. Suppose that good times (high demand) and bad times (low demand) are equally likely. The table shows wages and workforces in different times and locations. Wage $40 $20 Isolated Workforce 50 50 Good times (high demand) Bad times (low demand) A. Use a figure like Figure 3-3 to illustrate the situation. Wage $30 $30 Cluster Workforce 60 40 B. During good times, the benefit of being in the cluster as opposed to being isolated is, computed as.... C. During bad times, the cost of being in the cluster as opposed to being isolated is, computed as....
2. Consider the model of labor pooling, with each firm locating either in an isolated site or in a cluster with other fi rms. Suppose that good times (high demand) and bad times (low demand) are equally likely. The table shows wages and workforces in different times and locations. Wage $40 $20 Isolated Workforce 50 50 Good times (high demand) Bad times (low demand) A. Use a figure like Figure 3-3 to illustrate the situation. Wage $30 $30 Cluster Workforce 60 40 B. During good times, the benefit of being in the cluster as opposed to being isolated is, computed as.... C. During bad times, the cost of being in the cluster as opposed to being isolated is, computed as....
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter14: Labor Markets And Income
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1SCQ: Table 14.10 shows levels of employment (Labor), the marginal product at each of those levels, and...
Related questions
Question
Economics
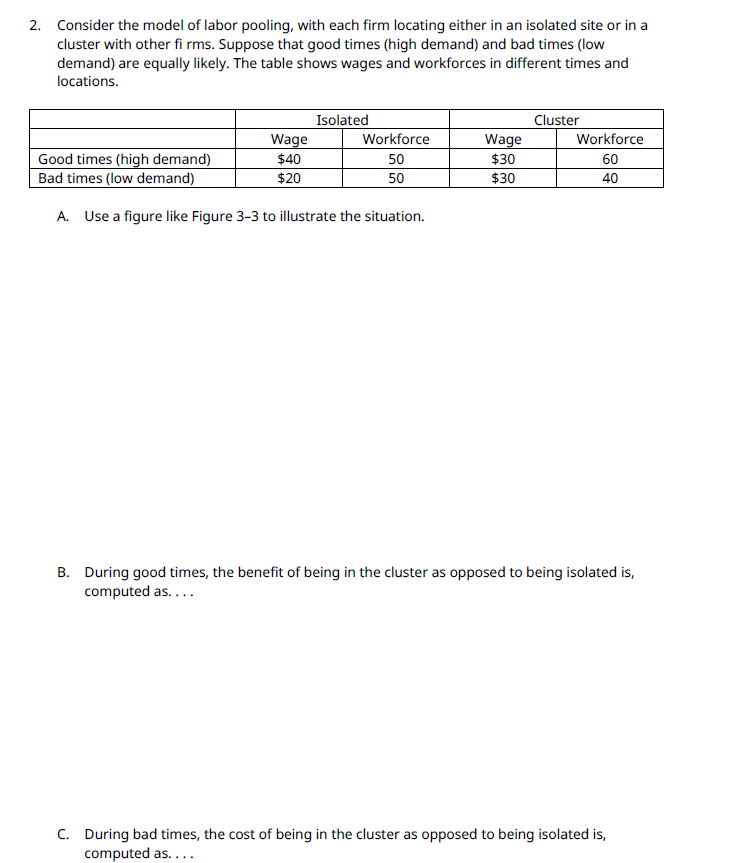
Transcribed Image Text:2. Consider the model of labor pooling, with each firm locating either in an isolated site or in a
cluster with other fi rms. Suppose that good times (high demand) and bad times (low
demand) are equally likely. The table shows wages and workforces in different times and
locations.
Wage
$40
$20
Isolated
Workforce
50
50
Good times (high demand)
Bad times (low demand)
A. Use a figure like Figure 3-3 to illustrate the situation.
Wage
$30
$30
Cluster
Workforce
60
40
B. During good times, the benefit of being in the cluster as opposed to being isolated is,
computed as....
C. During bad times, the cost of being in the cluster as opposed to being isolated is,
computed as....
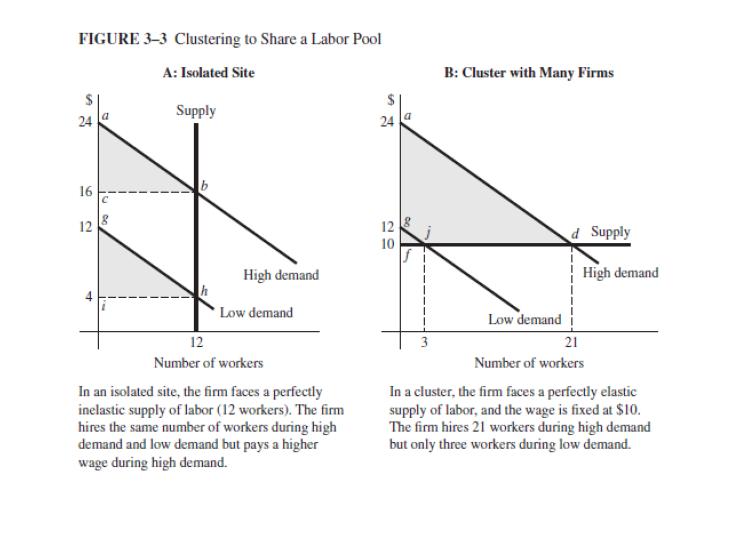
Transcribed Image Text:FIGURE 3-3 Clustering to Share a Labor Pool
A: Isolated Site
24
16
12
Supply
High demand
Low demand
12
Number of workers
In an isolated site, the firm faces a perfectly
inelastic supply of labor (12 workers). The firm
hires the same number of workers during high
demand and low demand but pays a higher
wage during high demand.
24
12
10
B: Cluster with Many Firms
Low demand
d Supply
High demand
21
Number of workers
In a cluster, the firm faces a perfectly elastic
supply of labor, and the wage is fixed at $10.
The firm hires 21 workers during high demand
but only three workers during low demand.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax