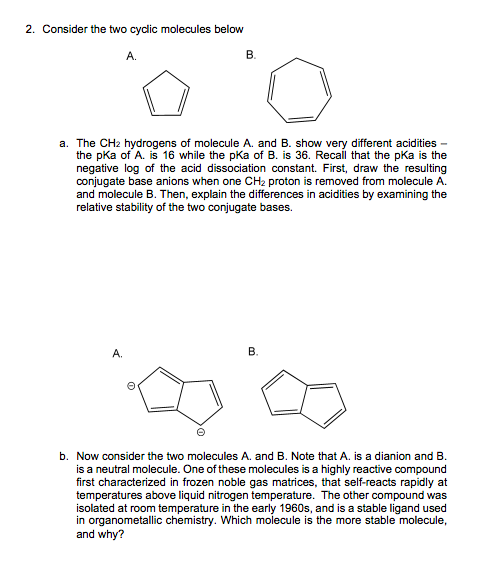
2. Consider the two cydlic molecules below A. B. a. The CH2 hydrogens of molecule A. and B. show very different acidities - the pka of A. is 16 while the pKa of B. is 36. Recall that the pka is the negative log of the acid dissociation constant. First, draw the resulting conjugate base anions when one CH2 proton is removed from molecule A. and molecule B. Then, explain the differences in acidities by examining the relative stability of the two conjugate bases.
Basics in Organic Reactions Mechanisms
In organic chemistry, the mechanism of an organic reaction is defined as a complete step-by-step explanation of how a reaction of organic compounds happens. A completely detailed mechanism would relate the first structure of the reactants with the last structure of the products and would represent changes in structure and energy all through the reaction step.
Heterolytic Bond Breaking
Heterolytic bond breaking is also known as heterolysis or heterolytic fission or ionic fission. It is defined as breaking of a covalent bond between two different atoms in which one atom gains both of the shared pair of electrons. The atom that gains both electrons is more electronegative than the other atom in covalent bond. The energy needed for heterolytic fission is called as heterolytic bond dissociation energy.
Polar Aprotic Solvent
Solvents that are chemically polar in nature and are not capable of hydrogen bonding (implying that a hydrogen atom directly linked with an electronegative atom is not found) are referred to as polar aprotic solvents. Some commonly used polar aprotic solvents are acetone, DMF, acetonitrile, DMSO, etc.
Oxygen Nucleophiles
Oxygen being an electron rich species with a lone pair electron, can act as a good nucleophile. Typically, oxygen nucleophiles can be found in these compounds- water, hydroxides and alcohols.
Carbon Nucleophiles
We are aware that carbon belongs to group IV and hence does not possess any lone pair of electrons. Implying that neutral carbon is not a nucleophile then how is carbon going to be nucleophilic? The answer to this is that when a carbon atom is attached to a metal (can be seen in the case of organometallic compounds), the metal atom develops a partial positive charge and carbon develops a partial negative charge, hence making carbon nucleophilic.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images






